SUSTAINABLE BUILDING DESIGN FOR TROPICAL CLIMATES Principles and Applications for Eastern Africa
…
303 pages
1 file

Sign up for access to the world's latest research
AI-generated Abstract
This paper discusses sustainable building design principles and their applications in tropical climates, specifically in Eastern Africa. It emphasizes the challenges posed by climate change and resource depletion, detailing the need for significant greenhouse gas emissions reductions to mitigate impacts on ecosystems and resources. The authors highlight the pressing need for strategies that allow economic development without increasing emissions, while also addressing the ecological footprints of countries in this region.
Figures (399)






































































































































































































































































































![FIGURE. 4.6-9 INTERACTIONS TABLE [CIBLE = TARGET]. Source: CERTIVEA, Référentiel pour la qualité environnementale des batiments — Batiments tertiaires, 2012 - http://www.certivea. fr/assets/ documentations/9be0d-Guide_Generique_20-01-2012.pdf](https://figures.academia-assets.com/63699567/figure_280.jpg)




![TABLE 5.1-1 ENERGY STORAGE TRANSFER LOSSES [%] Wastewater and solid wastes Recycling wastewater and solid wastes and using them as energy sources, is essential in an energy efficient city.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/63699567/table_035.jpg)












































































Key takeaways
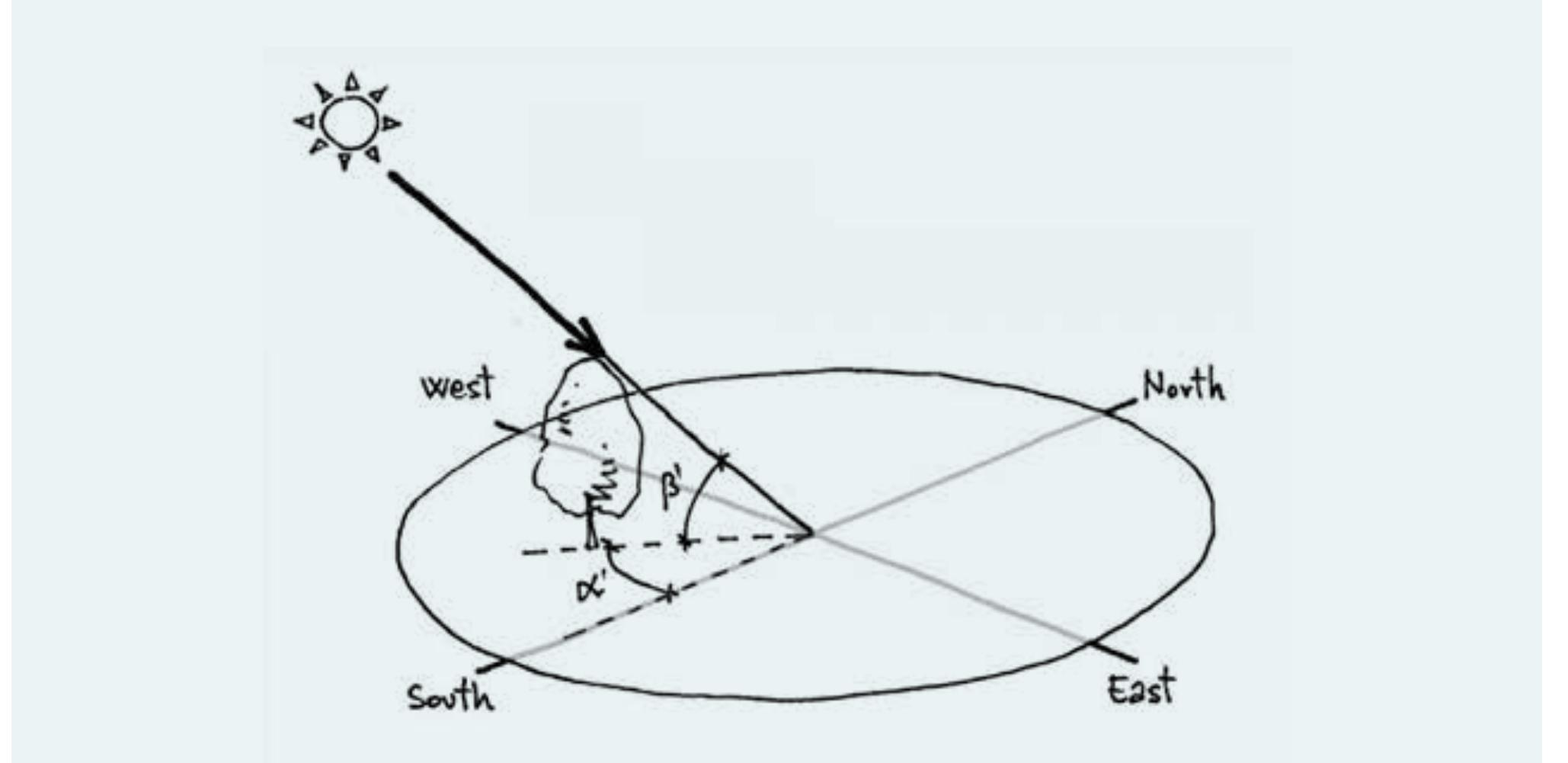
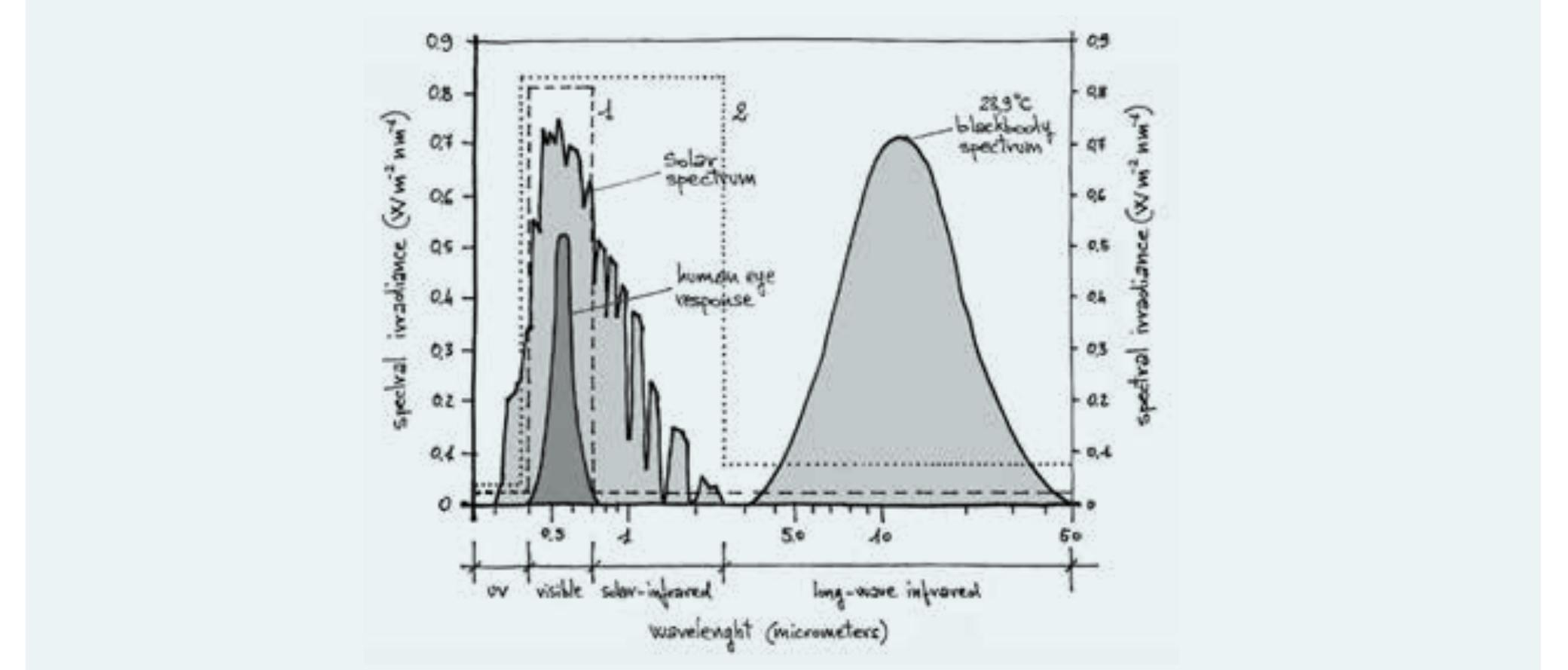
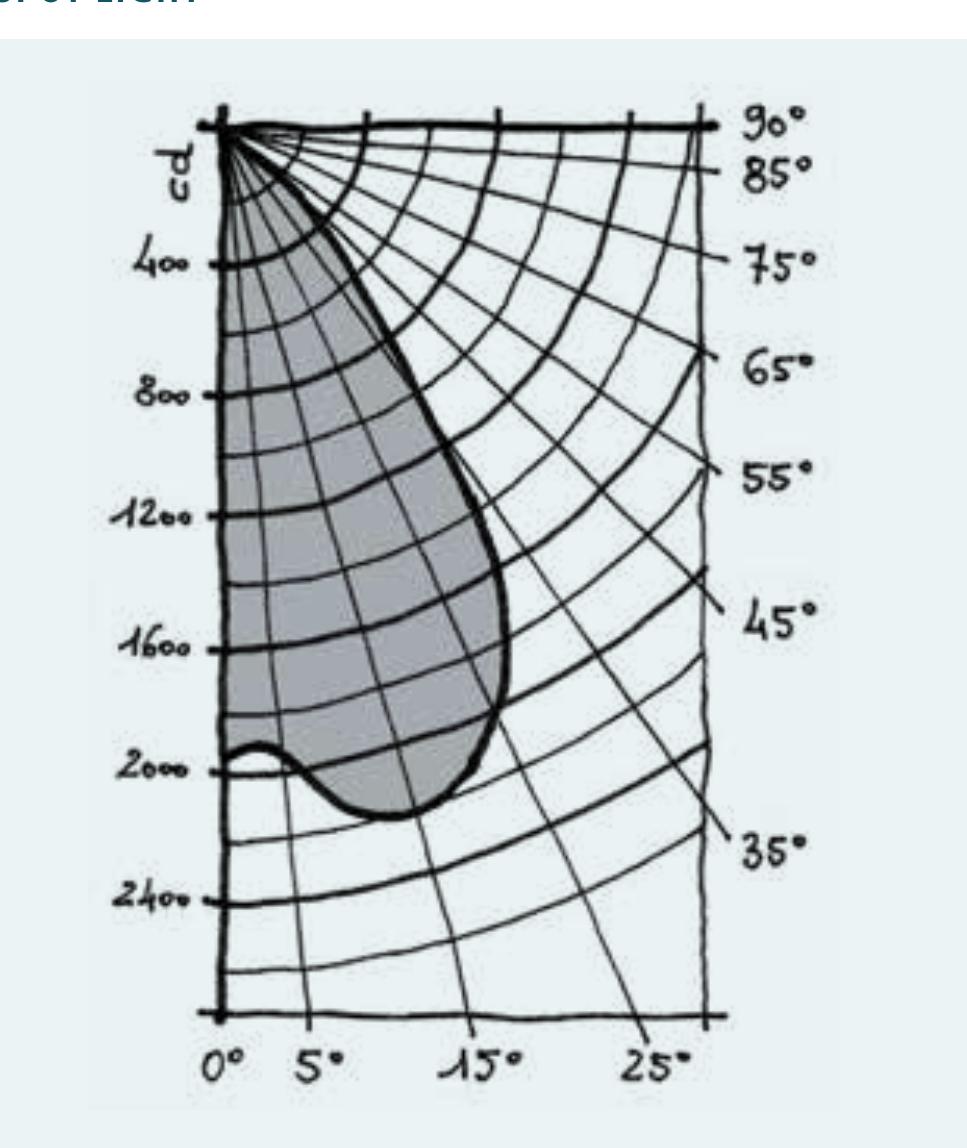
- Knowledge of solar geometry is very important for architectural design and energy efficiency strategies, since solar energy greatly influences the energy performance of buildings.
