Significance of landslide susceptibility maps in creation of spatial planning documentation
2019, Proceedings of the 4th Regional Symposium on Landslides in the Adriatic - Balkan Region

Sign up for access to the world's latest research
Abstract
Monitoring is important for assessing the stability of the ground and for confirming the validity of the design during the construction and operation of structures. The ideal monitoring system for projects in Rock and Geotechnical Engineering would be able to monitor the behavior of small to extensive areas continuously and automatically with high accuracy. In addition, the costs would be low and the system would be easy to handle. Satellite technology has the potential to realize the above monitoring system by combining it with conventional geotechnical instruments. In this paper, satellite technology for displacement monitoring, i.e., GPS and SAR, is firstly outlined and then the concept of spatiotemporal continuous displacement monitoring is introduced. The use of both satellite technology and geotechnical instruments is effective for geotechnical monitoring. Practical applications of GPS for landslide monitoring and collaborative researches using DInSAR with Balkan countries are described.


















































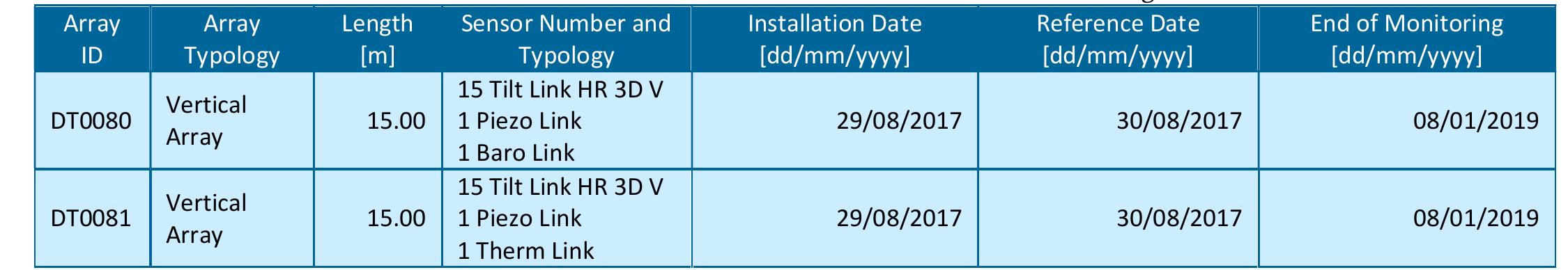
































