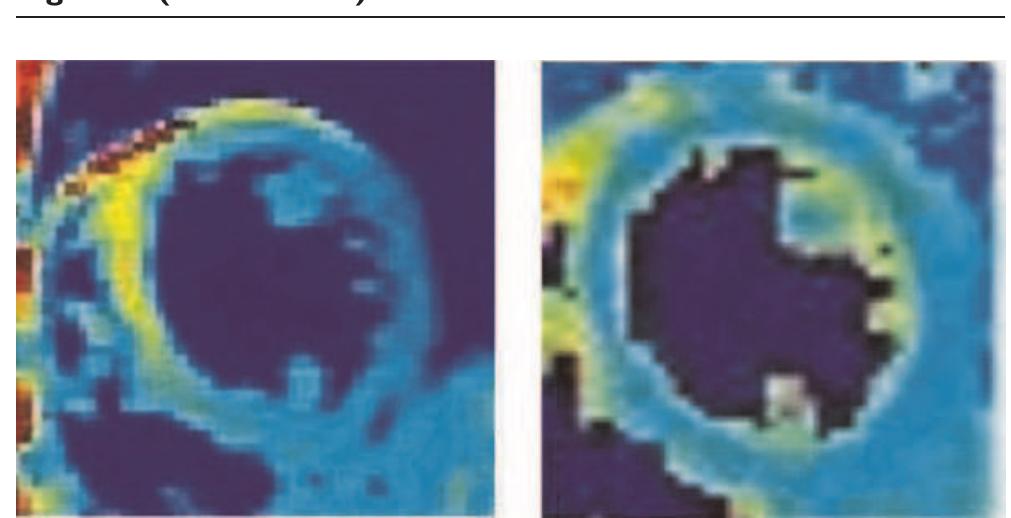
Visualizing regional myocardial oxygenation changes with statistically optimal colormaps
2009, Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance

Sign up for access to the world's latest research
Abstract
Introduction: Prophylactic implantation of a cardioverter/ defibrillator (ICD) has been shown to reduce mortality in patients with chronic myocardial infarction (CMI) and an increased risk for life threatening ventricular arrhythmia (VA). The use of ICDs in this large patient population is still limited by high costs and possible adverse events including inappropriate discharges and progression of heart failure. VA is related to infarct size and seems to be related to infarct morphology. Contrast enhanced cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (ceCMR) can detect and quantify myocardial fibrosis in the setting of CMI and might therefore be a valuable tool for a more accurate risk stratification in this setting. Hypothesis: ceCMR can identify the subgroup developing VA in patients with prophylactic ICD implantation following MADIT criteria. Methods: We prospectively enrolled 52 patients (49 males, age 69 ± 10 years) with CMI and clinical indication for ICD therapy following MADIT criteria. Prior to implantation (36 ± 78 days) patients were investigated on a 1.5 T clinical scanner (Siemens Avanto © , Germany) to assess left ventricular function (LVEF), LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and LV mass (sequence parameters: GRE SSFP, matrix 256 × 192, short axis stack; full LV coverage, no gap; slice thickness 6 mm). For quantitative assessment of infarct morphology late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) was performed including measurement of total and relative infarct mass (related to LV mass) and the degree of transmurality (DT) as defined by the percentage of transmurality in each scar. (sequence parameters: inversion recovery gradient echo; matrix 256 × 148, imaging 10 min after 0.2 μg/kg gadolinium DTPA; slice orientation equal to SSFP). MRI images were analysed using dedicated software (MASS © , Medis,




![Table | (abstract O4) Imaging parameters edematous myocardium (T1/T2 = 1119/101.8 ms) [2]. Phantom T| and T2 values were verified using a standard spin echo sequence. as and T2 values were verified using a standard spin echo sequence. In-vivo: T2 Maps were acquired in 9 healthy subjects to determine the normal range of T2 values. Three short-axis and two long-axis views were imaged during breath hold (duration ~5 HB) and in free breathing using navigator gating. In 5 subjects, four averages were acquired with navigator gating to test the benefits of increased SNR. Average T2 values were calculated in 16 myocardial segments using both methods and compared. Measurements were pooled to obtain global mean and standard deviation to investigate inter-subject and inter-segment variability.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/42742902/table_002.jpg)









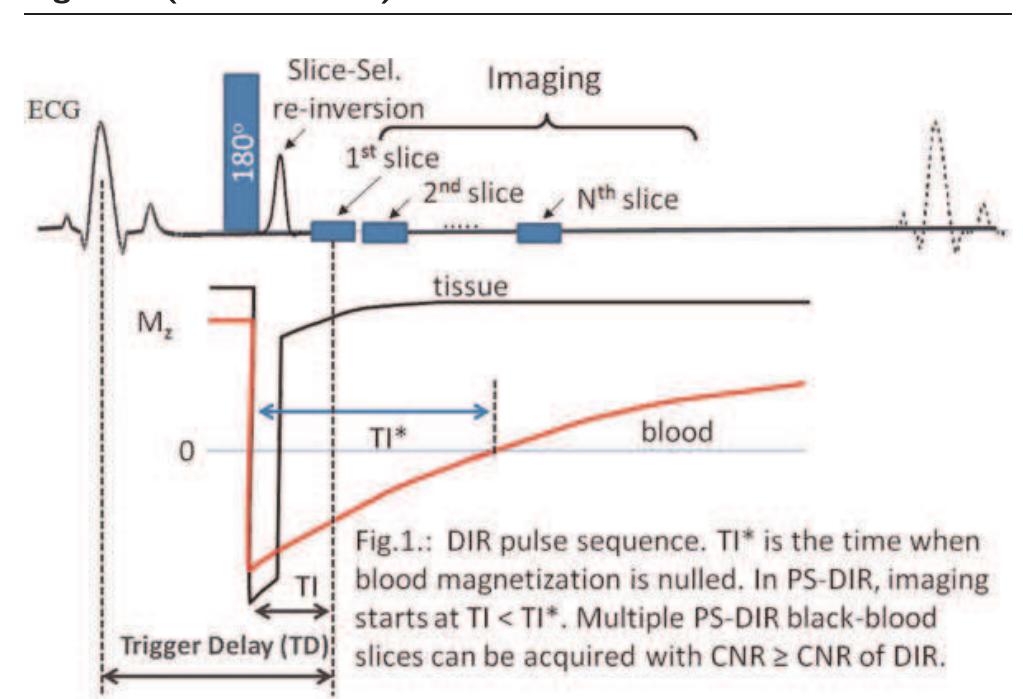

![Left: CNR (mean + stdev) at different TI values in PS-DIR signed images (red) and in DIR magnitude images at TI* (green). Right: Wall thickness at different Tl using PS-DIR images (red) and using DIR images at TI*. Note the agreement with the measurements using TI*. Dual-slice single breath-hold PS-DIR Coronary vessel wall black-blook imaging Experiments: Anatomical slices perpendicular to the proximal part of the right coronary artery (RCA) at end-systole were planned similar to a previously published methodology [7]. First, serial single-slice multi-phase PS-DIR images were acquired with incremental Tl ranging from 50 ms—500 ms in |5 healthy adult](https://figures.academia-assets.com/42742902/figure_015.jpg)









































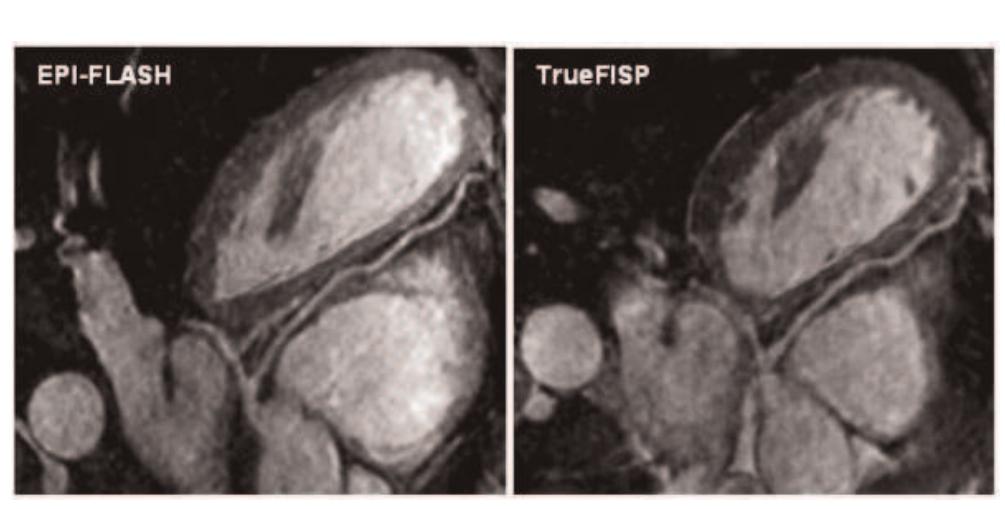
![Table | (abstract O47) Comparison between EPI-FLASH and TrueFISP with identical resolution and imaging time Volunteer imaging: 7 volunteers were scanned on a 1.5 T Espree scanner (Siemens Medical Solutions). Scan parameters were: TR = 11.3, TE = 4.27, flip angle = 25, 66 lines per heartbeat in a window of 124 ms, acquired k-space lines = 132, readout bandwidth = 977 Hz/pixel, Tl = 300 ms, matrix: 256 x 189 x 60, interpolated voxel size: 0.5 x 0.55 x | mm?. 0.2 mmol/kg body weight of Gd-DTPA was injected at 0.5 cc/sec [5]. The total imaging time for the whole-heart scan was](https://figures.academia-assets.com/42742902/table_012.jpg)