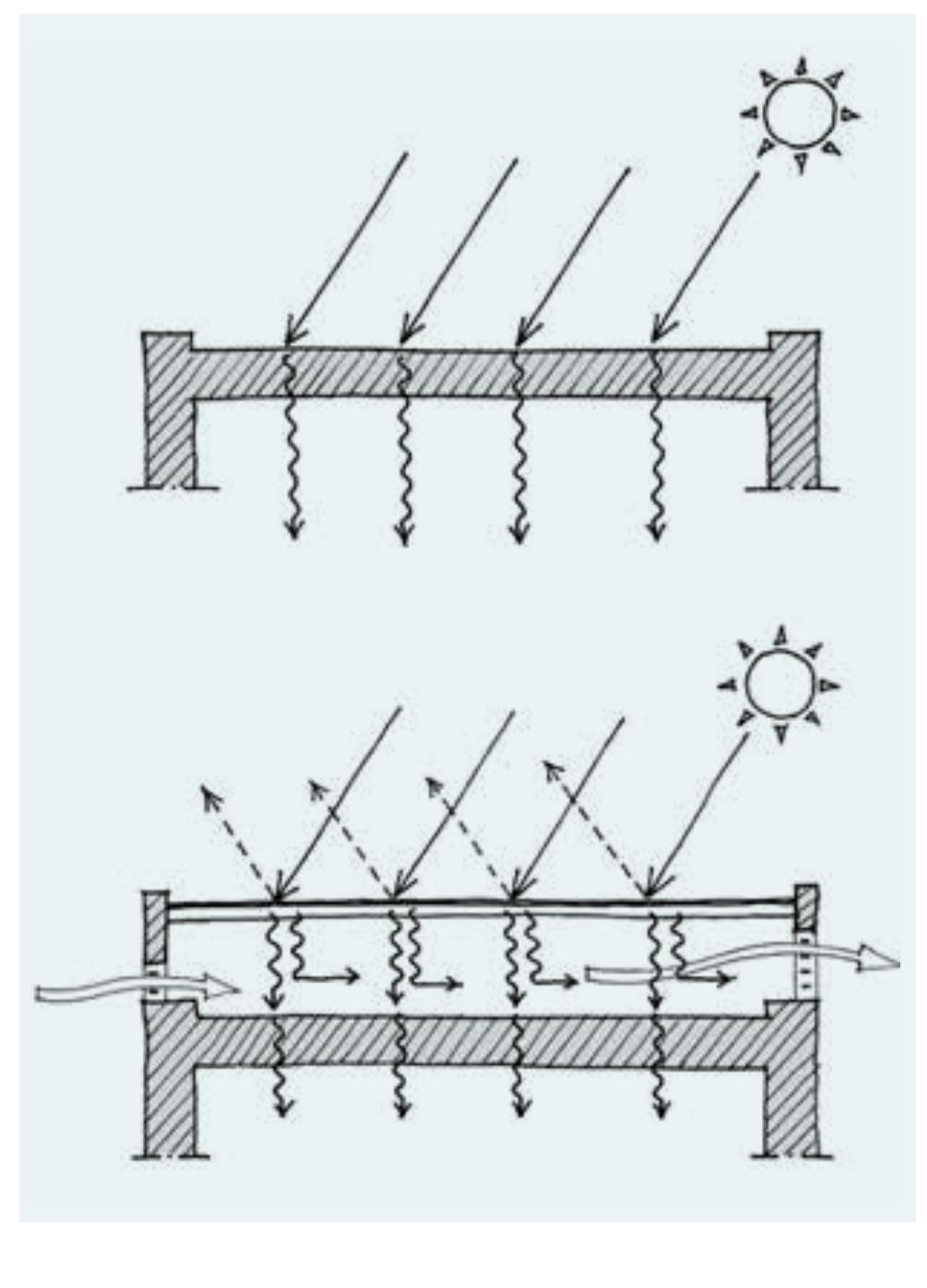
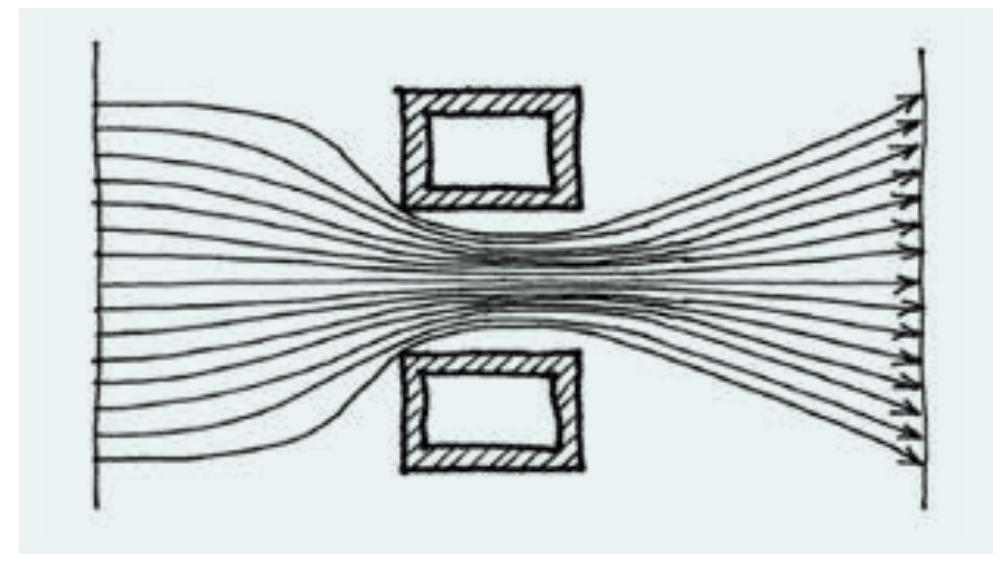
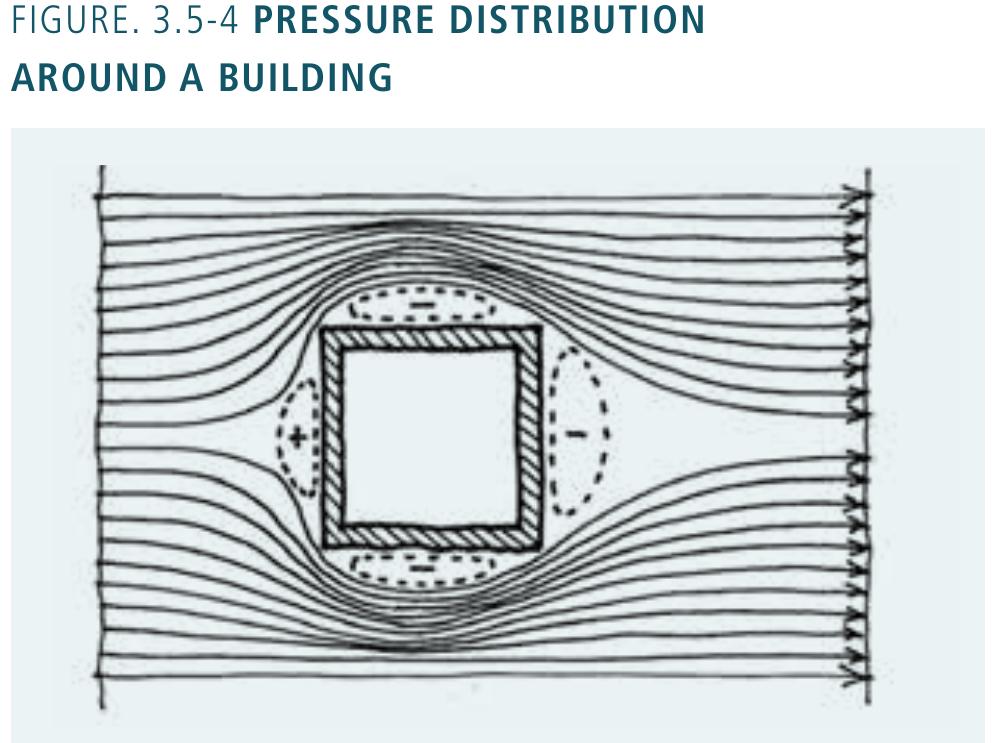
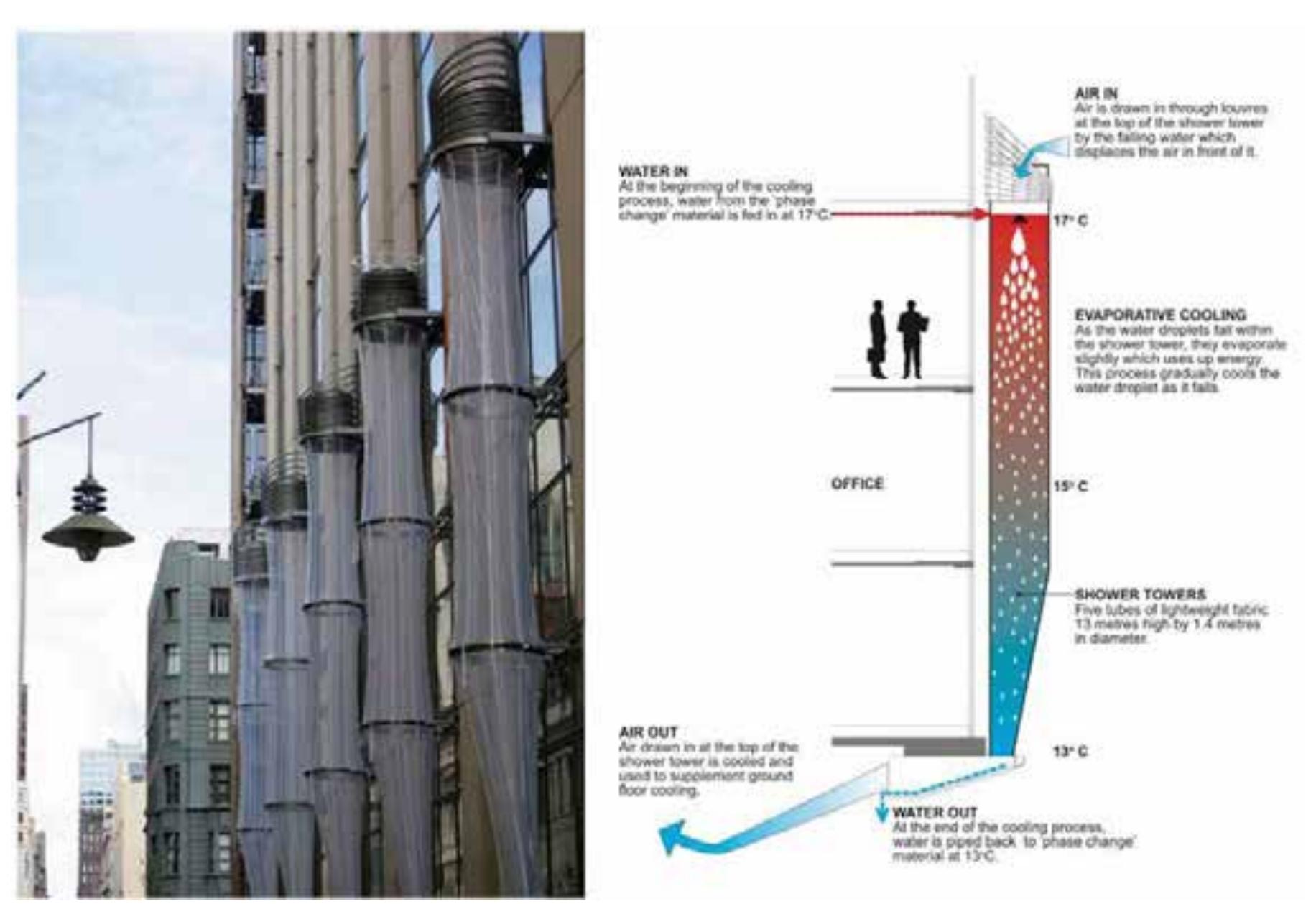
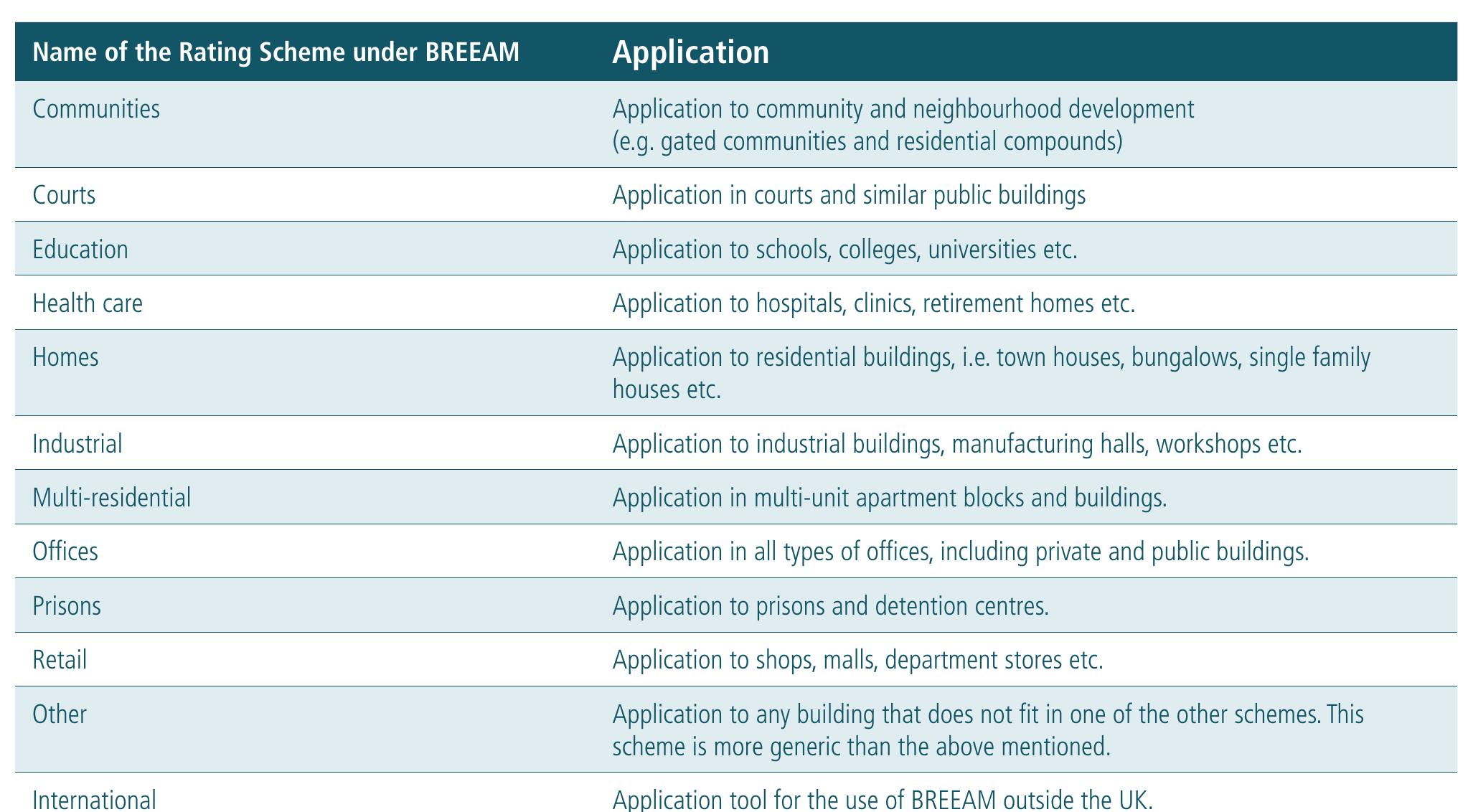
- Low energy urban design means that shading and illumination of surfaces as well as wind must be analysed so that shape, orientation and distances between buildings can be optimised in order to control solar radiation and ventilation, with the aim of reducing the energy demands of individual buildings.