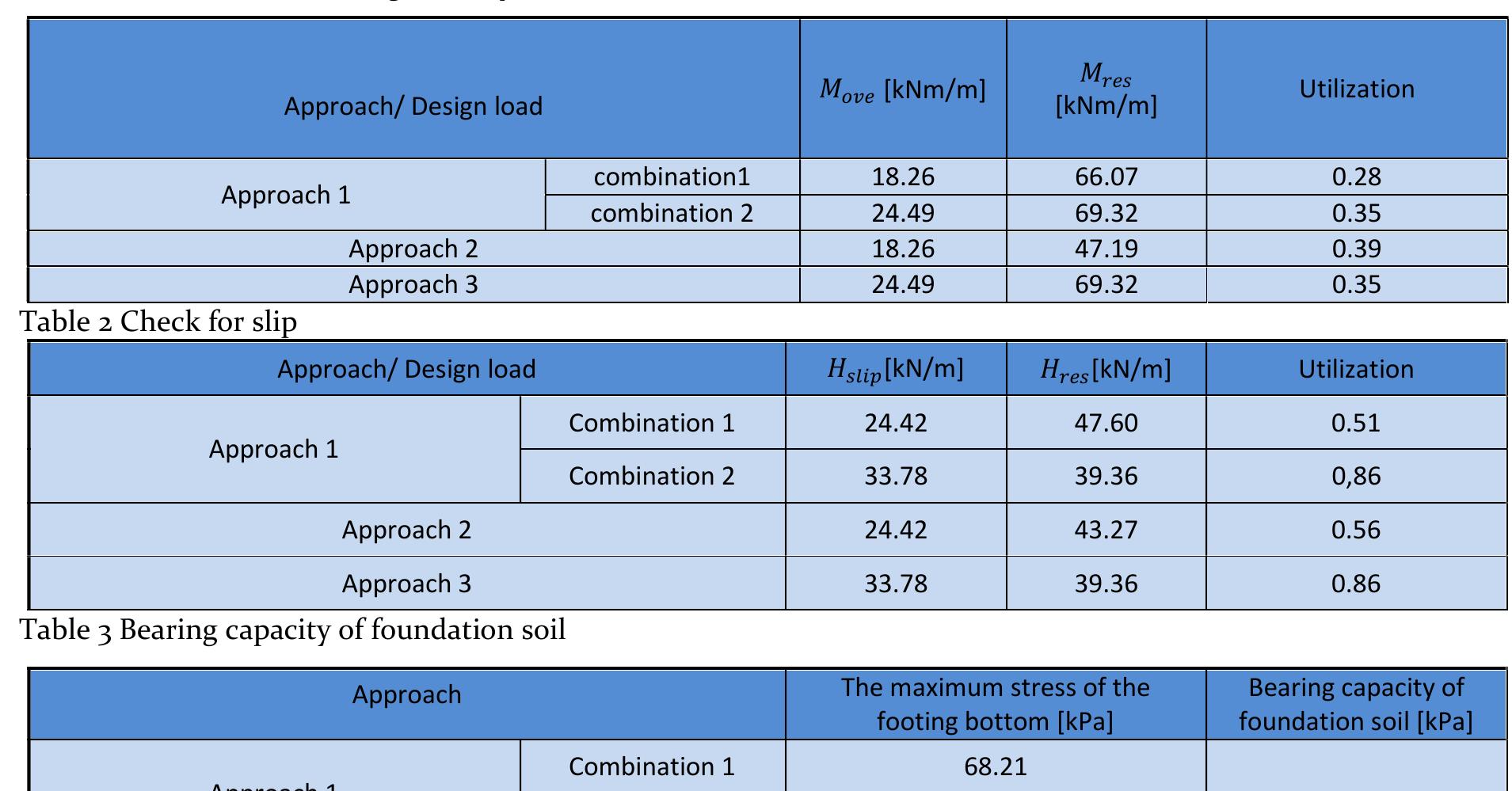

















































![Table 1 Piezometer monitoring [2]](https://figures.academia-assets.com/92741026/table_010.jpg)
![Figure 2 Landslide view, km 7+500[2] Figure 1 Geological mapping near km 7+500[2]](https://figures.academia-assets.com/92741026/figure_130.jpg)

![Figure 3 Landslide view, km 10+600[2]](https://figures.academia-assets.com/92741026/figure_132.jpg)
![Figure 4 Open slope near km 7+800[2] Geotechnical investigation On the area of unstable slopes of Orikum-Himare road, Shen Elize area the following works have been carried out:](https://figures.academia-assets.com/92741026/figure_133.jpg)

![Figure 5 Location of Boreholes [2]](https://figures.academia-assets.com/92741026/figure_135.jpg)
![Figure 7 Geological section from borehole BH-5 [2]](https://figures.academia-assets.com/92741026/figure_136.jpg)
![Figure 8 Typical residual direct shear test [2]](https://figures.academia-assets.com/92741026/figure_137.jpg)
![Figure 6 Geological section from borehole BH-3[2]](https://figures.academia-assets.com/92741026/figure_138.jpg)
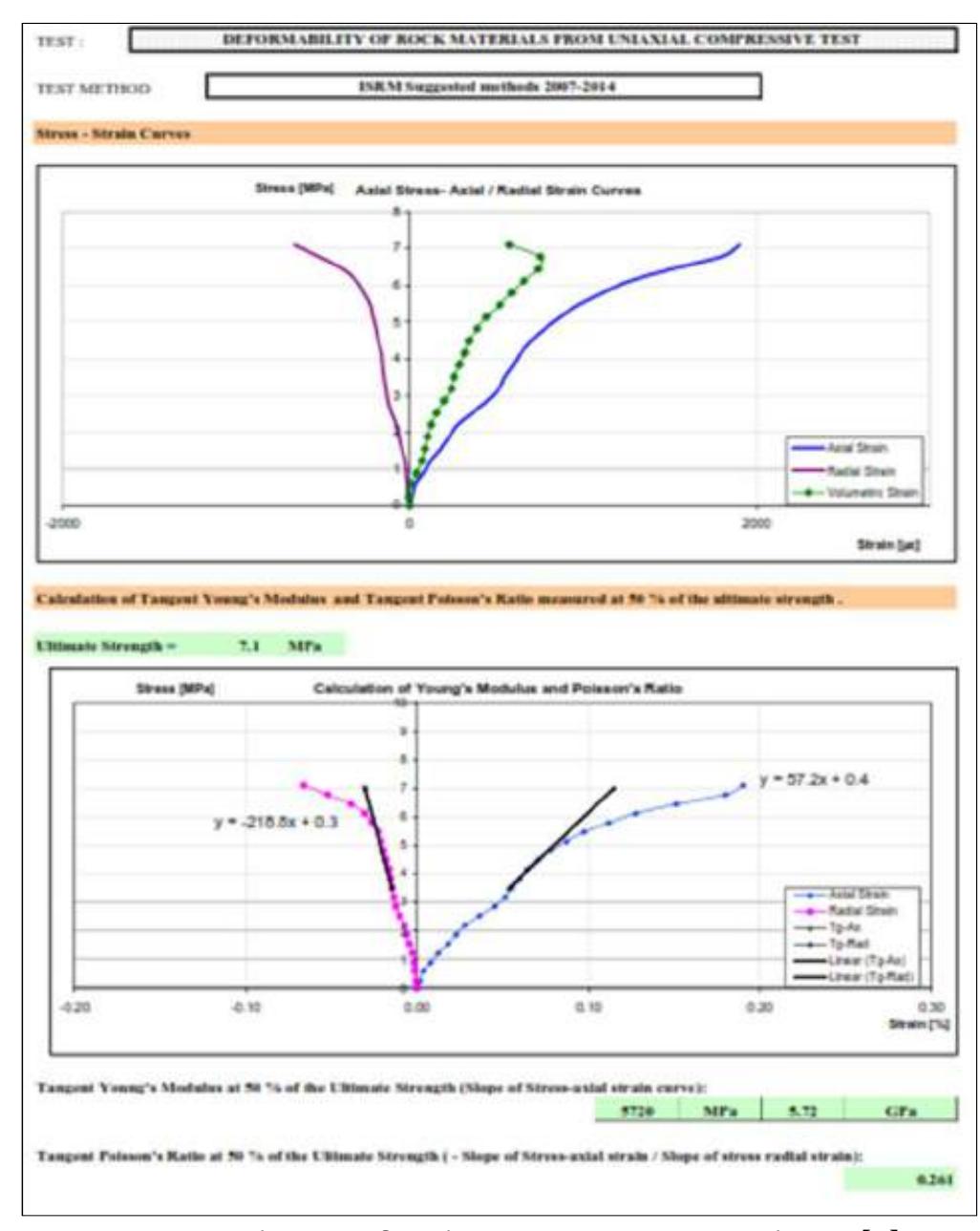
![Figure 9 Typical unconfined compressive strength test[2] Figure 10 Grain size distribution test[2]](https://figures.academia-assets.com/92741026/figure_140.jpg)
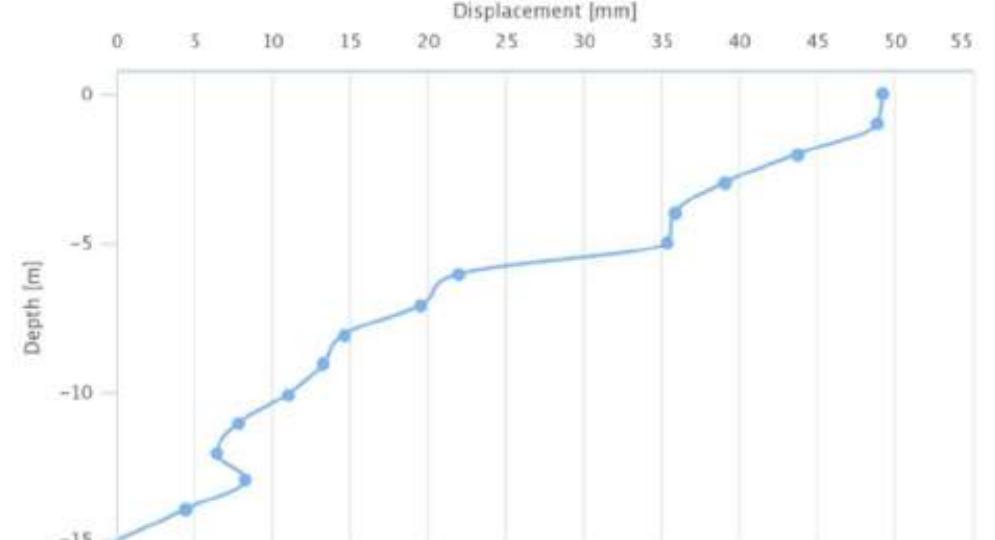