![Arrows identify patterns of MDE. a) transmural; b) subendocardial; c) EFE; d) subepicardial/intramural. Results: Of the 85 subjects included (65% male; median age at Fontan 4.5 [2.0, | 1.2] years; mean age at CMR 23.1 + | 1.2 years), 21 (25%) had positive MDE in the ventricular myocardium. MDE was seen in the following locations: dominant ventricle free wall (n = 13, 62%), secondary ventricle free wall (n = 9, 43%), septal insertion (n = 5, 24%), ventricular septum (n = 3, 14%), apex (n = 2, 10%), previous surgical sites (n = 2, 10%), and papillary muscle (n = 2, 10%). MDE was seen in the following patterns: transmural lesion](https://figures.academia-assets.com/42742902/figure_056.jpg)

![The T2 maps of a normal (a) and a DMD subject (b) showing the left ventricle in the short axis view. Values are mean + SD, median [25%, 75%], or n (%); ‘Student t test, *Mann-Whitney U test, *Fisher exact test, *Chi-squared test of independence.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/42742902/figure_057.jpg)








![Methods: Fifty elderly subjects [mean age = 65 (+ 8), 16/ 50 = 32% women] with at least one major cardiovascular risk factor (smoking, diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia) under- went MRI (1.5 T Siemens Sonata) for abdominal and peri-aortic adipose tissue quantification and aortic atherosclerosis asses-](https://figures.academia-assets.com/42742902/figure_067.jpg)






![appearance, E/A ratio, E/E’ ratio, stage of diastology, deceleration time (msec) and myocardial performance index [(isovolumic contraction time + isovolumic relaxation time)/ejection time]. DHE-MR images were obtained in standard long and short axis orientations (covering the entire LV), after injection of Gadolinium dimenglumine using an inversion recovery spoiled gradient echo sequence: TE 4 msec, TR 8 msec, flip angle 30°, bandwidth 140 Hz/pixel, 23 k-space lines acquired every other RR-interval, field of view (varied from 228-330 in the x-direction and 260-330 in the y-direction) and matrix size (varied from 140-180 in the x-direction and 256 in the y-direction). CMR was considered positive in the presence of DHE of entire sub- endocardium with extension into the neighboring myocardium.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/42742902/figure_072.jpg)









































































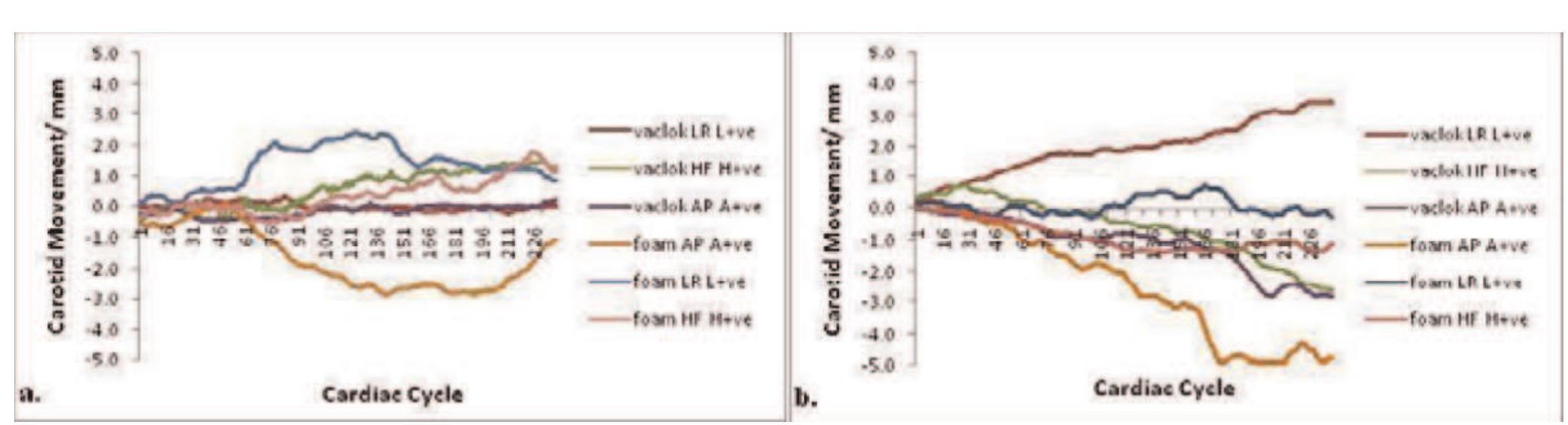
![Table | (abstract P24) Acquisition parameters for Tlw-SPACE and ce-MRA and bulk head motion during the long 3D acquisition time. Respiratory movement artefact is controversial [4], but Boussel [5] demonstrated its detrimental effect on carotid wall imaging, using real-time transaxial cines. However, during quiet supine respiration, breathing is predominantly diaphragmatic resulting in the greatest carotid movement in the head-foot direction. We used a novel high temporal resolution interleaved approach to study carotid artery movement in all directions, over the typical 3D scan duration, for a true representation of the potential problem for 3D imaging. Siemens, Erlangen) using two body matrix coils for the abdominal/pelvic area and a peripheral coil for thighs and lower legs. The imaging protocol included localizers, coronal acquisition of abdominal aorta and SFA using TIlw-SPACE, followed by ce-MRA covering the abdomen, thighs and the lower legs.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/42742902/table_029.jpg)












































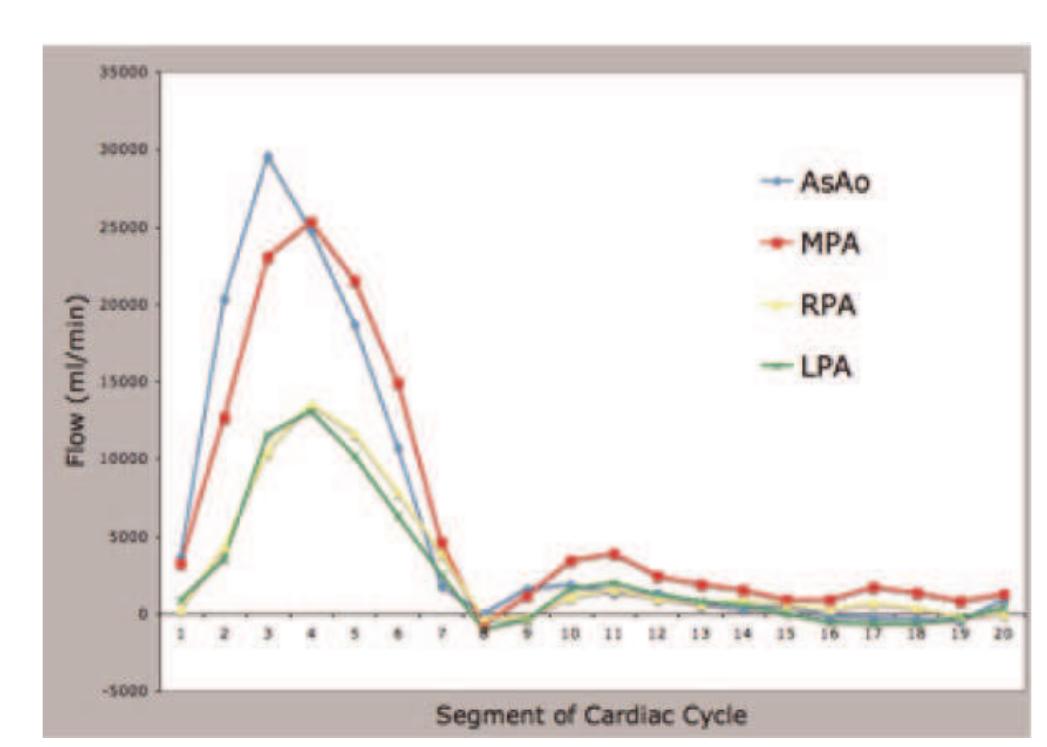
![Results: The dual cardiac phase whole heart scan was applied successfully in all patients. An example of each coronary segment is shown in figure |. The vessel length, diameter, sharpness and consensus score for each segment during systole and diastole are shown in Table |. Bland Altman plots of the systolic versus diastolic data from each coronary segment are shown in figure 2. No statistically difference was found comparing vessel length, diameter, sharpness for all vessels between systole and diastole. Moreover, no statistically differ- ence was found in image quality. Although, there was no difference for the mean vessel length, diameter, and sharpness, it was found that on a patient level, those parameters and image quality showed differences either favoring systolic or diastolic image acquisition for different coronary segments within the same patient. SEIS YSLONE GLI TERESI SLO Pildse HT COMPUTICLIOTT WIC LI WHOL heart approach allows retrospectively selection of the best image phase for coronary artery visualization without any scan time penalty. Methods: Eight children (age = 6.38 + 4.27, height = 116.57 + 30.77, weight = 23.57 + 14.25, Heart-rate = 85.02 + 8.59) with CHD were scanned under general anesthesia on a 1.5 T MR system (Achieva, Philips Healthcare). The cardiac rest period for end-systole and mid-diastole was determined from a 2D SSFP cine scan with high temporal resolution (TR/TE = 3.1/1.6 ms, flip angle 60°, slice thickness 6 mm, 60 to 80 cardiac phases). A previously developed free-breathing navigator gated 3D SSFP dual cardiac phase sequence [I] was then applied in sagittal orientation for imaging of the whole heart including the coronary arteries and great vessels (TR/TE = 3.4/1.7 ms, flip angle 90°, 60-120 slice, isotropic resolution of I-I.5 mm?, temporal resolution of 60 — 75 ms, Sense of 2 in AP direction). Data was obtained during end-systole and mid-diastole and the acquisition window of the 3D scan was adapted accordingly to the shortest rest period. Images were then reformatted along the major axes of the left and right coronary artery for both cardiac phases. Vessel length, diameter and sharpness of the visualized coronary arteries (RCA, LM, LAD, LCx) were measured using the “SoapBubble” software. Image quality was assessed by two independent observers. Statistical analysis and Bland Altman plots were used to compare the different data sets.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/42742902/figure_179.jpg)