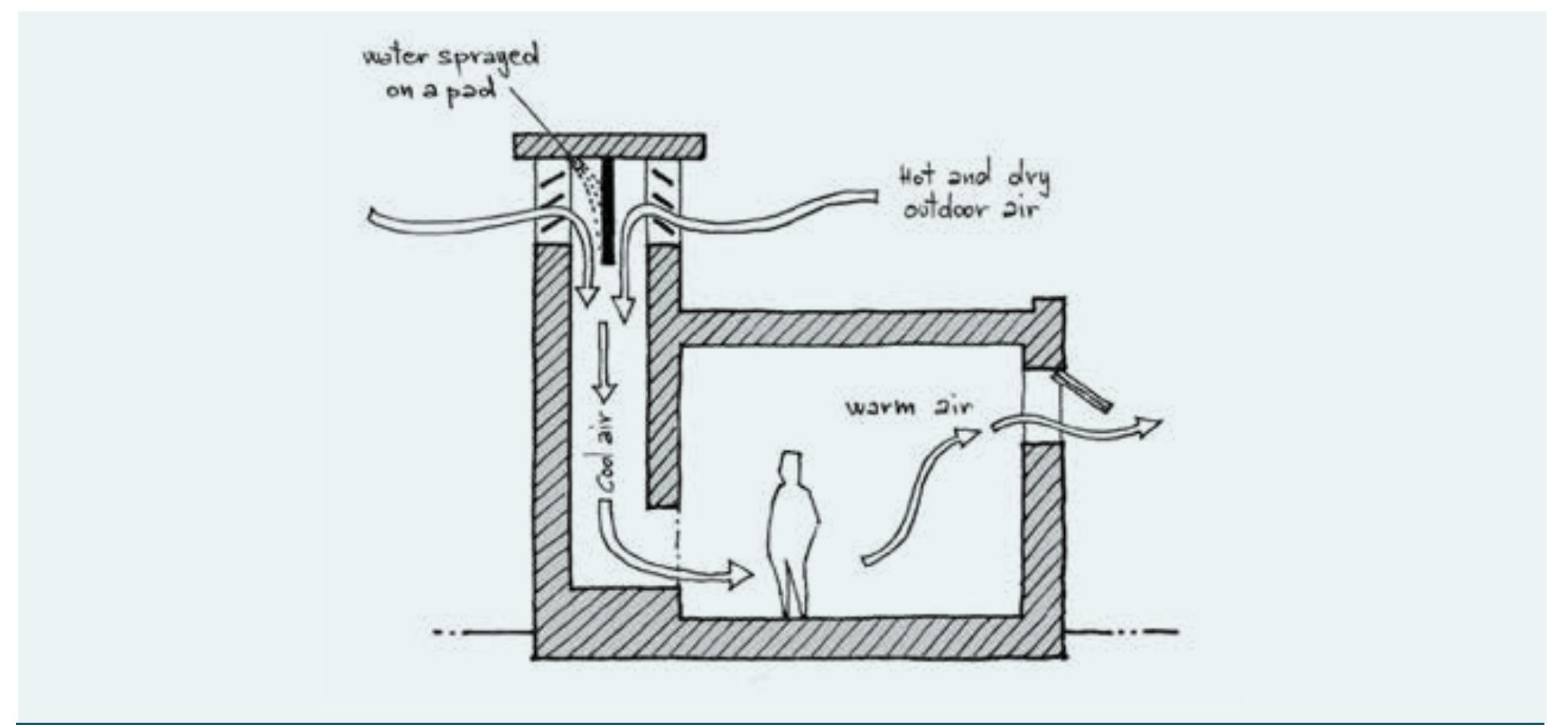
- The temperature inside the buildings is almost constant throughout the 24 hours and thermal comfort is entirely dependent on solar protection and natural ventilation.