![Depth of landslide according to the measurement in 16/05/2019 for BH-3 is 26 m depth; for BH-5 is 16.00 m depth. [2-4] Figure u1 Inclinometer results at BH-3 from January 2018 up to May 2019[2]](https://figures.academia-assets.com/92741026/figure_141.jpg)
![Table 2 Summary of physical-mechanical features[2]](https://figures.academia-assets.com/92741026/table_011.jpg)
![SEER, eeenes RE Ia Moderately strong, white to grey, fractured limestone, containing small karstic caves, the fractures and cavers are filled with silty clay and are rarely empty. Table 5 Summary of physical-mechanical features[2] SSO Up, enn! SERIA ort Weak to moderately weak, grey, mudstone and sandstone with fractures. The fractures are in dip angle 45 degree but have and small fracture in dip angle 5 degree, with undulated and slickensides surfaces.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/92741026/table_012.jpg)
![Table 3 Summary of physical-mechanical features[2]](https://figures.academia-assets.com/92741026/table_013.jpg)
![Table 4 Summary of physical-mechanical features [2]](https://figures.academia-assets.com/92741026/table_014.jpg)
![Figure 12 Inclinometer results at BH-5 from January 2018 up to May 2019[2]](https://figures.academia-assets.com/92741026/figure_142.jpg)










































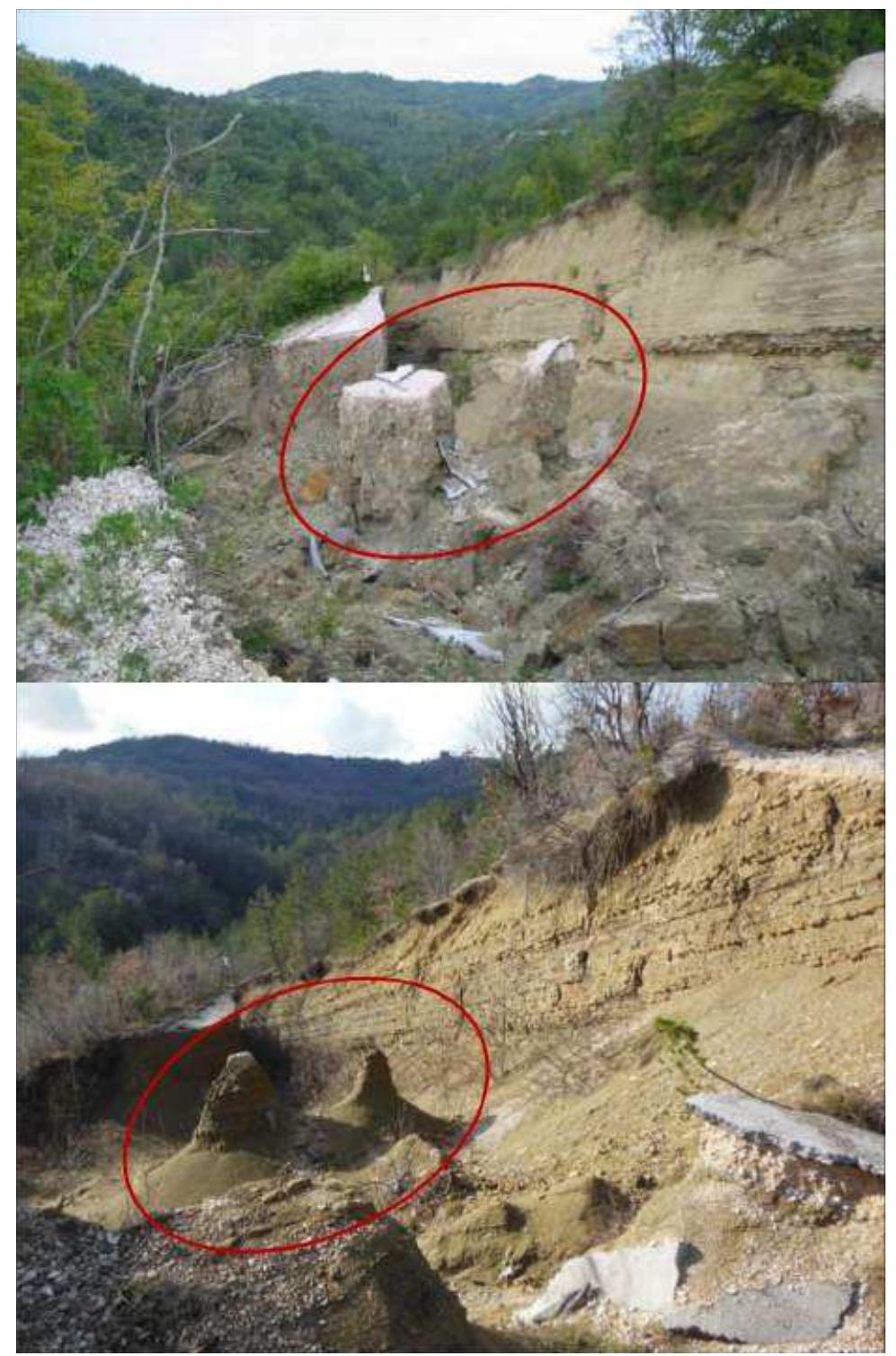