![Final myocardium contours on 4 different patients. Then the delineation of the myocardial contours is performed by alternating automatic deformation of a geometrical template and computation of a binary map of the enhanced areas. The template is ribbon-shaped with a variable width, its position is updated depending on image gray values. The map is a 2D binary image showing enhanced areas, it is updated by thresholding the image gray values in a region of interest centered on the endocardium, in order to include sub-endocardial scars. The segmentation is performed as follows: (1) automatic delineation of myocardial contours on short-axis LECMR slices [2],](https://figures.academia-assets.com/42742902/figure_182.jpg)









![First-pass perfusion image before (left) and after (right) KLT filtering. KLT filter provides marked noise suppression without loss of contrast between normally and abnormally perfused regions. Methods: Ten consecutive first-pass perfusion datasets inter- preted positive for ischemia or infarction were processed and analyzed retrospectively. All images were acquired using GRE-EPI with TSENSE acceleration rate 2 on a 1.5 T MR system (MAGNETOM Avanto, Siemens Healthcare, Germany). For each subject, all slices showing clinically interpreted perfusion defect were included in the analysis. Non-rigid body registration [3] was first performed on each series to allow for semi- quantitative analysis of signal enhancement, and to improve the](https://figures.academia-assets.com/42742902/figure_190.jpg)












![64-year-old female with mean PAP = 51 mmHg demonstrates hypertro- phy of SMT (septomarginal trabecula), white arrow, in a dilated right ventricle. Introduction: In the right ventricle (RV), the septomarginal trabecula (SMT) arises as a muscular band originating from the interventricular septum (IVS) at the lower segment of the crista supraventricularis. It forms a functional unit with the moderator band, which attaches to the lateral free wall of the RV [I, 2]. Strategically situated between the RV inflow and outflow tracts, the whole unit serves to help emptying blood into the pulmonary trunk during systole. Thus, it should be anticipated that the SMT may undergo changes in RV hypertrophy secondary to chronic pulmonary hypertension.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/42742902/figure_203.jpg)
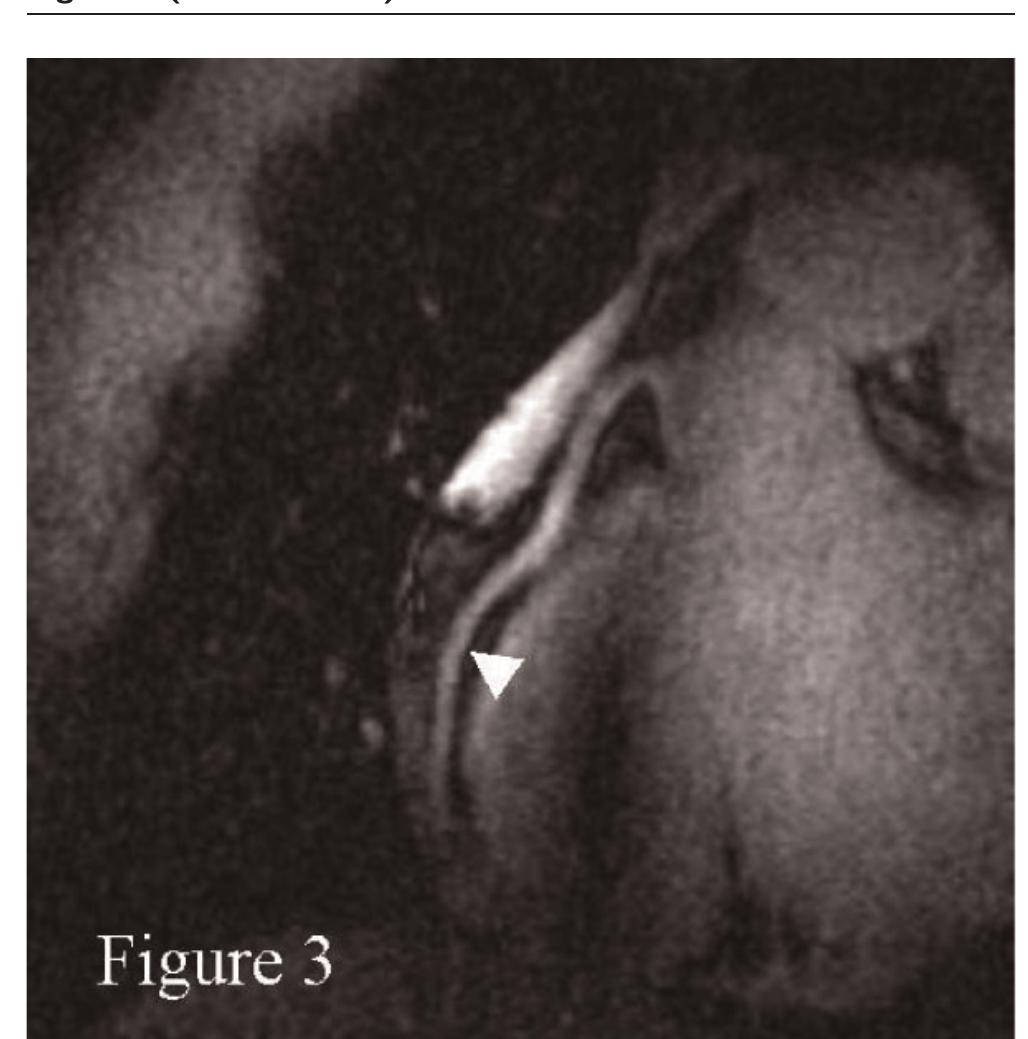
![Figure 3 (abstract P91) Methods: Imaging was performed in two centers; one using 3 T and the other using |.5 T MR systems. 33 catheter proven PAH patients (mean age = 61.4 + 12.1 years and mPAP = 45.9 + 12.4 mmHg) were enrolled in the study [Idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) = 21 and Scleroderma (SSc) = 12 patients]. Similarly, 9 healthy volunteers (mean age = 45.56 + 8.6 years) were included in the study for comparison. Short axis cine images were acquired using fast gradient echo technique. End diastolic frames were analyzed using MASS 6.2.1 software (Medis, the Netherlands). Starting from the basal slices, the SMT was identified in patients and controls as the most anterior trabeculation arising from the IVS below the outflow tract level. Two independent observers manually contoured and traced the SMT from its origin towards the apex where the moderator](https://figures.academia-assets.com/42742902/figure_204.jpg)

























![Methods: We retrospectively reviewed 7] consecutive cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) studies for BPA size and PCMR data. We also reviewed |3 consecutive pts who underwent both CMR and catheterization.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/42742902/figure_225.jpg)






















![Examples of T2* curve fitting using both truncation and offset models. Left: In vivo scan data; Right: Ex vivo heart data. Methods: A 23-year-old Thai female thalassemia majorpatient with longstanding cardiac and liver iron overload was studied. The patient underwent MRI scan using the bright blood T2* sequence [2] (twice for reproducibility) in Bangkok on a 1.5 T clinical scanner (GE Signa), again in London 9 days later on a 1.5 T one (Siemens Sonata), using the same sequence. The patient was also scanned using the black blood T2* sequence [4]. The patient died two weeks later. With full ethical approval, the donated heart was formalin fixed before being sliced axially. A](https://figures.academia-assets.com/42742902/figure_246.jpg)





