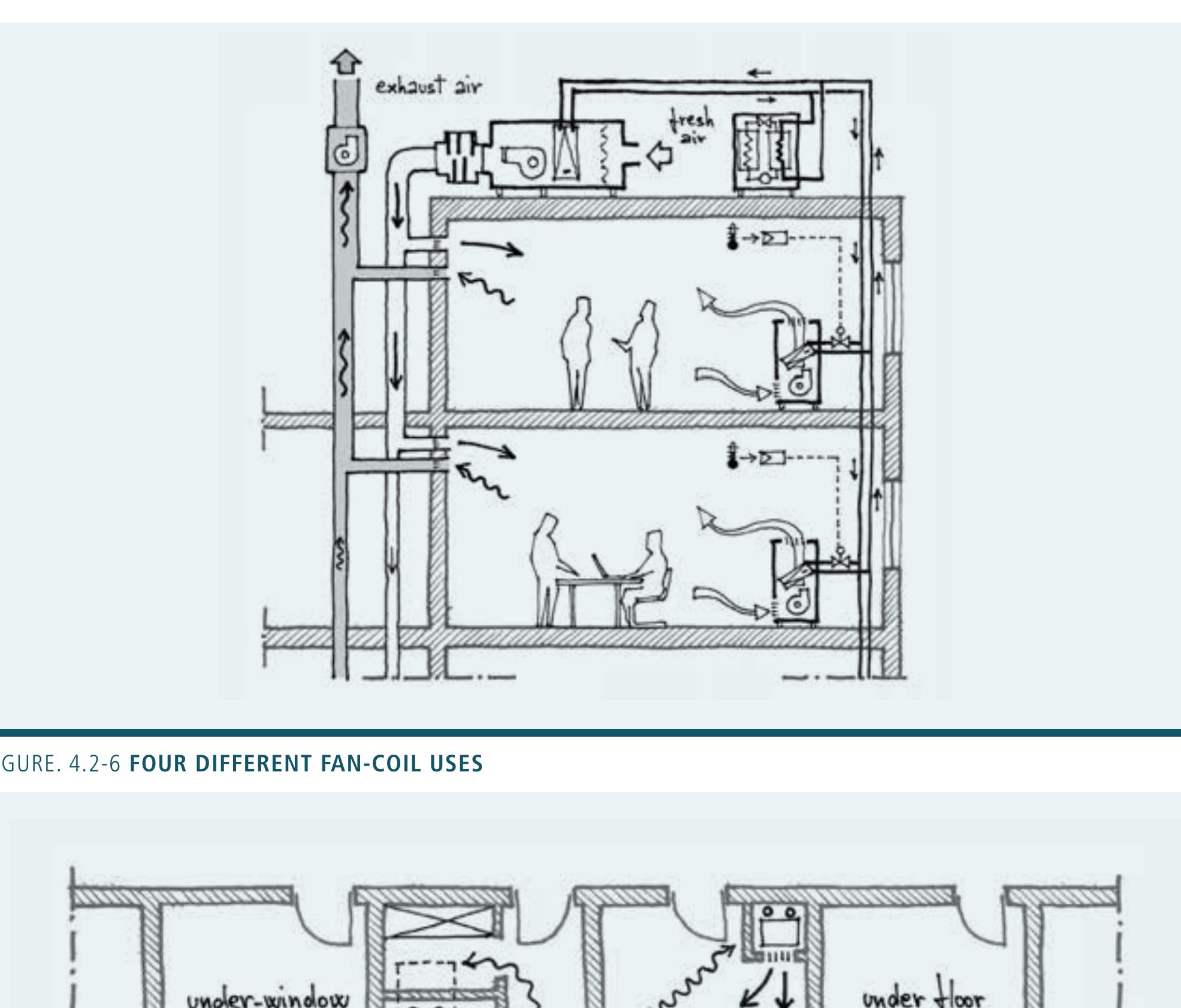
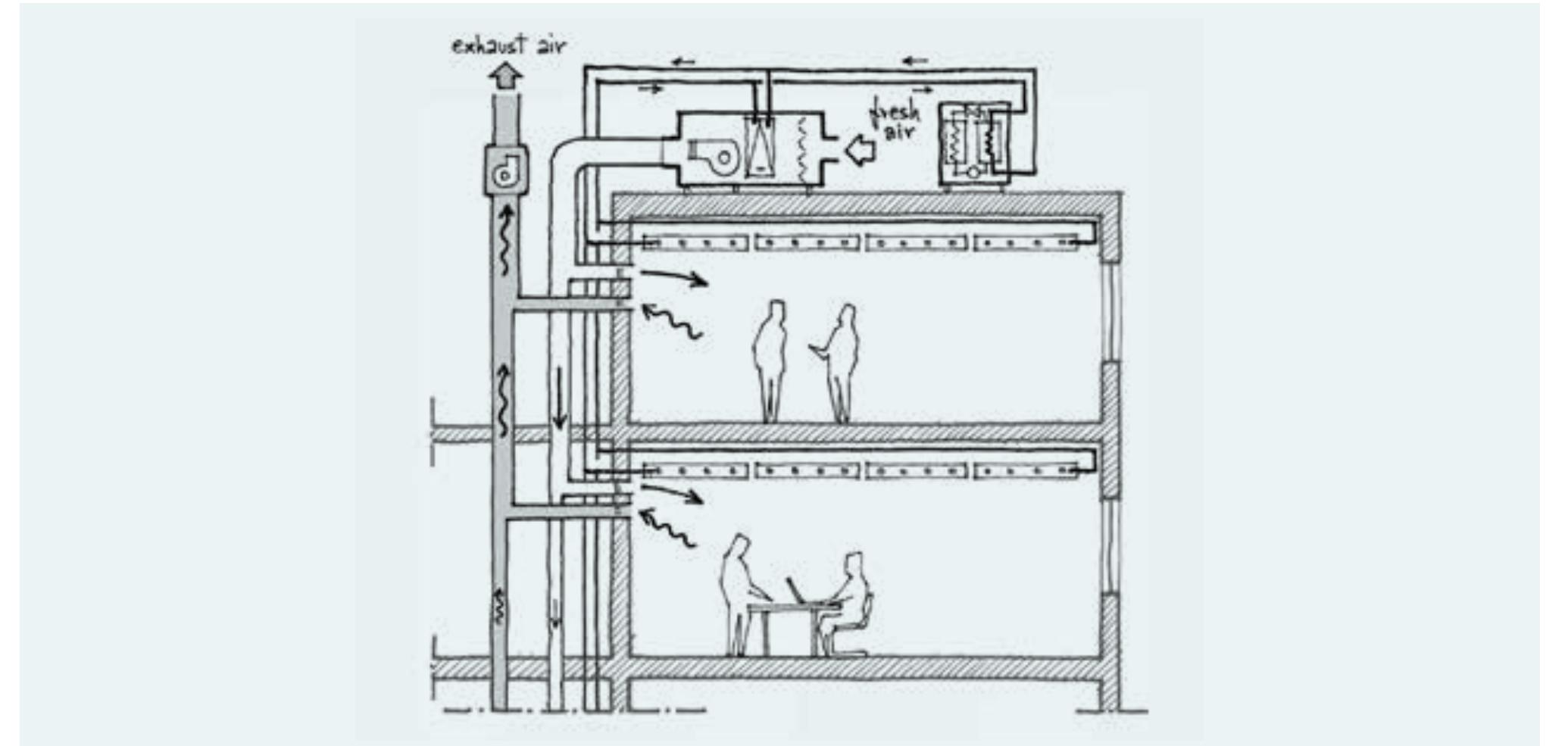
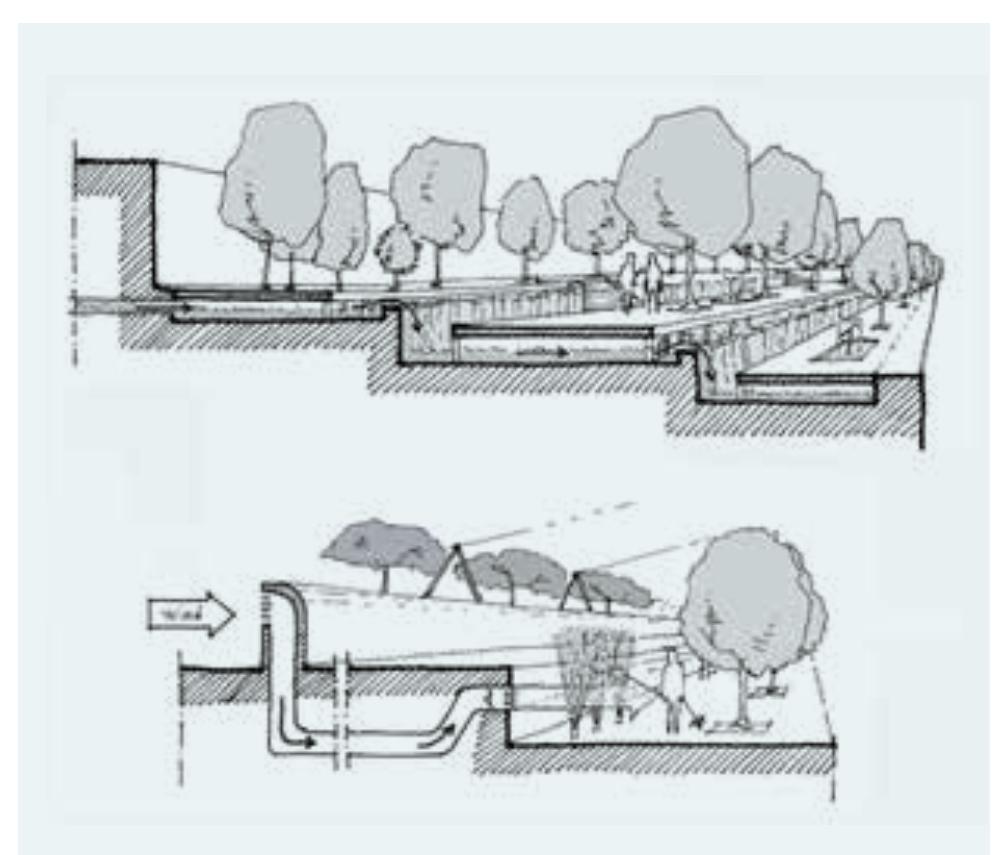
- In air systems, air is ducted into the different thermal zones of the building to transfer thermal energy and/or to provide ventilation.
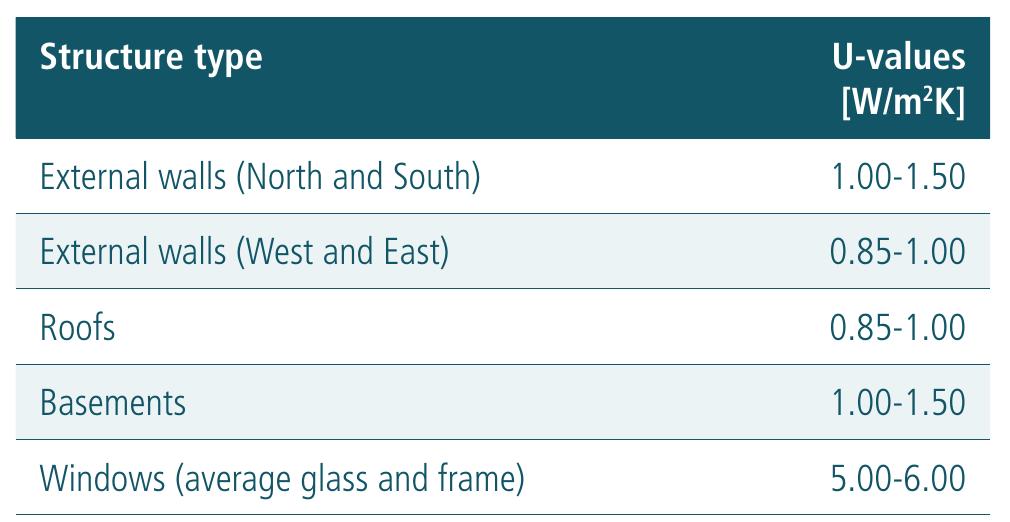
