The effect of the mode of applied breakage on coal yield
2017

Sign up for access to the world's latest research
Abstract
Thank you for the encouragement and support throughout my studies. Byrone Malay, my love… Thank you for the support and believing in me. Toffie, Rambo, and Einsteinie… You paved the road to my heart with paw prints. vii ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS First, I would like to thank God for giving me the opportunity and strength to complete this research study. "So do not fear, for I am with you; do not be dismayed, for I am your God. I will strengthen you and help you; I will uphold you with my righteous right hand." Isaiah 41:10 I would like to show gratitude by thanking the following individuals for guidance, motivation, support, and assistance during the course of this research study:















































































































































































































































































































































































































































Related papers
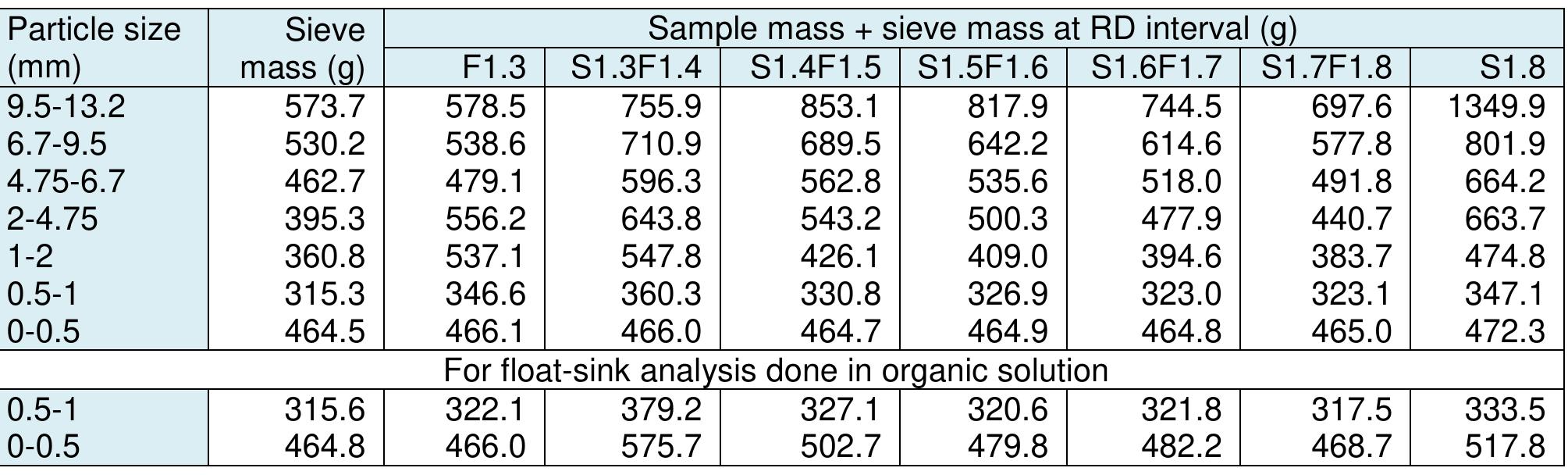
A number of simple field and laboratory studies and tests were carried out to visualize the nature and variation extent of mechanical properties with emphasis on cuttability across C1 coal seam in Parvade1 mine of Tabas located in east of Iran. Selection of the suitable coal winning machines and of the most effective and fitness bits for it and their arrangement on cutter head have a special relation to reach maximum productivity with minimum energy consumption. The effect of physico-mechanical properties on cuttability were studied in the laboratory and field for the C1 coal seam to identify the relevant parameters affecting the specific energy of coal cuttability. Field studies were also in-situ cuttability along with conducted over a number of active mechanized coal faces to study the geo-mining conditions of the site. The field and the laboratory data of coal cuttability was estimated due to the achieved results of uni-axial, shear, and tensile strength tests, as well as, Impact strength index, expanding bolt, and M.R.E. penetration tests on C1 coal seam.