![Figure 6 Model for testing anchors Table 5 Correction coefficients yeq2 for reducing the friction in determining the bearing capacity of piles in seismic conditions [34]. After analyzing results from the models, the following conclusions were made, about sand with different water content: Conclusion exerted by loading systems. The device is isolated from the building by vibration isolators. The device is designed to test the anchors in terms of static and dynamic conditions and the scope of testing is: ground acceleration — (0+0.4)g; displacement of the device - (2+3) cm; frequency - (2+12) Hz; overburden pressure - up to 4m soil layers; anchor force up to 10 KN.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/92741026/figure_173.jpg)
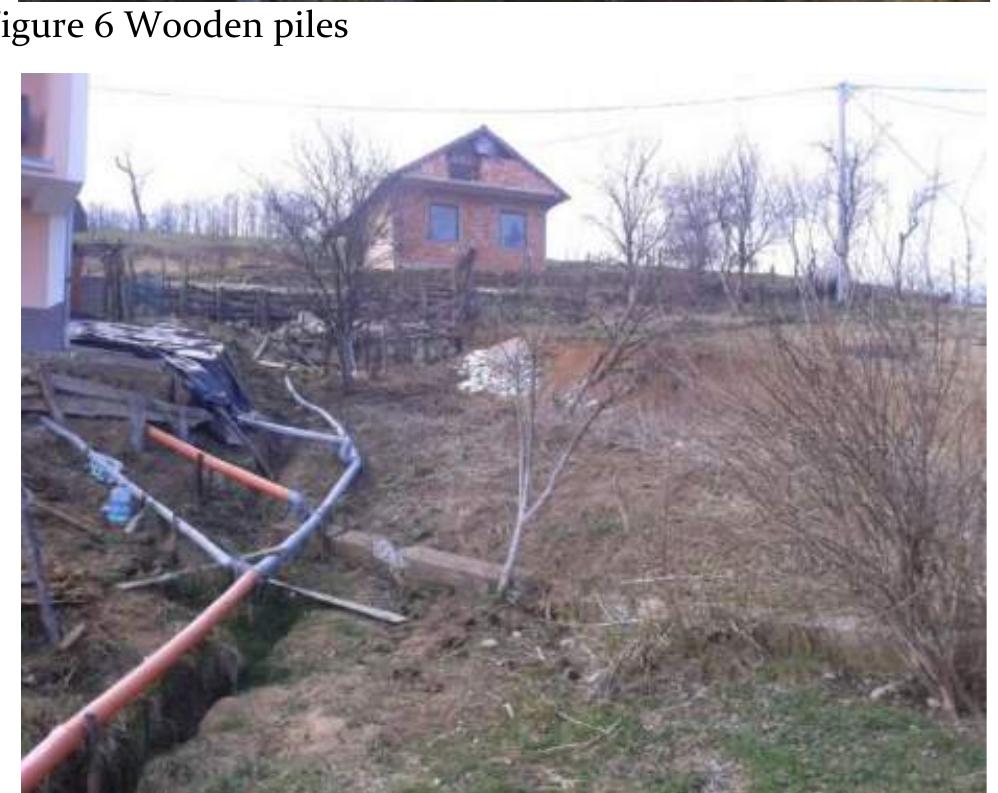
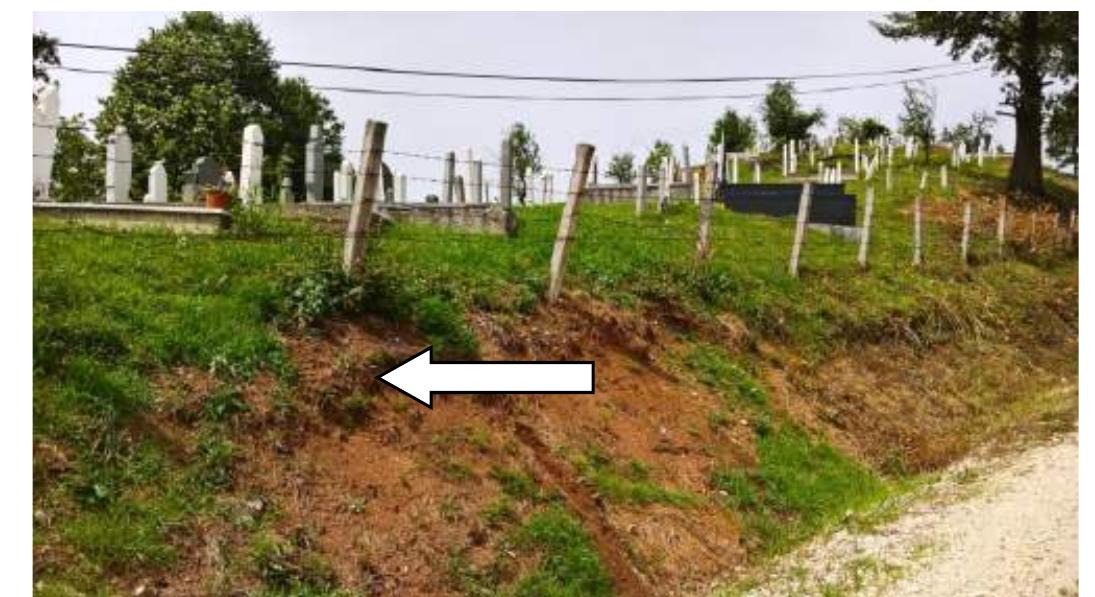

































































































![Figure 1 General view of the study area A slope in the village Velikyi Pereviz, Poltava region, Ukraine is selected for stability assessment (Fig. 1). The site is located on the left bank of the river Psel with absolute elevation of the earth's surface from 125.0 to 155.0 m. Geomorphologically, the territory belongs to the slope of the Poltava loess plateau (Fig. 2). According to the results of engineering-geological surveys, it is established that loamy deposits of Quaternary formation, represented by loess and loess-like (loam) loam, are