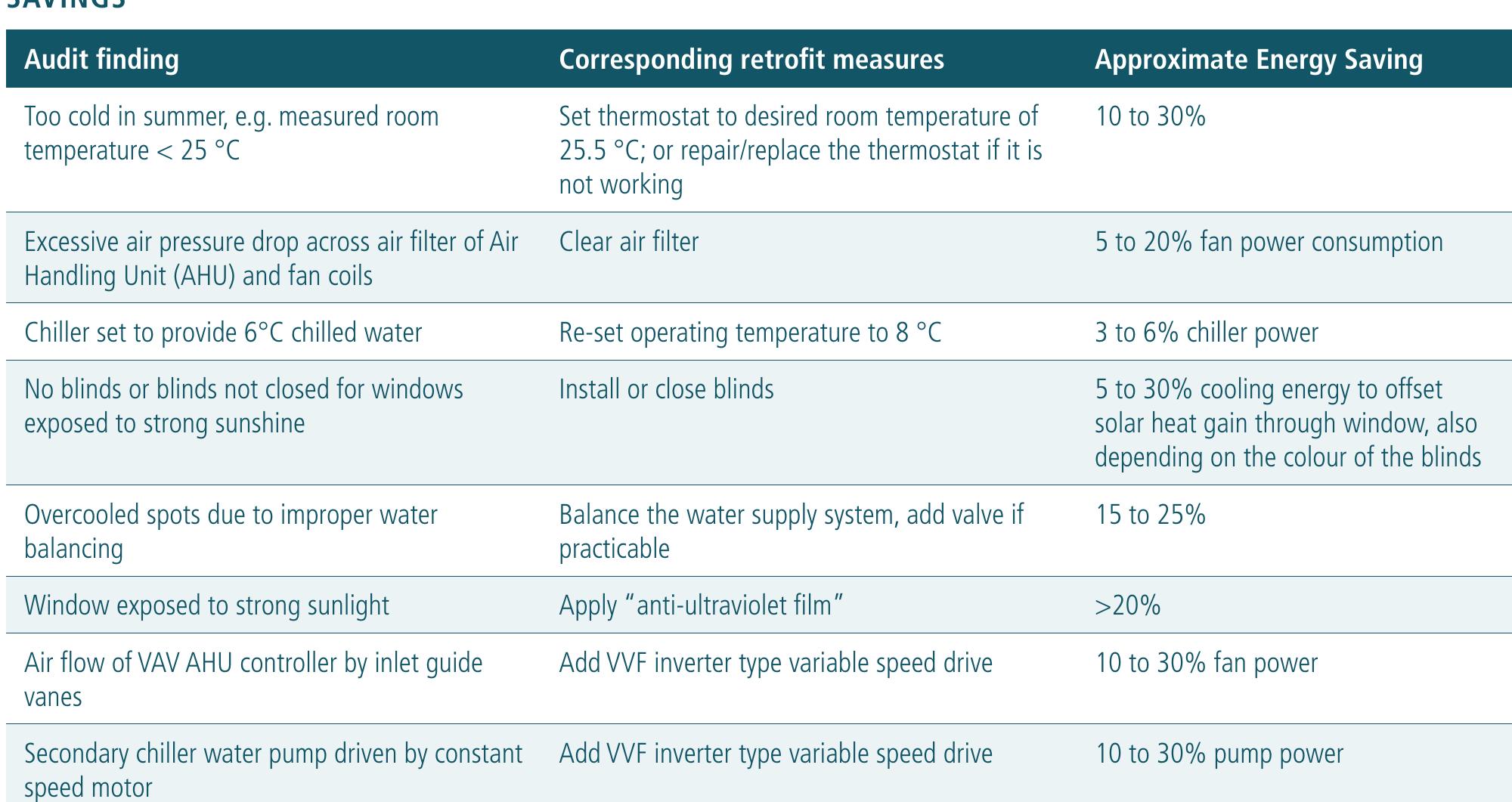
- "Energy performance" is defined as the calculated or measured amount of energy needed to meet the energy demands associated with a typical use of the building, which includes, inter alia, energy used for heating, cooling, ventilation, hot water and lighting.