Environmental Science Archives, 2024
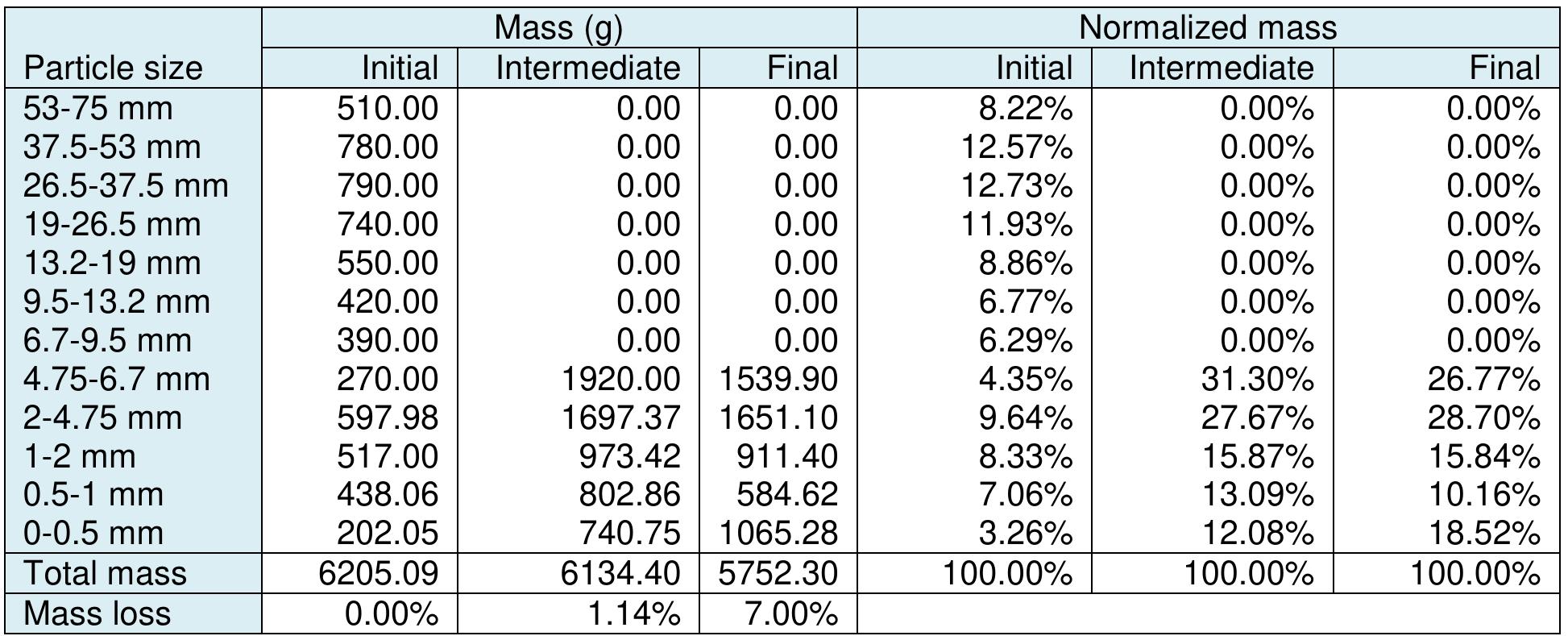
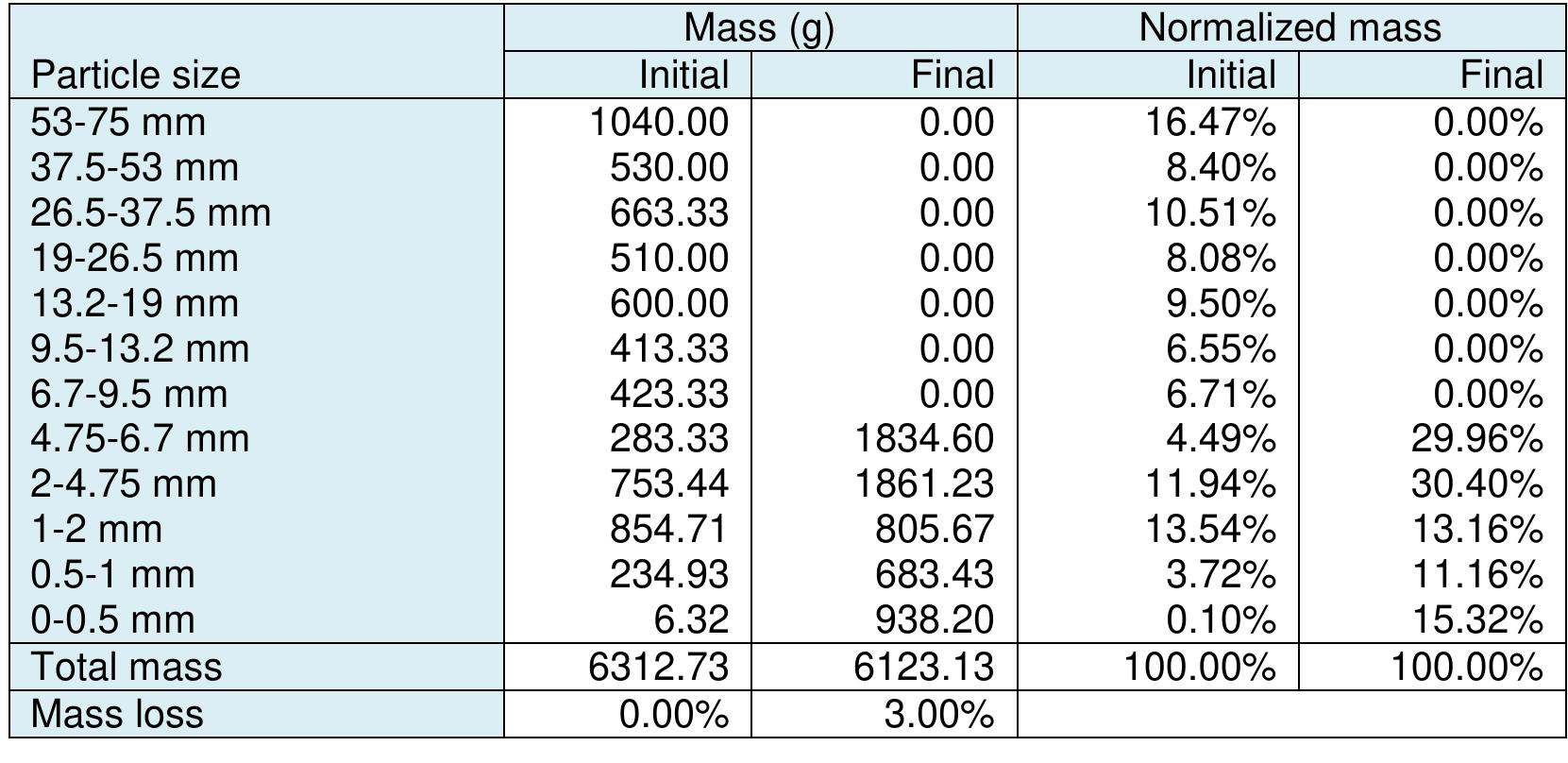
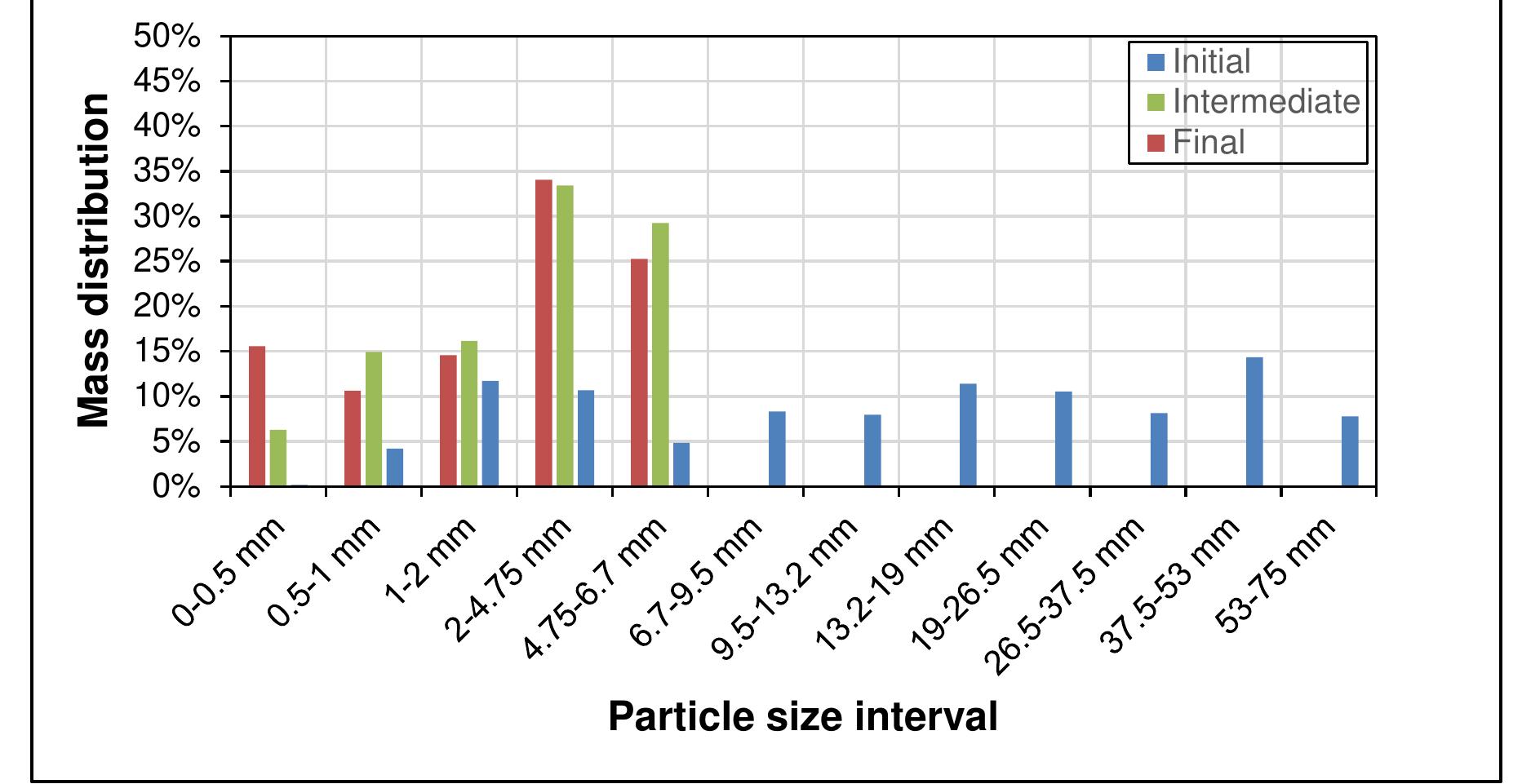
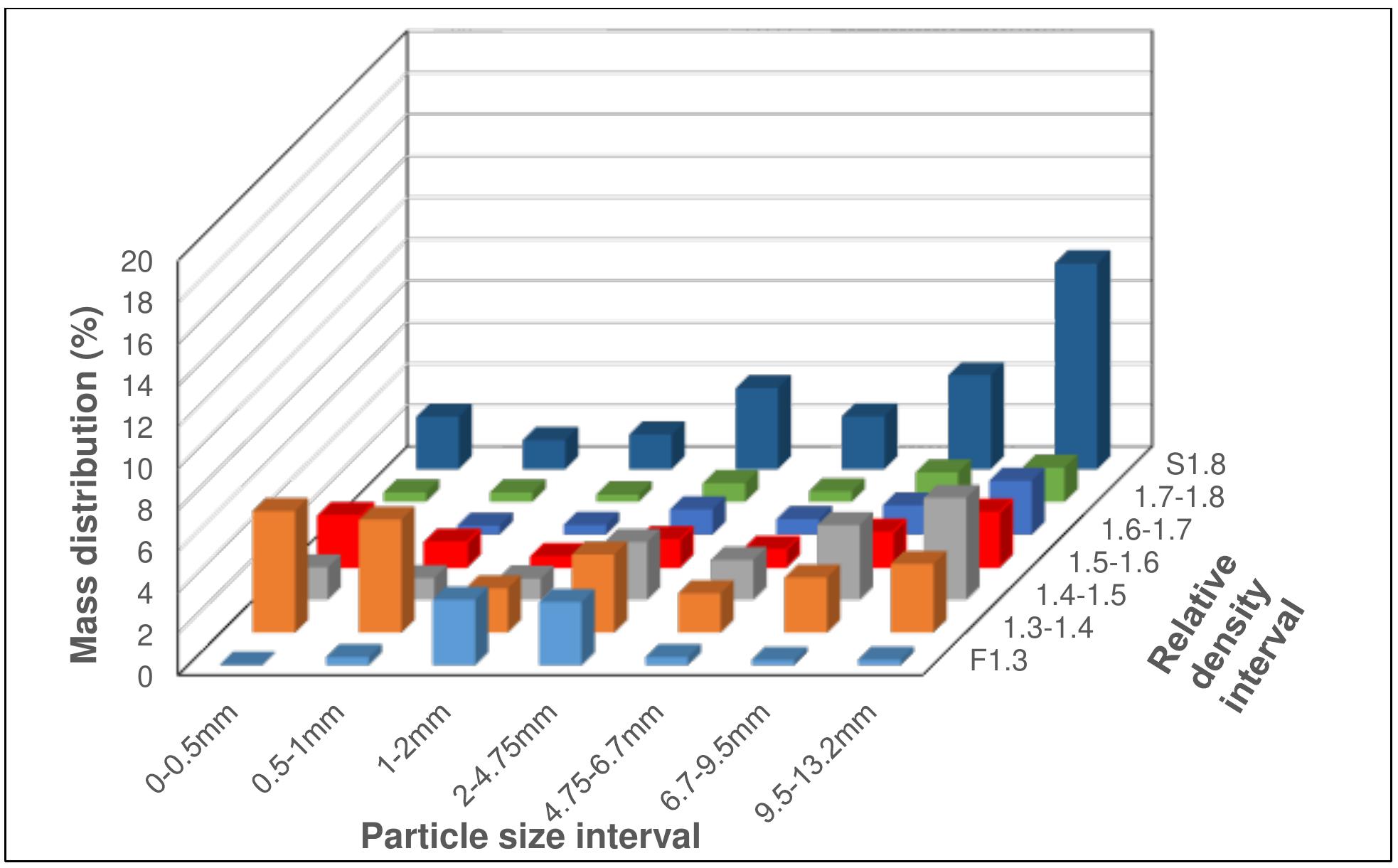
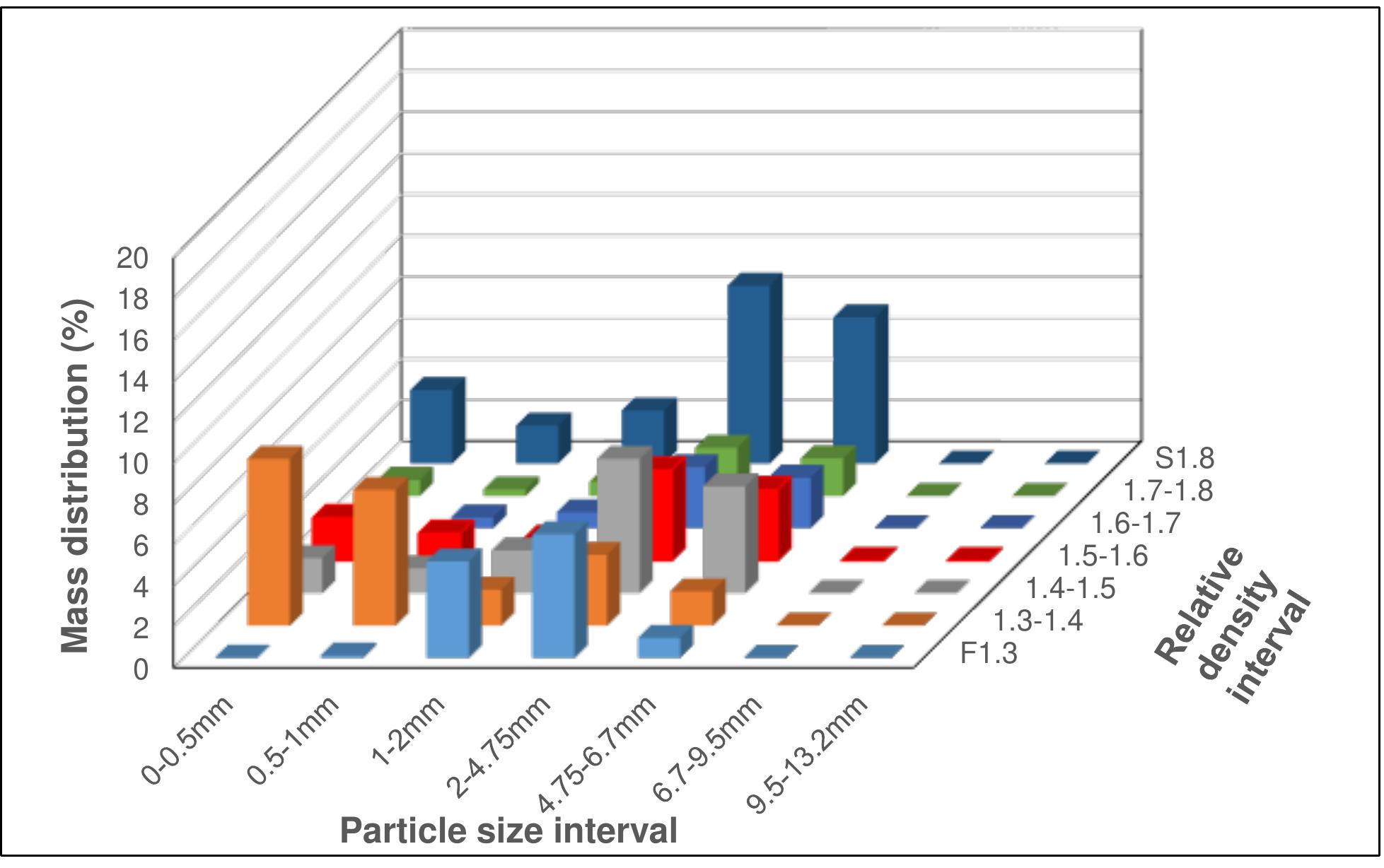
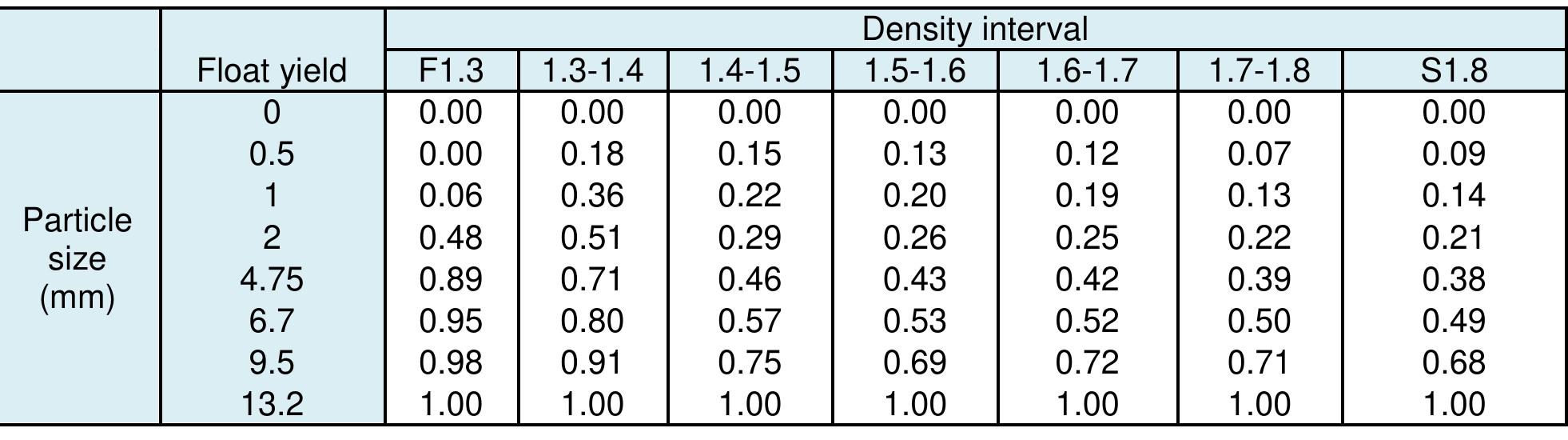
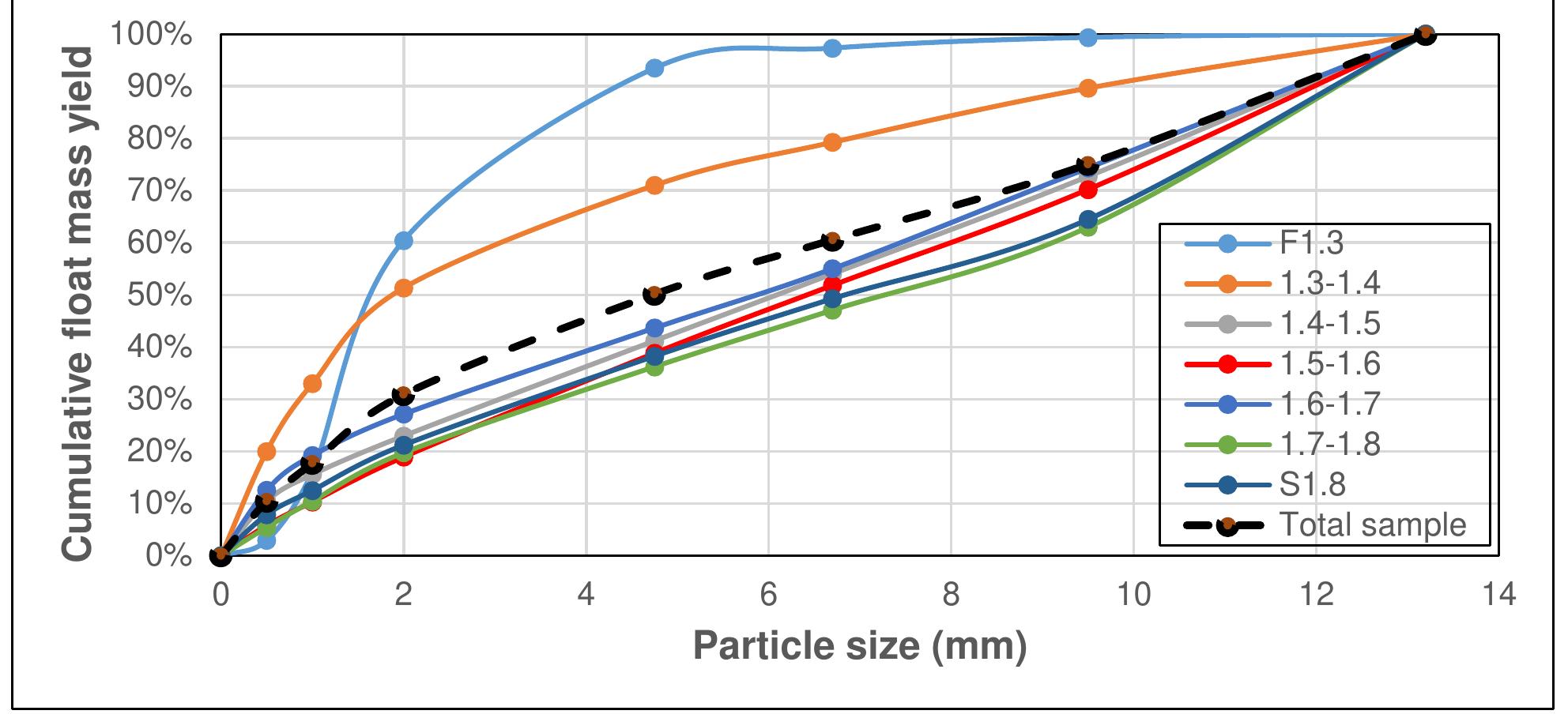
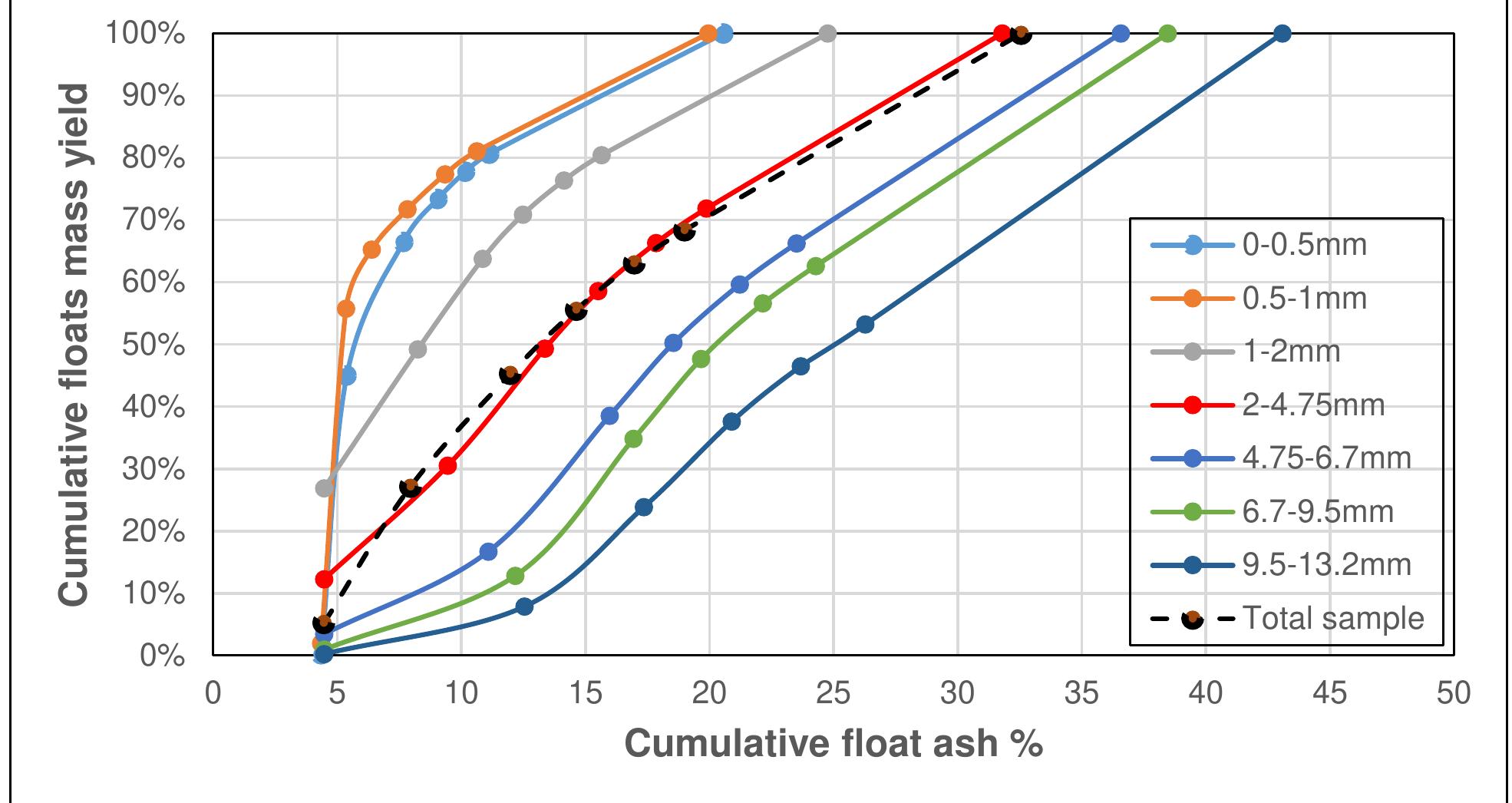
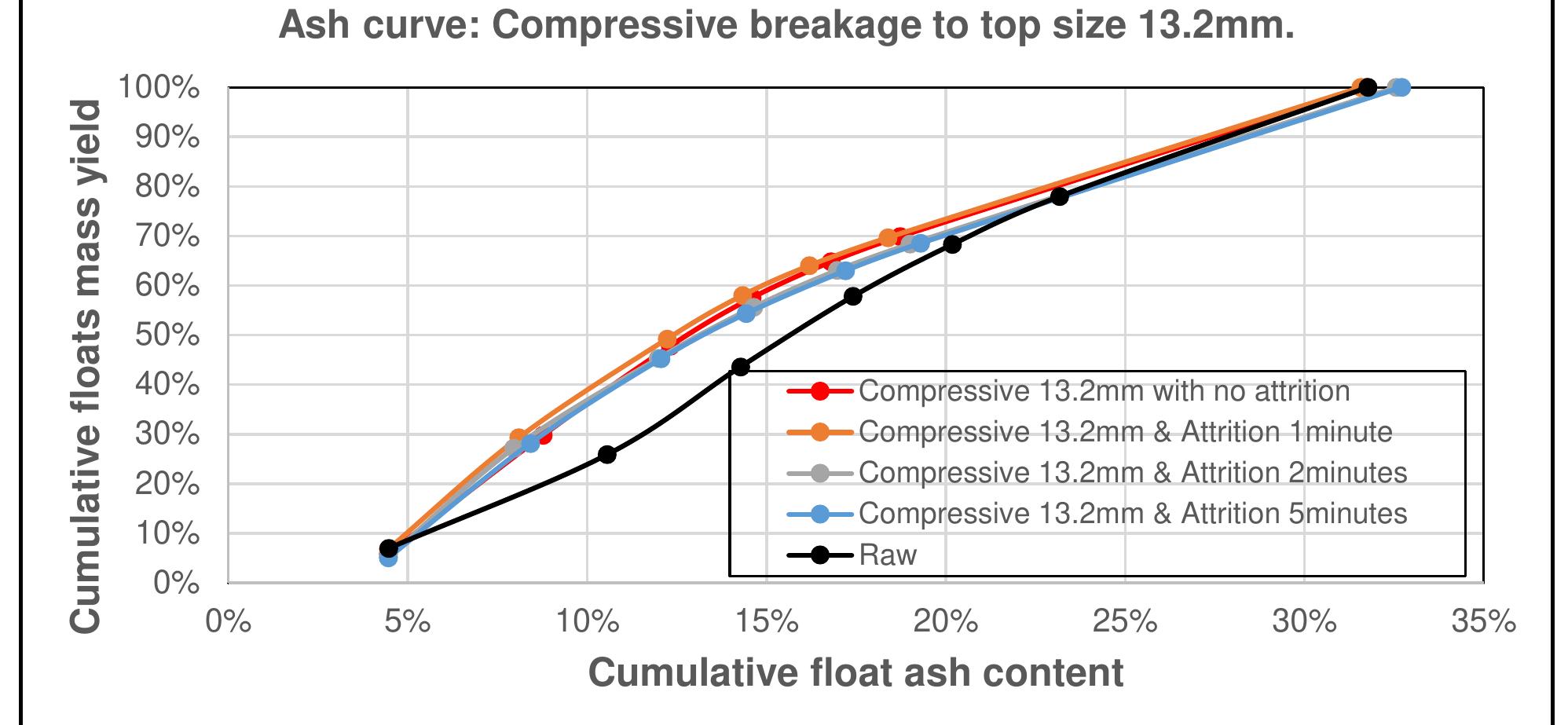
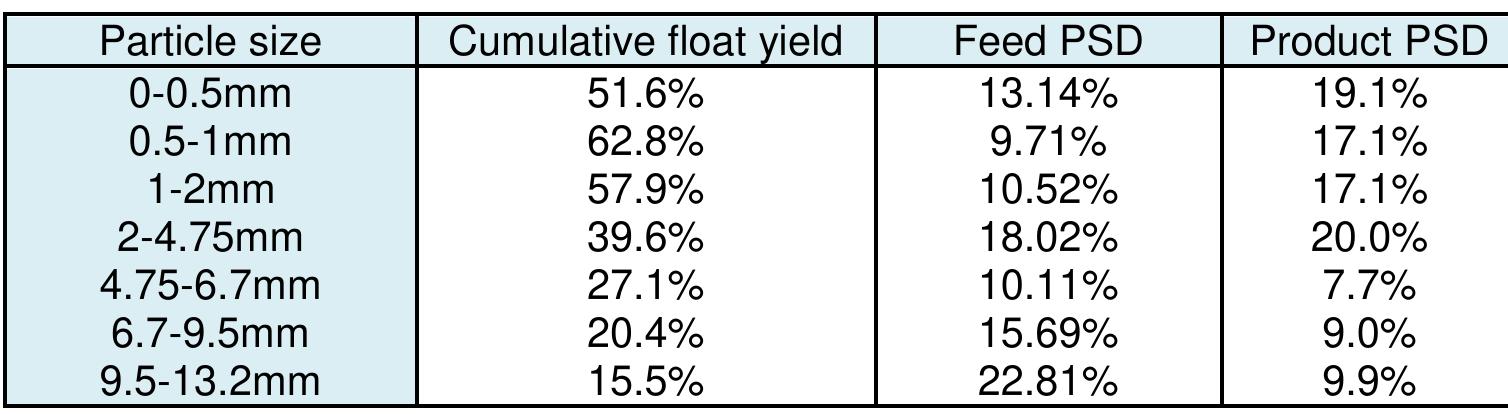
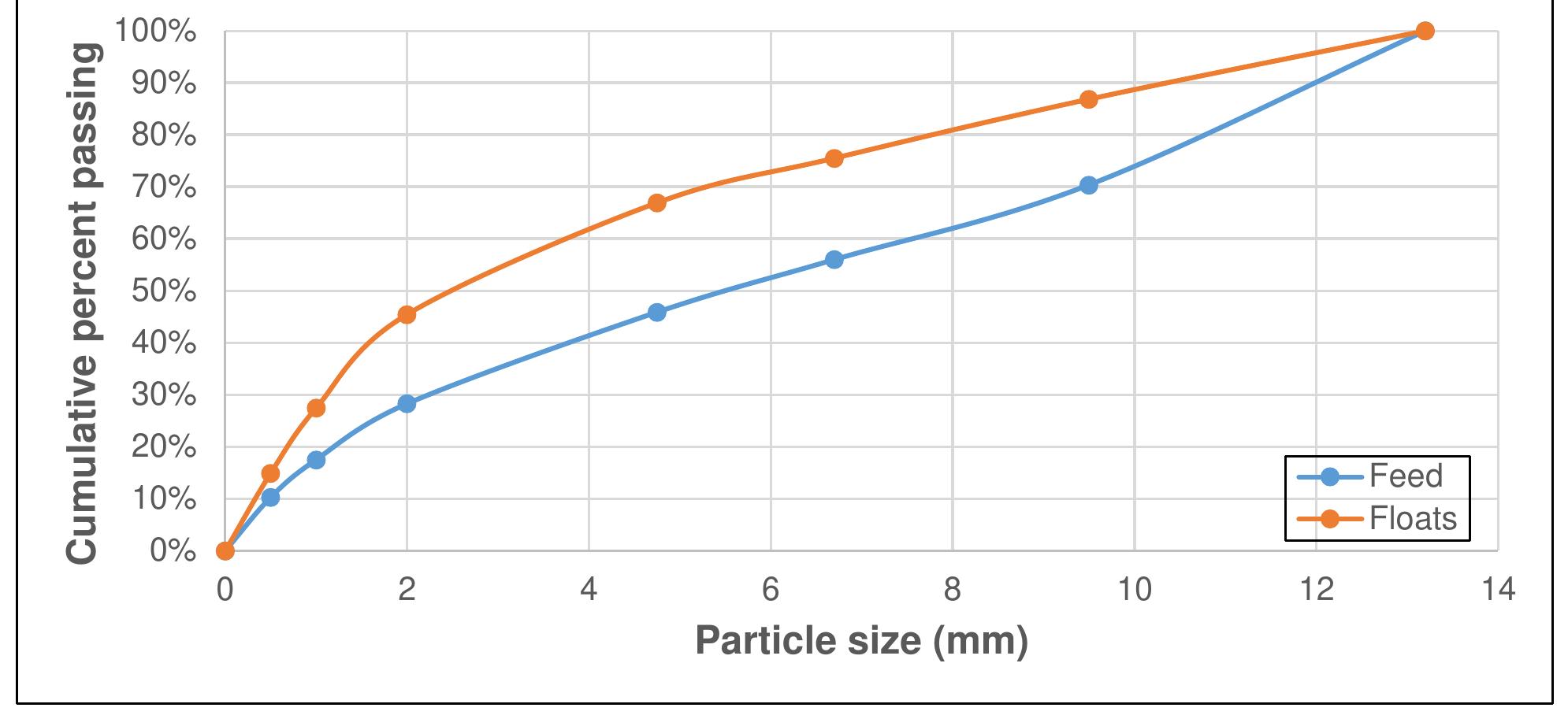
Coal is a heterogeneous rock with complex characteristics. Composition varies even in centimeters. Origin influences the composition of coal deposits, both organic and inorganic materials. The concentration of vitrinite or inertinite is determined by