![Table | (abstract P167) Basal slice mean peak tangential strain values and standard deviation for three confirmed ARVC cases, six suspected cases, and four normal volunteers for the LV and RV segments of abnormal strain and motion, which occur largely in the region of the RV insertion points and the LV inferior and anterior septum. Abnormal RV strain patterns were evident in 2 out of the 3 confirmed, and 3 out of the 6 suspected cases. The other confirmed case had a dilated RV but the strain pattern appeared normal. Table | presents regional peak tangential strains for the basal slice averaged for each group. A confidence measure for Ett was calculated based on the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the magnitude images. Only Ett strain values with confidence greater than 0.5 (normalized to max confidence in entire heart) were used to compute regional peak Ett strain. More than half of the data points in the diaphragmatic RV had to be discarded because of low SNR. Both confirmed and suspected ARVC cases have low peak strain values in the inferior and anterior septum and the RV free wall. Peak Ett is significantly less in ARVC and suspected ARVC cases compared to normals in the anterior septum (p < 0.005 and p < 0.05, respectively, student t-test). over two breath holds per slice. Imaging parameters include: FOV = 400 mn, slice thickness = 7.0 mm, TR = 24 ms, FOV phase = 62.5%, ETL = 9, segments = 18, cardiac phases = |0- 16, and displacement encoding frequency = 0.1 cycles/mm. Epicardial and endocardial contours were manually drawn for both the LV and RV on all cardiac phases. Phase unwrapping and tissue tracking were performed [5], and motion trajectories were estimated using temporal fitting with 5“ order Polynomial functions. Lagrangian strain taken tangential to the midwall (Ett) was computed from both the left ventricle (LV) and RV motion trajectories [3].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/42742902/table_059.jpg)












































![Table | (abstract P216) Optimal imaging parameters for cardiac imaging with T2w-SPACE as acute myocarditis and acute myocardial infarction [2, 3]. 3D acquisitions can provide high resolution images of the whole heart, allowing arbitrary views of the organ, and reducing partial volume effect. Conventional 3D TSE improves SNR but not sampling efficiency or spatial resolution. We propose a novel TSE technique for T2w 3D imaging of the whole heart that provides higher spatial resolution and reduces scan time per slice compared to 2D DB-TSE.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/42742902/table_068.jpg)













































![2) Update of k-space should smoothly vary over time (as in KT- BLAST/SLAM) avoiding sudden transitions between k-space regions to result in smoother transition between frames. Introduction: Previously, we developed a sparsely distribute k-space-time sampling approach termed BRISK, Block Regional Interpolation Scheme for K-space [I]. This approach allowed a nominal acceleration factor of 4 with good quality and low artifact. Others have developed alternative k-space-time sampling schemes, such as KT-BLAST and SLAM [2, 3]. We note that even at high acceleration factors, KT-BLAST/SLAM allowed a smooth transition from frame to frame, while BRISK experienced ringing artifacts. From these considerations we isolated key features that contribute to a successful k-space-time sparse sampling scheme: |) Update of k-space should be rapid near the center and lower near the periphery (as in BRISK) to capture highly dynamic features.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/42742902/figure_361.jpg)































![Simulation of magnetization signal intensity regrowth curves of blood (TI = 300 ms), diffuse fibrosis (T] = 350 ms) and normal myocardium (TI = 380 ms), after a 180° pulse. Zoomed view shows the difference in null times between blood, diffusely fibrosed myocardium and normal myocardium (ATI, and ATI,). Sb; is the blood signal intensity when normal myocardium is nulled, and Sb» is the blood signal intensity when diffusely fibrosed myocardium in nulled.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/42742902/figure_389.jpg)





