Related papers
Leadership and Management in Engineering, 2008
Our planet is warming because of human activities affecting the environment. Climate change is caused by a number of things, and it will take an enormous amount of concerted effort to fix it. It involves thinkers, politicians, professionals, and the public. Architects and engineers will have a major role to play in resolving the associated problems. This paper explores various architectural and building technologies that are employed to achieve a low-energy built environment. The paper concludes that designers of the next generation of buildings, whether residential, commercial, or institutional, should aim for "zero energy" buildings in which there will be no need to draw energy from a region's power grid. In this approach, climate and environment are used to advantage rather than being treated as adversaries and buildings become sources of energy, like batteries. A few illustrative buildings are discussed that represent the new generation of sustainable or green buildings. A lthough it has been known for some time, in his documentary film An Inconvenient Truth, former Vice President Al Gore has brought home the point to the masses that the global weather system is warming up. It signals that more energy will be squandered throughout our planet, and hence more wind storms and precipitations are on the horizon. There is another ominous danger, which is the uncertainty about the security of the fossil fuels that will be required to drive the world economy in the foreseeable future. As demand increasingly exceeds supply, oil prices will rise. At least half the oil reserves will be located in the volatile Middle East and there is a growing demand in developing countries like China and India that are industrializing and are large consumersofenergy. According to a February 2007 report by the U.N.'s Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, "warming of the climate system is unequivocal" and human activities have played a significant role by "overloading the atmosphere with carbon dioxide hence retaining solar heat that would otherwise radiate away" ͑Kluger 2007͒. Human interference in the form of
2017
The use of general descriptive names, registered names, trademarks, service marks, etc. in this publication does not imply, even in the absence of a specific statement, that such names are exempt from the relevant protective laws and regulations and therefore free for general use. The publisher, the authors and the editors are safe to assume that the advice and information in this book are believed to be true and accurate at the date of publication. Neither the publisher nor the authors or the editors give a warranty, express or implied, with respect to the material contained herein or for any errors or omissions that may have been made. The publisher remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Climate change is real and felt globally. Climatic factors such as intense solar radiation, high humidity and condensation, dust and sandstorms and flood affects the comfort of man and safety of built environment. Most of the climatic changes are due to human activities in the environment, particularly the built environment. These suggest that human activities and physical constituents of built environment interact with other climate drivers. These prompt the need for response,and response to climate change falls into two phases-mitigating and adaptation. Therefore, this paper discusses how climate change can be mitigated through green architecture in Nigeria. In this light, the paper will be a conceptual paper.The library research method was used in this study to gather secondary data from textbooks, articles and journals to develop a conceptual framework on how green architectural practices can be used to mitigate climate change in order to sustain built environment in Nigeria. This paper adopts the U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC) (2015) principles of green building and sustainable site design. It highlights climatic changes and their effects in Nigeria. It further discusses the concept and principles of green architecture. The study concludes that Nigerian built environment is vulnerable to the impact of climate change. Therefore, there is need for architects, builders, engineers and clients to promote and adopt green architectural practices in order to mitigate the effect of climate change for sustainable environment.
Global warming is defined as a rise in Earth's average temperature. As the Earth gets warmer, disasters such as droughts, hurricanes, and floods are becoming increasingly common. Most scientists, engineers, and activists express deep concern about changes in the planet's overall climate. The average air temperature above the surface of the Earth has risen by just below 1 degree Celsius, or 1.3 degrees Fahrenheit, over the past 100 years. Deforestation exacerbates the severity of global warming. The ocean, which holds about 50 times more carbon than the atmosphere, is an enormous carbon sink. However, the seas are no longer able to store carbon as effectively as they have in the past. Burning fossil fuels such as natural gas, oil, coal, and gasoline increases atmospheric carbon dioxide levels, and carbon dioxide is a major contributor to the greenhouse effect and global warming. Climate change will increase the number of people who suffer from heatwaves, floods, hurricanes, and droughts, leading to higher rates of death, illness, and injury. The threat of global warming continues to cause severe damage to the Earth's environment. Many people still do not fully understand the implications of global warming or consider it a significant problem for the future. However, global warming is already happening, and some of its devastating consequences are already being felt. It significantly impacts biodiversity and disrupts ecological balance. Due to the dangerous effects of global warming, many strategies need to be established. The report discusses global warming, outlines its causes and risks, and proposes solutions to this urgent issue. Above all, it is crucial to seriously consider alternative energy sources (biomass, wind, hydro, geothermal, and solar). One of the key strategies to counter the ever-increasing global warming is the identification and use of renewable energy sources.
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, 2019
Sustainable Design Concept for Building Services SUB CODE:BCV306C_Prof.Mahadeva M, Assistant Professor, ISRO-IIRS Institute Coordinator Dept. Of Civil Engineering, 2024
Overview of Sustainability – Global energy scenario, carbon footprint and climate action, Net zero in carbon offsetting, water neutral, Sustainable construction and resource management. Green buildings - Selection of site – preservation and planning, influence of climate on buildings, basics of climatology, Earth –Sun relationship, Solar angles and sun path diagram, Design of shading systems.

Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
Related papers
Global Warming of 1.5°C
Research & Development
International journal of scientific and management research, 2022
Ambiente & Sociedade, 2016
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2019
Energy and Buildings, 2020
ENERGY, ENVIRONMENT & STORAGE, 2021
Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy, 2018
 Josielyn Arreza
Josielyn Arreza