the nature and origin of the coal during the formation. Fluctuation and rates of down-warping or up-warping influence the accumulation of inorganic materials. The rank of the coal is determined by the thermal treatment undergone by the coal deposits over the period. Internal Moisture content depends upon the rank of the coal. Surface moisture content is based on the size of mined and crushed coal. Beneficiation of coal is a process of reducing the inorganic materials.
Powder Technology, 2014
The breakage characteristics of low rank coals were tested in a laboratory using ECO coal from an Indonesian mine as the feed material. The grinding test results were used to fit the parameters of the breakage functions of an existing continuous hammer mill model. The mill holdup , specific energy and projection rate to the screen were analyzed to observe the effects of operating conditions. The results indicate that for each underscreen aperture there exists a characteristic threshold point of the feed rate above which over-grinding occurs. This threshold point can be used to determine the optimal operating conditions of the breakage process. Additionally, a scale-up model of the hammer mill is established based on the energy-size relationship to predict the mill capacity as a function of the mill design and the operating parameters. A comparison between the prediction from the model and the manufacturer's data illustrates that the model based on Rittinger's theory fits the breakage characteristics of the hammer mill better than the models based on Bond's and Kick's theories. The established scale-up model agrees well with the manufacturer's test data within an acceptable degree of accuracy.
Energy & Fuels, 2008
An experimental study was conducted to investigate the devolatilization characteristics of five Australian coals in a thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) reactor by varying the coal lump size and the temperature. The swelling ratio was measured after thermal treatment of coal lumps in a horizontal tube furnace at 1273 K while the cracks generated in the lumpy char samples were examined using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Physical and chemical properties of coal and char samples were measured using CO 2 gas adsorption, Hg porosimetry, X-ray fluorescence (XRF) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). Under all the tested conditions, the total volatile yield of lumpy coals was found to be not influenced by either the temperature or particle size and was similar to that indicated in proximate coal analysis. However, as expected, the devolatilization rates were found to increase with increasing temperature as well as the increasing amount of volatiles present in the coal. The study further demonstrated that the effect of coal properties on the devolatilization rates of lumpy coals may not be significant as the rates decrease with increasing lump size, such that coal lumps with sizes more than 10 mm indicated similar orders of reaction rates. The apparent activation energy of coal lumps indicated a linear correlation with the stack height of the carbon crystallite of coals. The study demonstrated that the cracking and swelling behavior of coals was influenced by physical as well as chemical properties, particularly their modification during devolatilization conditions. The study showed that coals with low volatiles indicated high cracking which would increase further with increasing lump size in accordance with the size effect. The cracking tendency of coals appeared to have a reciprocal association with swelling tendency such that less swelling coals are more vulnerable to cracking.