Related papers
Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 2009
Introduction: Prophylactic implantation of a cardioverter/ defibrillator (ICD) has been shown to reduce mortality in patients with chronic myocardial infarction (CMI) and an increased risk for life threatening ventricular arrhythmia (VA). The use of ICDs in this large patient population is still limited by high costs and possible adverse events including inappropriate discharges and progression of heart failure. VA is related to infarct size and seems to be related to infarct morphology. Contrast enhanced cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (ceCMR) can detect and quantify myocardial fibrosis in the setting of CMI and might therefore be a valuable tool for a more accurate risk stratification in this setting. Hypothesis: ceCMR can identify the subgroup developing VA in patients with prophylactic ICD implantation following MADIT criteria. Methods: We prospectively enrolled 52 patients (49 males, age 69 ± 10 years) with CMI and clinical indication for ICD therapy following MADIT criteria. Prior to implantation (36 ± 78 days) patients were investigated on a 1.5 T clinical scanner (Siemens Avanto © , Germany) to assess left ventricular function (LVEF), LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and LV mass (sequence parameters: GRE SSFP, matrix 256 × 192, short axis stack; full LV coverage, no gap; slice thickness 6 mm). For quantitative assessment of infarct morphology late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) was performed including measurement of total and relative infarct mass (related to LV mass) and the degree of transmurality (DT) as defined by the percentage of transmurality in each scar. (sequence parameters: inversion recovery gradient echo; matrix 256 × 148, imaging 10 min after 0.2 μg/kg gadolinium DTPA; slice orientation equal to SSFP). MRI images were analysed using dedicated software (MASS © , Medis,
Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 2009
Introduction: Prophylactic implantation of a cardioverter/ defibrillator (ICD) has been shown to reduce mortality in patients with chronic myocardial infarction (CMI) and an increased risk for life threatening ventricular arrhythmia (VA). The use of ICDs in this large patient population is still limited by high costs and possible adverse events including inappropriate discharges and progression of heart failure. VA is related to infarct size and seems to be related to infarct morphology. Contrast enhanced cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (ceCMR) can detect and quantify myocardial fibrosis in the setting of CMI and might therefore be a valuable tool for a more accurate risk stratification in this setting. Hypothesis: ceCMR can identify the subgroup developing VA in patients with prophylactic ICD implantation following MADIT criteria. Methods: We prospectively enrolled 52 patients (49 males, age 69 ± 10 years) with CMI and clinical indication for ICD therapy following MADIT criteria. Prior to implantation (36 ± 78 days) patients were investigated on a 1.5 T clinical scanner (Siemens Avanto © , Germany) to assess left ventricular function (LVEF), LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and LV mass (sequence parameters: GRE SSFP, matrix 256 × 192, short axis stack; full LV coverage, no gap; slice thickness 6 mm). For quantitative assessment of infarct morphology late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) was performed including measurement of total and relative infarct mass (related to LV mass) and the degree of transmurality (DT) as defined by the percentage of transmurality in each scar. (sequence parameters: inversion recovery gradient echo; matrix 256 × 148, imaging 10 min after 0.2 μg/kg gadolinium DTPA; slice orientation equal to SSFP). MRI images were analysed using dedicated software (MASS © , Medis,
Journal of …, 2009
Introduction: Prophylactic implantation of a cardioverter/ defibrillator (ICD) has been shown to reduce mortality in patients with chronic myocardial infarction (CMI) and an increased risk for life threatening ventricular arrhythmia (VA). The use of ICDs in this large patient population is still limited by high costs and possible adverse events including inappropriate discharges and progression of heart failure. VA is related to infarct size and seems to be related to infarct morphology. Contrast enhanced cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (ceCMR) can detect and quantify myocardial fibrosis in the setting of CMI and might therefore be a valuable tool for a more accurate risk stratification in this setting. Hypothesis: ceCMR can identify the subgroup developing VA in patients with prophylactic ICD implantation following MADIT criteria. Methods: We prospectively enrolled 52 patients (49 males, age 69 ± 10 years) with CMI and clinical indication for ICD therapy following MADIT criteria. Prior to implantation (36 ± 78 days) patients were investigated on a 1.5 T clinical scanner (Siemens Avanto © , Germany) to assess left ventricular function (LVEF), LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and LV mass (sequence parameters: GRE SSFP, matrix 256 × 192, short axis stack; full LV coverage, no gap; slice thickness 6 mm). For quantitative assessment of infarct morphology late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) was performed including measurement of total and relative infarct mass (related to LV mass) and the degree of transmurality (DT) as defined by the percentage of transmurality in each scar. (sequence parameters: inversion recovery gradient echo; matrix 256 × 148, imaging 10 min after 0.2 μg/kg gadolinium DTPA; slice orientation equal to SSFP). MRI images were analysed using dedicated software (MASS © , Medis,
Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 2009
Introduction: Prophylactic implantation of a cardioverter/ defibrillator (ICD) has been shown to reduce mortality in patients with chronic myocardial infarction (CMI) and an increased risk for life threatening ventricular arrhythmia (VA). The use of ICDs in this large patient population is still limited by high costs and possible adverse events including inappropriate discharges and progression of heart failure. VA is related to infarct size and seems to be related to infarct morphology. Contrast enhanced cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (ceCMR) can detect and quantify myocardial fibrosis in the setting of CMI and might therefore be a valuable tool for a more accurate risk stratification in this setting. Hypothesis: ceCMR can identify the subgroup developing VA in patients with prophylactic ICD implantation following MADIT criteria. Methods: We prospectively enrolled 52 patients (49 males, age 69 ± 10 years) with CMI and clinical indication for ICD therapy following MADIT criteria. Prior to implantation (36 ± 78 days) patients were investigated on a 1.5 T clinical scanner (Siemens Avanto © , Germany) to assess left ventricular function (LVEF), LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and LV mass (sequence parameters: GRE SSFP, matrix 256 × 192, short axis stack; full LV coverage, no gap; slice thickness 6 mm). For quantitative assessment of infarct morphology late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) was performed including measurement of total and relative infarct mass (related to LV mass) and the degree of transmurality (DT) as defined by the percentage of transmurality in each scar. (sequence parameters: inversion recovery gradient echo; matrix 256 × 148, imaging 10 min after 0.2 μg/kg gadolinium DTPA; slice orientation equal to SSFP). MRI images were analysed using dedicated software (MASS © , Medis,
European Radiology, 2008
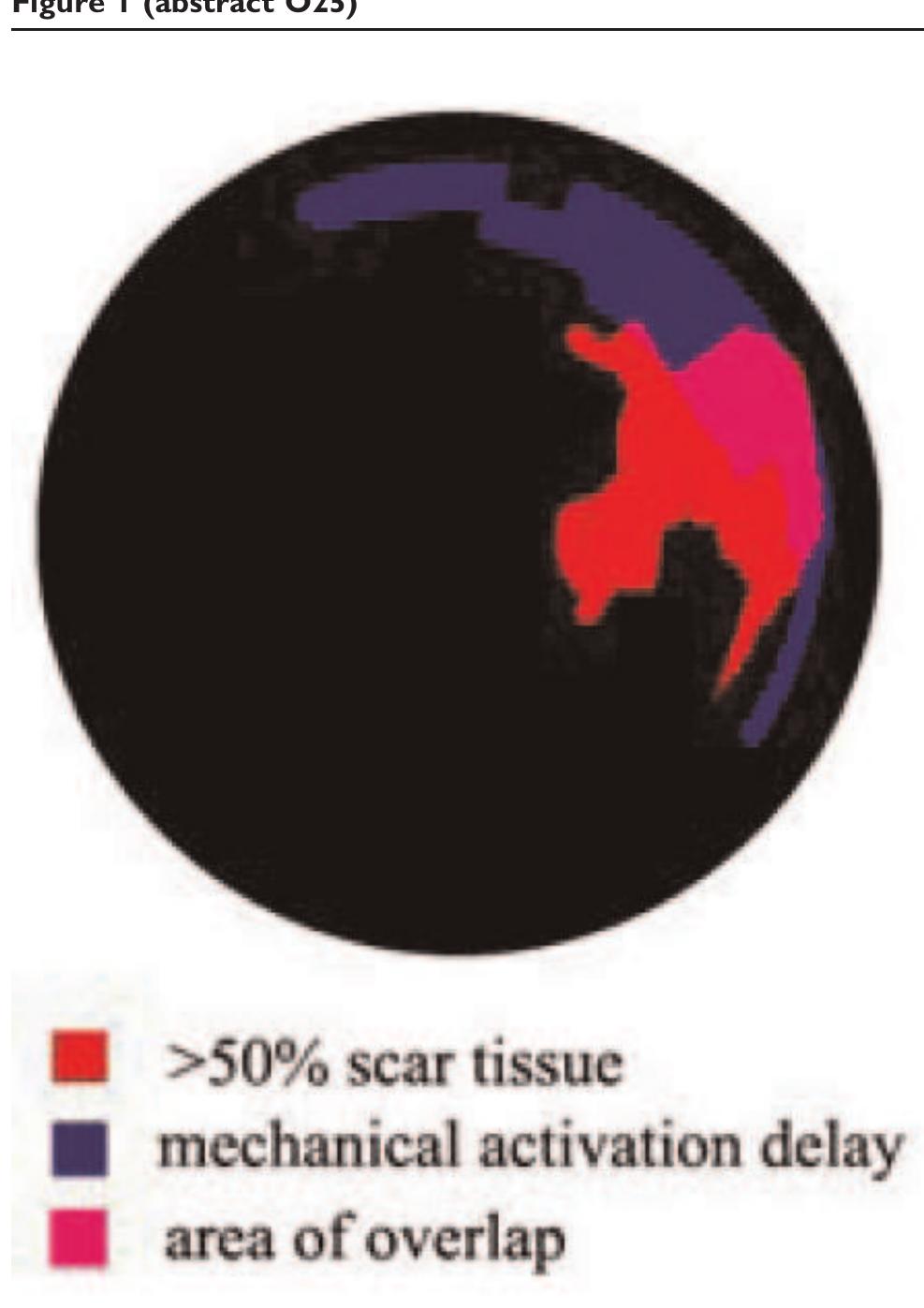
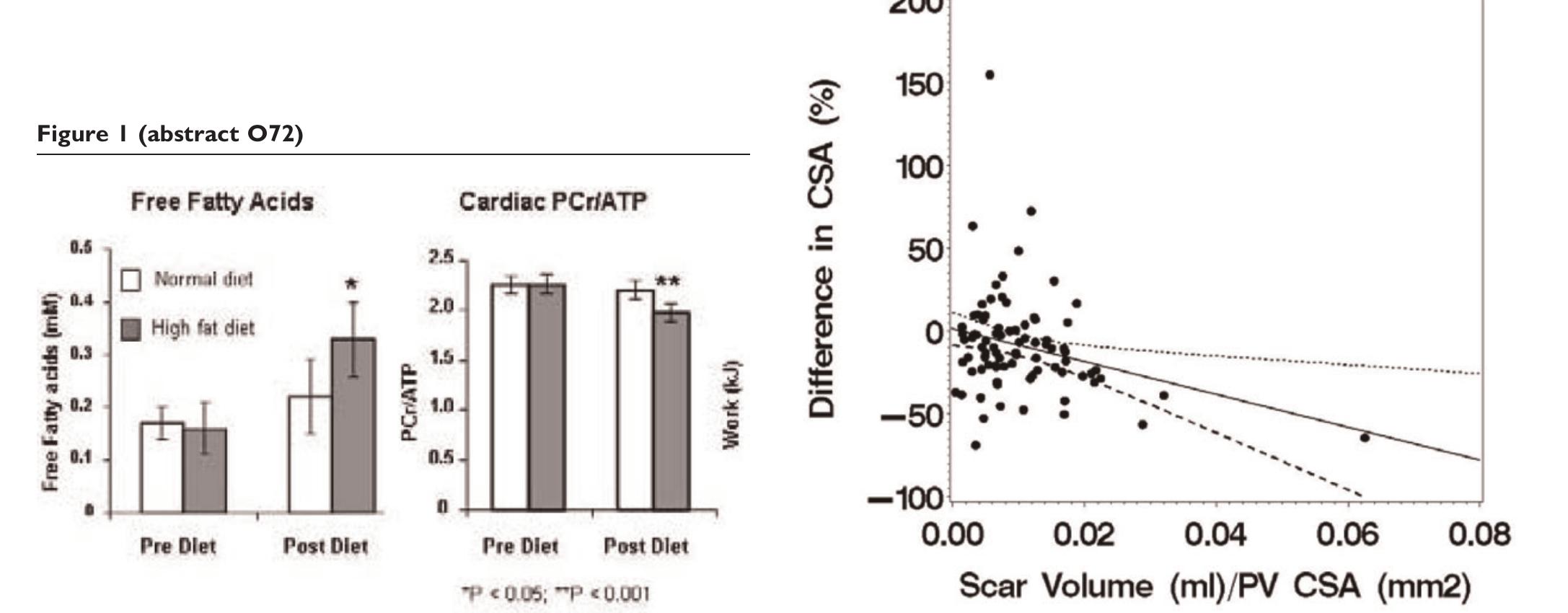
Robust assessment of the transmural extent of myocardial infarction in late gadolinium-enhanced MRI studies using appropriate angular and circumferential subdivision of the myocardium Abstract A computer-assisted method is proposed to estimate transmural extent of myocardial infarction. In 40 patients with chronic myocardial infarction and 3 control subjects, late gadolinium enhancement images were acquired with magnetic resonance imaging. Segmental infarct transmural extent was visually assessed by two experts on a 5-point scale. A fuzzy c-means algorithm was applied on both the cavity and myocardium to estimate an enhancement index for 12 sub-regions of each segment. A threshold was defined on a training database (n=29) to establish the transmurality extent of each subsegment and was applied to the validation database (n=14). Interobserver reproducibility reached an absolute agreement (Aa) of 85% and a kappa value (κ) of 0.83 when considering the whole training database; Aa decreased to 62% and κ to 0.68 when excluding homogeneous segments. On the validation database, segments were subdivided into three angular sub-segments. Then, interobserver visual reproducibility reached Aa of 93% and κ of 0.92. Moreover, the absolute comparison of each expert with the computerassisted method yielded Aa higher than 88% and κ higher than 0.86. The computer-assisted method quantifies infarct transmurality without defining remote and infarcted regions, and the transmural extent is accurately characterized when dividing each segment into three angular sub-segments.
Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 2009