involved in the slope structure. The slope from the surface is covered with loose and deluvial deposits with a depth of about 5 m. The groundwater level was recorded only in the middle part of the slope. Groundwater was not detected on the plateau and down the slope (Fig. 3). 9 boreholes were drilled (fig. 3), 24 intact samples were taken. Selected samples for each layer were subjected to 6 The nature of the slip surface is often determined not so much by the stress-strain state of the soil mass, but by the natural conditions and geological structure of the soil mass. The method of wedges or sliding block method [Cheng] with polygonal slip surface was used to evaluate slope stability. It is most commonly used in the following cases:](https://figures.academia-assets.com/92741026/figure_260.jpg)




![Figure 5 Scheme for calculating by the Wedge method For a plane problem, these slip surfaces with some approximations can be replaced in the plane of the drawing by one or another number of straight lines - slip lines (Fig. 5). Within the straight lines, blocks of soil are allocated, the weight Q and the angle of inclination a to the horizontal are calculated. The shear force of the block is equal to F = Q - sina, and the resultant holding force is R = Q - cosa - tgp + cst - £, where is £ the block sliding length. The difference between these values will correspond to the shear pressure E. If there is a slope of the filtration flow in the soil, an additional pressure Fy will be acting [Lim et al.].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/92741026/figure_264.jpg)









































































Related papers
Proceedings of the 4th Regional Symposium on Landslides in the Adriatic - Balkan Region, 2019
Monitoring is important for assessing the stability of the ground and for confirming the validity of the design during the construction and operation of structures. The ideal monitoring system for projects in Rock and Geotechnical Engineering would be able to monitor the behavior of small to extensive areas continuously and automatically with high accuracy. In addition, the costs would be low and the system would be easy to handle. Satellite technology has the potential to realize the above monitoring system by combining it with conventional geotechnical instruments. In this paper, satellite technology for displacement monitoring, i.e., GPS and SAR, is firstly outlined and then the concept of spatiotemporal continuous displacement monitoring is introduced. The use of both satellite technology and geotechnical instruments is effective for geotechnical monitoring. Practical applications of GPS for landslide monitoring and collaborative researches using DInSAR with Balkan countries are described.