2010
Proceedings of the 2010 Coal Operators\u27 Conference. All papers in these proceedings are peer reviewed in accordance with the AUSIMM publication standard
Journal of Minerals and Materials Characterization and Engineering, 2009
The effects of igneous intrusion on coal are observed in various parts of the world. It is found that igneous intrusions have altered the quality and characteristics, especially the coke ability of the coals. It has been estimated that a large quantity of heat affected (jhama) coal is reserved in the Jharia collieries of India. Nowadays, apart from difficulties of mining, its utilization is the biggest issue. This paper presents a brief overview of heat altered coal and also highlights some studies, undertaken in Tata Steel to make best possible metallurgical use of jhama especially in steel industry.
2002
Kömür küllerinin yakma sistemlerinde cüruf oluşturma ve kirletme eğilimini önceden tahmin etmek için çok sayıda ampirik parametre geliştirilmiştir. Ancak, henüz bu indislerden hiç birisi küllerin kirletme ve cüruf oluşturma eğilimini açıklamakta yeterli olamamıştır. Önceleri bu parametrelerin çoğu külün bileşimi ile ilişkilendirilmişken, günümüzde, yakma kazanlanndaki kirletme, cüruflaşma ve korozyon gibi sorunların ortaya çıkmasında veya önlenmesinde külün mineral madde İçeriğinin de önemli bir rol oynadığı anlaşılmıştır. Bu çalışmada külün cüruf oluşturma ve kirletme eğilimini önceden tahmin etmek üzere türetilen ampirik parametre kısaca tanıtılarak, Afşin-Elbistan linyitlerinin cüruf oluşturma ve kirletme Özellikleri tanıtılmıştır.
Fuel, 2015
It was possible to reduce the ash content up to 70% by this method. Silica and alumina content reduces by nearly 51.3% and 58.8% respectively. The product coal was not contaminated by alkali content. Significant reduction in phosphorus content observed after the acid treatment. The crucible swelling number of the feed coal does not get significantly affected after the alkali and acid treatments.
Production Engineering Archives
The need to classify rocks in terms of workability stems primarily from the need to choose the appropriate, most effective diagnostic method (DM) and way of mining the given rock. Studying and measuring the workability of rocks is extremely difficult due to the fact that workability depends on many various factors. There are many DM for determining the workability of rocks, but none of them take into account the influence of all factors, hence the obtained results are only indicative. In the article, many DM and ways of determining the cutting resistance with the use of various devices are presented and characterized. The principles of their operations are presented, as well as the DM of measuring the cutting resistance and its utilitarian usefulness in forecasting the selection of mining machines on the basis of cutting for specific mining and geological conditions. The core of the problem is confirmed by the number of covered DM and tools in various research centers around the wor...
International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2015
Typical samples on an air-dried basis have 14.2% moisture, 4.3-13.8% ash and 0.57-2.54% total sulfur with a mean random ulminite reflectance (%Rr) between 0.46 and 0.49%. Contents lists available at ScienceDirect
AIP Conference Proceedings, 2018
Acoustic emission (AE) is a well-established method for geophysical calculations. Nowadays, it is widely used for damage evaluation. For a better understanding of the damage mechanics of materials such as rocks, the sonic wave that has led to AE, has been used to monitor stresses, which induce crack closure, crack initiation and crack damage. In the present study, an AE system was used to study the behaviour of discontinuities on some Tanjung Enim brown coal samples, which were subjected to uniaxial compression. As such, several samples were vacuumed in a container filled with 100% carbon dioxide (CO 2) after the adsorption of high saturated CO 2 at a certain pressure for 84 h prior to the testing. Meanwhile, some samples were vacuumed unsaturated. In order to determine whether CO 2 had any adverse effect on the strength of coal, the comparison was performed between the unsaturated and saturated samples. Moreover, strain gauges were installed on the samples and the measured axial and volumetric strains were studied in conjunction with the AE counts. By virtue of this, the AE method was reliable to detect the onset of pre-crack initiation and the crack damage stress threshold of the black coal samples. Crack initiation and crack closure of the samples subjected to stress corresponding to the percentage of the peak strength when compared to the unsaturated and saturated samples. Nevertheless, crack damage occurred at a higher percentage of peak strength for in unsaturated condition compared to CO 2 saturated samples. The results indicated that sorption of CO 2 can cause the reduction in strength of the brown coal samples when tested under the uniaxial compression. As the coal samples were highly heteregeneous, more tests are required to confirm whether the adsorption of CO 2 will cause strength reduction in coal. This will eventually identify the actual underlying CO 2 sorption mechanisms. c arbon dioxide can be stored in coal under three different states: as an adsorbed gas by adsorbing onto the surface of the micro-, meso-and macropore and fracture systems within the coal; as a absorbed gas; as a free gas in the voids
2012
Proceedings of the 2012 Coal Operators\u27 Conference. All papers in these proceedings are peer reviewed. ISBN: 978 1 921522 57 4
2013
On behalf of the organising committee I welcome you to the 13 th Coal Operators Conference (Coal2013). The conference series, held annually at the University of Wollongong, become a well recognised entity with diverse interests on coal mining operations. As a unique Australian coal mining forum, it is very humbling to see broader paper contributions and participation in the conference, from both surface and underground operators. It is particularly pleasing to have more papers from surface mining operations; therefore, I welcome Dr John Hoelle to the editorial panel with responsibility on surface mining. Of course our conference is also enriched by international participation from various coal producing countries. Primarily the conference will remain focused in serving the interests of the Australia coal mining industry, as initially planned. More papers, reporting on new ideas and innovations, are being presented in the conference, and the number of quality papers is increasing year by year. This demonstrates the importance and credibility of the conference. Also, more companies are supporting the conference in the form of sponsorship or exhibiting their products. Industry support in the form of sponsorship is vital for the viability of the conference and therefore much appreciated. Coal Operators' Conference online holds 431 records, which have been downloaded a total of 265 500 by January 2013. This access is not confined to Australia alone, other countries making frequent access include USA, China, UK, Germany and Iran. More than 130 countries have accessed the conference publications since the papers went online in 2008. I would therefore, like to take this opportunity of extending a special thanks to Michael Organ, Manager -Repository Services of the UOW
2014
On behalf of the organising committee I welcome you to the 14 th Coal Operators Conference (Coal2014).The duration of the conference has been extended for three days because of the increasing number of good quality and innovative papers presented. 42 papers out of a total of 49 will be presented on topics covering both surface and underground mining, and includes papers on geology, geophysical logging, geotechnical engineering, rock fracture mechanics, general ground control, heading development, longwall mining, pillar design, information technology, rock cutting and rock bolting, mine ventilation, mine gases and fugitive gas emissions, outburst control, mine safety and risk management. A number of Australian mine operators, consultants, research organisations and academics are show-casing their cutting edge research findings in the conference.
Related topics

Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
 Wilmeri Potgieter
Wilmeri Potgieter