Introduction: Prophylactic implantation of a cardioverter/ defibrillator (ICD) has been shown to reduce mortality in patients with chronic myocardial infarction (CMI) and an increased risk for life threatening ventricular arrhythmia (VA). The use of ICDs in this large patient population is still limited by high costs and possible adverse events including inappropriate discharges and progression of heart failure. VA is related to infarct size and seems to be related to infarct morphology. Contrast enhanced cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (ceCMR) can detect and quantify myocardial fibrosis in the setting of CMI and might therefore be a valuable tool for a more accurate risk stratification in this setting. Hypothesis: ceCMR can identify the subgroup developing VA in patients with prophylactic ICD implantation following MADIT criteria. Methods: We prospectively enrolled 52 patients (49 males, age 69 ± 10 years) with CMI and clinical indication for ICD therapy following MADIT criteria. Prior to implantation (36 ± 78 days) patients were investigated on a 1.5 T clinical scanner (Siemens Avanto © , Germany) to assess left ventricular function (LVEF), LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and LV mass (sequence parameters: GRE SSFP, matrix 256 × 192, short axis stack; full LV coverage, no gap; slice thickness 6 mm). For quantitative assessment of infarct morphology late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) was performed including measurement of total and relative infarct mass (related to LV mass) and the degree of transmurality (DT) as defined by the percentage of transmurality in each scar. (sequence parameters: inversion recovery gradient echo; matrix 256 × 148, imaging 10 min after 0.2 μg/kg gadolinium DTPA; slice orientation equal to SSFP). MRI images were analysed using dedicated software (MASS © , Medis, Netherlands). LGE was defined as myocardial areas with signal intensity above the average plus 5 SD of the remote myocardium. After implantation, patients were followed up including ICD readout after 3 and than every 6 months for a mean of 945 ± 344 days. ICD data were evaluated by an experienced electrophysiologist. Primary endpoint was the occurrence of an appropriate discharge (DC), antitachycard pacing (ATP) or death from cardiac cause. Results: The endpoint occurred in 10 patients (3 DC, 6 ATP, 1 death). These patients had a higher relative infarct mass (28 ± 7% vs. 22 ± 11%, p = 0.03) as well as high degree of transmurality (64 ± 22% vs. 44 ± 25%, p = 0.05). Their LVEF (29 ± 8% vs. 30 ± 4%, p = 0.75), LV mass (148 ± 29 g vs. 154 ± 42 g, p = 0.60), LVEDV (270 ± 133 ml vs. 275 ± 83 ml, p = 0.90) or total infarct mass (43 ± 19 g vs. 37 ± 21 g, p = 0.43) were however not significant from the group with no events. In a cox proportional hazards regression model including LVEF, LVEDV, LV mass, DT and age, only degree of transmurality and relative infarct mass emerged as independent predictors of the primary end point (p = 0.009). In CMI-patients fulfilling MADIT criteria ceCMR could show that the extent and transmurality of myocardial scarring are independent predictors for life threatening ventricular arrhythmia or death. This additional information could lead to more precise risk stratification and might reduce adverse events and cost of ICD therapy in this patient population. Larger trials are needed to confirm this finding.
Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 2009
Introduction: Prophylactic implantation of a cardioverter/ defibrillator (ICD) has been shown to reduce mortality in patients with chronic myocardial infarction (CMI) and an increased risk for life threatening ventricular arrhythmia (VA). The use of ICDs in this large patient population is still limited by high costs and possible adverse events including inappropriate discharges and progression of heart failure. VA is related to infarct size and seems to be related to infarct morphology. Contrast enhanced cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (ceCMR) can detect and quantify myocardial fibrosis in the setting of CMI and might therefore be a valuable tool for a more accurate risk stratification in this setting. Hypothesis: ceCMR can identify the subgroup developing VA in patients with prophylactic ICD implantation following MADIT criteria. Methods: We prospectively enrolled 52 patients (49 males, age 69 ± 10 years) with CMI and clinical indication for ICD therapy following MADIT criteria. Prior to implantation (36 ± 78 days) patients were investigated on a 1.5 T clinical scanner (Siemens Avanto © , Germany) to assess left ventricular function (LVEF), LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and LV mass (sequence parameters: GRE SSFP, matrix 256 × 192, short axis stack; full LV coverage, no gap; slice thickness 6 mm). For quantitative assessment of infarct morphology late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) was performed including measurement of total and relative infarct mass (related to LV mass) and the degree of transmurality (DT) as defined by the percentage of transmurality in each scar. (sequence parameters: inversion recovery gradient echo; matrix 256 × 148, imaging 10 min after 0.2 μg/kg gadolinium DTPA; slice orientation equal to SSFP). MRI images were analysed using dedicated software (MASS © , Medis,
Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 2009
Introduction: Prophylactic implantation of a cardioverter/ defibrillator (ICD) has been shown to reduce mortality in patients with chronic myocardial infarction (CMI) and an increased risk for life threatening ventricular arrhythmia (VA). The use of ICDs in this large patient population is still limited by high costs and possible adverse events including inappropriate discharges and progression of heart failure. VA is related to infarct size and seems to be related to infarct morphology. Contrast enhanced cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (ceCMR) can detect and quantify myocardial fibrosis in the setting of CMI and might therefore be a valuable tool for a more accurate risk stratification in this setting. Hypothesis: ceCMR can identify the subgroup developing VA in patients with prophylactic ICD implantation following MADIT criteria. Methods: We prospectively enrolled 52 patients (49 males, age 69 ± 10 years) with CMI and clinical indication for ICD therapy following MADIT criteria. Prior to implantation (36 ± 78 days) patients were investigated on a 1.5 T clinical scanner (Siemens Avanto © , Germany) to assess left ventricular function (LVEF), LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and LV mass (sequence parameters: GRE SSFP, matrix 256 × 192, short axis stack; full LV coverage, no gap; slice thickness 6 mm). For quantitative assessment of infarct morphology late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) was performed including measurement of total and relative infarct mass (related to LV mass) and the degree of transmurality (DT) as defined by the percentage of transmurality in each scar. (sequence parameters: inversion recovery gradient echo; matrix 256 × 148, imaging 10 min after 0.2 μg/kg gadolinium DTPA; slice orientation equal to SSFP). MRI images were analysed using dedicated software (MASS © , Medis,
Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 2009
Introduction: Prophylactic implantation of a cardioverter/ defibrillator (ICD) has been shown to reduce mortality in patients with chronic myocardial infarction (CMI) and an increased risk for life threatening ventricular arrhythmia (VA). The use of ICDs in this large patient population is still limited by high costs and possible adverse events including inappropriate discharges and progression of heart failure. VA is related to infarct size and seems to be related to infarct morphology. Contrast enhanced cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (ceCMR) can detect and quantify myocardial fibrosis in the setting of CMI and might therefore be a valuable tool for a more accurate risk stratification in this setting. Hypothesis: ceCMR can identify the subgroup developing VA in patients with prophylactic ICD implantation following MADIT criteria. Methods: We prospectively enrolled 52 patients (49 males, age 69 ± 10 years) with CMI and clinical indication for ICD therapy following MADIT criteria. Prior to implantation (36 ± 78 days) patients were investigated on a 1.5 T clinical scanner (Siemens Avanto © , Germany) to assess left ventricular function (LVEF), LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and LV mass (sequence parameters: GRE SSFP, matrix 256 × 192, short axis stack; full LV coverage, no gap; slice thickness 6 mm). For quantitative assessment of infarct morphology late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) was performed including measurement of total and relative infarct mass (related to LV mass) and the degree of transmurality (DT) as defined by the percentage of transmurality in each scar. (sequence parameters: inversion recovery gradient echo; matrix 256 × 148, imaging 10 min after 0.2 μg/kg gadolinium DTPA; slice orientation equal to SSFP). MRI images were analysed using dedicated software (MASS © , Medis,
Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 2009
Introduction: Prophylactic implantation of a cardioverter/ defibrillator (ICD) has been shown to reduce mortality in patients with chronic myocardial infarction (CMI) and an increased risk for life threatening ventricular arrhythmia (VA). The use of ICDs in this large patient population is still limited by high costs and possible adverse events including inappropriate discharges and progression of heart failure. VA is related to infarct size and seems to be related to infarct morphology. Contrast enhanced cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (ceCMR) can detect and quantify myocardial fibrosis in the setting of CMI and might therefore be a valuable tool for a more accurate risk stratification in this setting. Hypothesis: ceCMR can identify the subgroup developing VA in patients with prophylactic ICD implantation following MADIT criteria. Methods: We prospectively enrolled 52 patients (49 males, age 69 ± 10 years) with CMI and clinical indication for ICD therapy following MADIT criteria. Prior to implantation (36 ± 78 days) patients were investigated on a 1.5 T clinical scanner (Siemens Avanto © , Germany) to assess left ventricular function (LVEF), LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and LV mass (sequence parameters: GRE SSFP, matrix 256 × 192, short axis stack; full LV coverage, no gap; slice thickness 6 mm). For quantitative assessment of infarct morphology late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) was performed including measurement of total and relative infarct mass (related to LV mass) and the degree of transmurality (DT) as defined by the percentage of transmurality in each scar. (sequence parameters: inversion recovery gradient echo; matrix 256 × 148, imaging 10 min after 0.2 μg/kg gadolinium DTPA; slice orientation equal to SSFP). MRI images were analysed using dedicated software (MASS © , Medis,