2019
Monitoring is important for assessing the stability of the ground and for confirming the validity of the design during the construction and operation of structures. The ideal monitoring system for projects in Rock and Geotechnical Engineering would be able to monitor the behavior of small to extensive areas continuously and automatically with high accuracy. In addition, the costs would be low and the system would be easy to handle. Satellite technology has the potential to realize the above monitoring system by combining it with conventional geotechnical instruments. In this paper, satellite technology for displacement monitoring, i.e., GPS and SAR, is firstly outlined and then the concept of spatiotemporal continuous displacement monitoring is introduced. The use of both satellite technology and geotechnical instruments is effective for geotechnical monitoring. Practical applications of GPS for landslide monitoring and collaborative researches using DInSAR with Balkan countries are described.
2019
Monitoring is important for assessing the stability of the ground and for confirming the validity of the design during the construction and operation of structures. The ideal monitoring system for projects in Rock and Geotechnical Engineering would be able to monitor the behavior of small to extensive areas continuously and automatically with high accuracy. In addition, the costs would be low and the system would be easy to handle. Satellite technology has the potential to realize the above monitoring system by combining it with conventional geotechnical instruments. In this paper, satellite technology for displacement monitoring, i.e., GPS and SAR, is firstly outlined and then the concept of spatiotemporal continuous displacement monitoring is introduced. The use of both satellite technology and geotechnical instruments is effective for geotechnical monitoring. Practical applications of GPS for landslide monitoring and collaborative researches using DInSAR with Balkan countries are described.
Proceedings of the 4th Regional Symposium on Landslides in the Adriatic - Balkan Region, 2019
Monitoring is important for assessing the stability of the ground and for confirming the validity of the design during the construction and operation of structures. The ideal monitoring system for projects in Rock and Geotechnical Engineering would be able to monitor the behavior of small to extensive areas continuously and automatically with high accuracy. In addition, the costs would be low and the system would be easy to handle. Satellite technology has the potential to realize the above monitoring system by combining it with conventional geotechnical instruments. In this paper, satellite technology for displacement monitoring, i.e., GPS and SAR, is firstly outlined and then the concept of spatiotemporal continuous displacement monitoring is introduced. The use of both satellite technology and geotechnical instruments is effective for geotechnical monitoring. Practical applications of GPS for landslide monitoring and collaborative researches using DInSAR with Balkan countries are described.
2019
Monitoring is important for assessing the stability of the ground and for confirming the validity of the design during the construction and operation of structures. The ideal monitoring system for projects in Rock and Geotechnical Engineering would be able to monitor the behavior of small to extensive areas continuously and automatically with high accuracy. In addition, the costs would be low and the system would be easy to handle. Satellite technology has the potential to realize the above monitoring system by combining it with conventional geotechnical instruments. In this paper, satellite technology for displacement monitoring, i.e., GPS and SAR, is firstly outlined and then the concept of spatiotemporal continuous displacement monitoring is introduced. The use of both satellite technology and geotechnical instruments is effective for geotechnical monitoring. Practical applications of GPS for landslide monitoring and collaborative researches using DInSAR with Balkan countries are described.
Proceedings of the 4th Regional Symposium on Landslides in the Adriatic - Balkan Region, 2019
Monitoring is important for assessing the stability of the ground and for confirming the validity of the design during the construction and operation of structures. The ideal monitoring system for projects in Rock and Geotechnical Engineering would be able to monitor the behavior of small to extensive areas continuously and automatically with high accuracy. In addition, the costs would be low and the system would be easy to handle. Satellite technology has the potential to realize the above monitoring system by combining it with conventional geotechnical instruments. In this paper, satellite technology for displacement monitoring, i.e., GPS and SAR, is firstly outlined and then the concept of spatiotemporal continuous displacement monitoring is introduced. The use of both satellite technology and geotechnical instruments is effective for geotechnical monitoring. Practical applications of GPS for landslide monitoring and collaborative researches using DInSAR with Balkan countries are described.