Introduction: Prophylactic implantation of a cardioverter/ defibrillator (ICD) has been shown to reduce mortality in patients with chronic myocardial infarction (CMI) and an increased risk for life threatening ventricular arrhythmia (VA). The use of ICDs in this large patient population is still limited by high costs and possible adverse events including inappropriate discharges and progression of heart failure. VA is related to infarct size and seems to be related to infarct morphology. Contrast enhanced cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (ceCMR) can detect and quantify myocardial fibrosis in the setting of CMI and might therefore be a valuable tool for a more accurate risk stratification in this setting. Hypothesis: ceCMR can identify the subgroup developing VA in patients with prophylactic ICD implantation following MADIT criteria. Methods: We prospectively enrolled 52 patients (49 males, age 69 ± 10 years) with CMI and clinical indication for ICD therapy following MADIT criteria. Prior to implantation (36 ± 78 days) patients were investigated on a 1.5 T clinical scanner (Siemens Avanto © , Germany) to assess left ventricular function (LVEF), LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and LV mass (sequence parameters: GRE SSFP, matrix 256 × 192, short axis stack; full LV coverage, no gap; slice thickness 6 mm). For quantitative assessment of infarct morphology late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) was performed including measurement of total and relative infarct mass (related to LV mass) and the degree of transmurality (DT) as defined by the percentage of transmurality in each scar. (sequence parameters: inversion recovery gradient echo; matrix 256 × 148, imaging 10 min after 0.2 μg/kg gadolinium DTPA; slice orientation equal to SSFP). MRI images were analysed using dedicated software (MASS © , Medis,
Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 2009
Introduction: Prophylactic implantation of a cardioverter/ defibrillator (ICD) has been shown to reduce mortality in patients with chronic myocardial infarction (CMI) and an increased risk for life threatening ventricular arrhythmia (VA). The use of ICDs in this large patient population is still limited by high costs and possible adverse events including inappropriate discharges and progression of heart failure. VA is related to infarct size and seems to be related to infarct morphology. Contrast enhanced cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (ceCMR) can detect and quantify myocardial fibrosis in the setting of CMI and might therefore be a valuable tool for a more accurate risk stratification in this setting. Hypothesis: ceCMR can identify the subgroup developing VA in patients with prophylactic ICD implantation following MADIT criteria. Methods: We prospectively enrolled 52 patients (49 males, age 69 ± 10 years) with CMI and clinical indication for ICD therapy following MADIT criteria. Prior to implantation (36 ± 78 days) patients were investigated on a 1.5 T clinical scanner (Siemens Avanto © , Germany) to assess left ventricular function (LVEF), LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and LV mass (sequence parameters: GRE SSFP, matrix 256 × 192, short axis stack; full LV coverage, no gap; slice thickness 6 mm). For quantitative assessment of infarct morphology late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) was performed including measurement of total and relative infarct mass (related to LV mass) and the degree of transmurality (DT) as defined by the percentage of transmurality in each scar. (sequence parameters: inversion recovery gradient echo; matrix 256 × 148, imaging 10 min after 0.2 μg/kg gadolinium DTPA; slice orientation equal to SSFP). MRI images were analysed using dedicated software (MASS © , Medis,
Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 2009
Introduction: Prophylactic implantation of a cardioverter/ defibrillator (ICD) has been shown to reduce mortality in patients with chronic myocardial infarction (CMI) and an increased risk for life threatening ventricular arrhythmia (VA). The use of ICDs in this large patient population is still limited by high costs and possible adverse events including inappropriate discharges and progression of heart failure. VA is related to infarct size and seems to be related to infarct morphology. Contrast enhanced cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (ceCMR) can detect and quantify myocardial fibrosis in the setting of CMI and might therefore be a valuable tool for a more accurate risk stratification in this setting. Hypothesis: ceCMR can identify the subgroup developing VA in patients with prophylactic ICD implantation following MADIT criteria. Methods: We prospectively enrolled 52 patients (49 males, age 69 ± 10 years) with CMI and clinical indication for ICD therapy following MADIT criteria. Prior to implantation (36 ± 78 days) patients were investigated on a 1.5 T clinical scanner (Siemens Avanto © , Germany) to assess left ventricular function (LVEF), LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and LV mass (sequence parameters: GRE SSFP, matrix 256 × 192, short axis stack; full LV coverage, no gap; slice thickness 6 mm). For quantitative assessment of infarct morphology late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) was performed including measurement of total and relative infarct mass (related to LV mass) and the degree of transmurality (DT) as defined by the percentage of transmurality in each scar. (sequence parameters: inversion recovery gradient echo; matrix 256 × 148, imaging 10 min after 0.2 μg/kg gadolinium DTPA; slice orientation equal to SSFP). MRI images were analysed using dedicated software (MASS © , Medis, Netherlands). LGE was defined as myocardial areas with signal intensity above the average plus 5 SD of the remote myocardium. After implantation, patients were followed up including ICD readout after 3 and than every 6 months for a mean of 945 ± 344 days. ICD data were evaluated by an experienced electrophysiologist. Primary endpoint was the occurrence of an appropriate discharge (DC), antitachycard pacing (ATP) or death from cardiac cause. Results: The endpoint occurred in 10 patients (3 DC, 6 ATP, 1 death). These patients had a higher relative infarct mass (28 ± 7% vs. 22 ± 11%, p = 0.03) as well as high degree of transmurality (64 ± 22% vs. 44 ± 25%, p = 0.05). Their LVEF (29 ± 8% vs. 30 ± 4%, p = 0.75), LV mass (148 ± 29 g vs. 154 ± 42 g, p = 0.60), LVEDV (270 ± 133 ml vs. 275 ± 83 ml, p = 0.90) or total infarct mass (43 ± 19 g vs. 37 ± 21 g, p = 0.43) were however not significant from the group with no events. In a cox proportional hazards regression model including LVEF, LVEDV, LV mass, DT and age, only degree of transmurality and relative infarct mass emerged as independent predictors of the primary end point (p = 0.009). Conclusion: In CMI-patients fulfilling MADIT criteria ceCMR could show that the extent and transmurality of myocardial scarring are independent predictors for life threatening ventricular arrhythmia or death. This additional information could lead to more precise risk stratification and might reduce adverse events and cost of ICD therapy in this patient population. Larger trials are needed to confirm this finding.
Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 2009
Introduction: Prophylactic implantation of a cardioverter/ defibrillator (ICD) has been shown to reduce mortality in patients with chronic myocardial infarction (CMI) and an increased risk for life threatening ventricular arrhythmia (VA). The use of ICDs in this large patient population is still limited by high costs and possible adverse events including inappropriate discharges and progression of heart failure. VA is related to infarct size and seems to be related to infarct morphology. Contrast enhanced cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (ceCMR) can detect and quantify myocardial fibrosis in the setting of CMI and might therefore be a valuable tool for a more accurate risk stratification in this setting. Hypothesis: ceCMR can identify the subgroup developing VA in patients with prophylactic ICD implantation following MADIT criteria. Methods: We prospectively enrolled 52 patients (49 males, age 69 ± 10 years) with CMI and clinical indication for ICD therapy following MADIT criteria. Prior to implantation (36 ± 78 days) patients were investigated on a 1.5 T clinical scanner (Siemens Avanto © , Germany) to assess left ventricular function (LVEF), LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and LV mass (sequence parameters: GRE SSFP, matrix 256 × 192, short axis stack; full LV coverage, no gap; slice thickness 6 mm). For quantitative assessment of infarct morphology late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) was performed including measurement of total and relative infarct mass (related to LV mass) and the degree of transmurality (DT) as defined by the percentage of transmurality in each scar. (sequence parameters: inversion recovery gradient echo; matrix 256 × 148, imaging 10 min after 0.2 μg/kg gadolinium DTPA; slice orientation equal to SSFP). MRI images were analysed using dedicated software (MASS © , Medis, Netherlands). LGE was defined as myocardial areas with signal intensity above the average plus 5 SD of the remote myocardium. After implantation, patients were followed up including ICD readout after 3 and than every 6 months for a mean of 945 ± 344 days. ICD data were evaluated by an experienced electrophysiologist. Primary endpoint was the occurrence of an appropriate discharge (DC), antitachycard pacing (ATP) or death from cardiac cause. Results: The endpoint occurred in 10 patients (3 DC, 6 ATP, 1 death). These patients had a higher relative infarct mass (28 ± 7% vs. 22 ± 11%, p = 0.03) as well as high degree of transmurality (64 ± 22% vs. 44 ± 25%, p = 0.05). Their LVEF (29 ± 8% vs. 30 ± 4%, p = 0.75), LV mass (148 ± 29 g vs. 154 ± 42 g, p = 0.60), LVEDV (270 ± 133 ml vs. 275 ± 83 ml, p = 0.90) or total infarct mass (43 ± 19 g vs. 37 ± 21 g, p = 0.43) were however not significant from the group with no events. In a cox proportional hazards regression model including LVEF, LVEDV, LV mass, DT and age, only degree of transmurality and relative infarct mass emerged as independent predictors of the primary end point (p = 0.009). Conclusion: In CMI-patients fulfilling MADIT criteria ceCMR could show that the extent and transmurality of myocardial scarring are independent predictors for life threatening ventricular arrhythmia or death. This additional information could lead to more precise risk stratification and might reduce adverse events and cost of ICD therapy in this patient population. Larger trials are needed to confirm this finding.
Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 2009
Introduction: Prophylactic implantation of a cardioverter/ defibrillator (ICD) has been shown to reduce mortality in patients with chronic myocardial infarction (CMI) and an increased risk for life threatening ventricular arrhythmia (VA). The use of ICDs in this large patient population is still limited by high costs and possible adverse events including inappropriate discharges and progression of heart failure. VA is related to infarct size and seems to be related to infarct morphology. Contrast enhanced cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (ceCMR) can detect and quantify myocardial fibrosis in the setting of CMI and might therefore be a valuable tool for a more accurate risk stratification in this setting. Hypothesis: ceCMR can identify the subgroup developing VA in patients with prophylactic ICD implantation following MADIT criteria. Methods: We prospectively enrolled 52 patients (49 males, age 69 ± 10 years) with CMI and clinical indication for ICD therapy following MADIT criteria. Prior to implantation (36 ± 78 days) patients were investigated on a 1.5 T clinical scanner (Siemens Avanto © , Germany) to assess left ventricular function (LVEF), LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and LV mass (sequence parameters: GRE SSFP, matrix 256 × 192, short axis stack; full LV coverage, no gap; slice thickness 6 mm). For quantitative assessment of infarct morphology late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) was performed including measurement of total and relative infarct mass (related to LV mass) and the degree of transmurality (DT) as defined by the percentage of transmurality in each scar. (sequence parameters: inversion recovery gradient echo; matrix 256 × 148, imaging 10 min after 0.2 μg/kg gadolinium DTPA; slice orientation equal to SSFP). MRI images were analysed using dedicated software (MASS © , Medis,
Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2010
Purpose-To demonstrate the advantages of Signal Intensity Percent-Infarct-Mapping (SI-PIM) using the standard delayed enhancement (DE) acquisition in assessing viability following myocardial infarction (MI). SI-PIM quantifies MI density with a voxel-by-voxel resolution in clinically used DE images. Materials and Methods-In canines (n=6), 96h after reperfused MI and administration of 0.2mmol/kg Gd(DTPA), ex-vivo DE images were acquired and SI-PIMs calculated. SI-PIM data were compared with data from DE images analyzed with several thresholding levels using SI remote+2SD , SI remote+6SD , SI full width half maximum (SI FWHM), and with triphenyl-tetrazoliumchloride (TTC) staining. SI-PIM was also compared to R1 percent infarct mapping (R1-PIM). Results-Left ventricular infarct volumes (IV) in DE images, IV SIremote+2SD and IV SIremote+6SD overestimated (p<0.05) TTC by medians of 13.21ml [10.2; 15.2] and 6.2ml [3.79; 8.23], respectively. SI FWHM , SI-PIM and R1-PIM, however, only non-significantly underestimated TTC, by medians of −0.10ml [−0.12, −0.06], −0.86ml [−1.04; 1.54] and −1.30ml [−4.99; −0.29], respectively. The Infarct-Involved Voxel Volume (IIVV) of SI-PIM, 32.4ml [21.2, 46.3] is higher (p<0.01) than IIVVs of SI FWHM 8.3ml [3.79, 19.0]. SI-PIM FWHM , however, underestimates TTC (−5.74ml [−11.89; −2.52] (p<0.01)). Thus SI-PIM outperforms SI FWHM because larger IIVVs are obtained, and thus PIs both in the rim and the core of the infarcted tissue are characterized, in contradistinction from DE-SI FWHM which shows mainly the infarct core. Conclusion-We have shown here, ex vivo, that SI-PIM has the same advantages as R1-PIM, but it is based on the scanning sequences of DE imaging, and thus it is obtainable within the same short scanning time as DE. This makes it a practical method for clinical studies.
Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 2009
Introduction: Prophylactic implantation of a cardioverter/ defibrillator (ICD) has been shown to reduce mortality in patients with chronic myocardial infarction (CMI) and an increased risk for life threatening ventricular arrhythmia (VA). The use of ICDs in this large patient population is still limited by high costs and possible adverse events including inappropriate discharges and progression of heart failure. VA is related to infarct size and seems to be related to infarct morphology. Contrast enhanced cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (ceCMR) can detect and quantify myocardial fibrosis in the setting of CMI and might therefore be a valuable tool for a more accurate risk stratification in this setting. Hypothesis: ceCMR can identify the subgroup developing VA in patients with prophylactic ICD implantation following MADIT criteria. Methods: We prospectively enrolled 52 patients (49 males, age 69 ± 10 years) with CMI and clinical indication for ICD therapy following MADIT criteria. Prior to implantation (36 ± 78 days) patients were investigated on a 1.5 T clinical scanner (Siemens Avanto © , Germany) to assess left ventricular function (LVEF), LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and LV mass (sequence parameters: GRE SSFP, matrix 256 × 192, short axis stack; full LV coverage, no gap; slice thickness 6 mm). For quantitative assessment of infarct morphology late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) was performed including measurement of total and relative infarct mass (related to LV mass) and the degree of transmurality (DT) as defined by the percentage of transmurality in each scar. (sequence parameters: inversion recovery gradient echo; matrix 256 × 148, imaging 10 min after 0.2 μg/kg gadolinium DTPA; slice orientation equal to SSFP). MRI images were analysed using dedicated software (MASS © , Medis,
Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 2009
Introduction: Prophylactic implantation of a cardioverter/ defibrillator (ICD) has been shown to reduce mortality in patients with chronic myocardial infarction (CMI) and an increased risk for life threatening ventricular arrhythmia (VA). The use of ICDs in this large patient population is still limited by high costs and possible adverse events including inappropriate discharges and progression of heart failure. VA is related to infarct size and seems to be related to infarct morphology. Contrast enhanced cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (ceCMR) can detect and quantify myocardial fibrosis in the setting of CMI and might therefore be a valuable tool for a more accurate risk stratification in this setting. Hypothesis: ceCMR can identify the subgroup developing VA in patients with prophylactic ICD implantation following MADIT criteria. Methods: We prospectively enrolled 52 patients (49 males, age 69 ± 10 years) with CMI and clinical indication for ICD therapy following MADIT criteria. Prior to implantation (36 ± 78 days) patients were investigated on a 1.5 T clinical scanner (Siemens Avanto © , Germany) to assess left ventricular function (LVEF), LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and LV mass (sequence parameters: GRE SSFP, matrix 256 × 192, short axis stack; full LV coverage, no gap; slice thickness 6 mm). For quantitative assessment of infarct morphology late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) was performed including measurement of total and relative infarct mass (related to LV mass) and the degree of transmurality (DT) as defined by the percentage of transmurality in each scar. (sequence parameters: inversion recovery gradient echo; matrix 256 × 148, imaging 10 min after 0.2 μg/kg gadolinium DTPA; slice orientation equal to SSFP). MRI images were analysed using dedicated software (MASS © , Medis, Netherlands). LGE was defined as myocardial areas with signal intensity above the average plus 5 SD of the remote myocardium. After implantation, patients were followed up including ICD readout after 3 and than every 6 months for a mean of 945 ± 344 days. ICD data were evaluated by an experienced electrophysiologist. Primary endpoint was the occurrence of an appropriate discharge (DC), antitachycard pacing (ATP) or death from cardiac cause. Results: The endpoint occurred in 10 patients (3 DC, 6 ATP, 1 death). These patients had a higher relative infarct mass (28 ± 7% vs. 22 ± 11%, p = 0.03) as well as high degree of transmurality (64 ± 22% vs. 44 ± 25%, p = 0.05). Their LVEF (29 ± 8% vs. 30 ± 4%, p = 0.75), LV mass (148 ± 29 g vs. 154 ± 42 g, p = 0.60), LVEDV (270 ± 133 ml vs. 275 ± 83 ml, p = 0.90) or total infarct mass (43 ± 19 g vs. 37 ± 21 g, p = 0.43) were however not significant from the group with no events. In a cox proportional hazards regression model including LVEF, LVEDV, LV mass, DT and age, only degree of transmurality and relative infarct mass emerged as independent predictors of the primary end point (p = 0.009). Conclusion: In CMI-patients fulfilling MADIT criteria ceCMR could show that the extent and transmurality of myocardial scarring are independent predictors for life threatening ventricular arrhythmia or death. This additional information could lead to more precise risk stratification and might reduce adverse events and cost of ICD therapy in this patient population. Larger trials are needed to confirm this finding.
Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 2009
Introduction: Prophylactic implantation of a cardioverter/ defibrillator (ICD) has been shown to reduce mortality in patients with chronic myocardial infarction (CMI) and an increased risk for life threatening ventricular arrhythmia (VA). The use of ICDs in this large patient population is still limited by high costs and possible adverse events including inappropriate discharges and progression of heart failure. VA is related to infarct size and seems to be related to infarct morphology. Contrast enhanced cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (ceCMR) can detect and quantify myocardial fibrosis in the setting of CMI and might therefore be a valuable tool for a more accurate risk stratification in this setting. Hypothesis: ceCMR can identify the subgroup developing VA in patients with prophylactic ICD implantation following MADIT criteria. Methods: We prospectively enrolled 52 patients (49 males, age 69 ± 10 years) with CMI and clinical indication for ICD therapy following MADIT criteria. Prior to implantation (36 ± 78 days) patients were investigated on a 1.5 T clinical scanner (Siemens Avanto © , Germany) to assess left ventricular function (LVEF), LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and LV mass (sequence parameters: GRE SSFP, matrix 256 × 192, short axis stack; full LV coverage, no gap; slice thickness 6 mm). For quantitative assessment of infarct morphology late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) was performed including measurement of total and relative infarct mass (related to LV mass) and the degree of transmurality (DT) as defined by the percentage of transmurality in each scar. (sequence parameters: inversion recovery gradient echo; matrix 256 × 148, imaging 10 min after 0.2 μg/kg gadolinium DTPA; slice orientation equal to SSFP). MRI images were analysed using dedicated software (MASS © , Medis,
Related topics

Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
 Richard Tang
Richard Tang