University Studies in Humanities,Lebanese University, 2020
The Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) monitoring of landslides is often needed for natural hazard study, analysis, or even as precaution alert. A local permanent GNSS network is installed to receive (x, y, and z) positions to estimate and monitor landslides concerning reference stations. In this paper for local monitoring, coordinates accuracy and reliability of Happy Survey company monitoring system receivers are experimentally investigated in the area of Brienz/Brienzauls. Three monitoring stations were placed. With a minimum baseline (1.7 km long) between the geodetic reference receiver, the three monitoring GNSS stations continuously register positioning data for 11 months: data were processed by hourly sessions and the results provide comparisons between readings and the calculation of the mean absolute differences and the standard deviation of differences of horizontal and vertical landslides at all stations. The standard deviation ellipses of all coordinates readings were calculated in a GIS environment to understand the degree and directions of the displacements. The results of the correlation analysis prove the similarity between monitoring stations, Standard Deviation Ellipses SDE analyzed landslides movement and direction at each monitoring station, and this experiment shows that in Brienz/Brienzauls the landslide degree recorded by GNSS coordinates differences is independent of the slope degree of the study area.
Landslide Science and Practice, 2013
2019
Monitoring is important for assessing the stability of the ground and for confirming the validity of the design during the construction and operation of structures. The ideal monitoring system for projects in Rock and Geotechnical Engineering would be able to monitor the behavior of small to extensive areas continuously and automatically with high accuracy. In addition, the costs would be low and the system would be easy to handle. Satellite technology has the potential to realize the above monitoring system by combining it with conventional geotechnical instruments. In this paper, satellite technology for displacement monitoring, i.e., GPS and SAR, is firstly outlined and then the concept of spatiotemporal continuous displacement monitoring is introduced. The use of both satellite technology and geotechnical instruments is effective for geotechnical monitoring. Practical applications of GPS for landslide monitoring and collaborative researches using DInSAR with Balkan countries are described.
2010
Slow-moving landslide studies over large areas call for multidisciplinary analyses supported by accurate ground displacement measurements. At present, conventional techniques can be valuably complemented by innovative satellite techniques, such as Differential SAR Interferometry (DInSAR), furnishing huge amounts of data at competitively affordable costs. This work investigates the DInSAR data potential in landslide studies starting from the awareness of the present constraints of the technique. To this end, with reference to a sample area, located in central-southern Italy, for which detailed base and thematic maps are available, an original tool for “a priori DInSAR landslide visibility zoning” is proposed to address the choice of the most suitable image datasets. Subsequently, referring to the visible zones, the perspective of using DInSAR data for checking/updating landslide inventory maps at 1:25,000 scale is shown.
Related topics
Related papers
2019
Monitoring is important for assessing the stability of the ground and for confirming the validity of the design during the construction and operation of structures. The ideal monitoring system for projects in Rock and Geotechnical Engineering would be able to monitor the behavior of small to extensive areas continuously and automatically with high accuracy. In addition, the costs would be low and the system would be easy to handle. Satellite technology has the potential to realize the above monitoring system by combining it with conventional geotechnical instruments. In this paper, satellite technology for displacement monitoring, i.e., GPS and SAR, is firstly outlined and then the concept of spatiotemporal continuous displacement monitoring is introduced. The use of both satellite technology and geotechnical instruments is effective for geotechnical monitoring. Practical applications of GPS for landslide monitoring and collaborative researches using DInSAR with Balkan countries are described.
Proceedings of the 4th Regional Symposium on Landslides in the Adriatic - Balkan Region, 2019
Monitoring is important for assessing the stability of the ground and for confirming the validity of the design during the construction and operation of structures. The ideal monitoring system for projects in Rock and Geotechnical Engineering would be able to monitor the behavior of small to extensive areas continuously and automatically with high accuracy. In addition, the costs would be low and the system would be easy to handle. Satellite technology has the potential to realize the above monitoring system by combining it with conventional geotechnical instruments. In this paper, satellite technology for displacement monitoring, i.e., GPS and SAR, is firstly outlined and then the concept of spatiotemporal continuous displacement monitoring is introduced. The use of both satellite technology and geotechnical instruments is effective for geotechnical monitoring. Practical applications of GPS for landslide monitoring and collaborative researches using DInSAR with Balkan countries are described.
Proceedings of the 4th Regional Symposium on Landslides in the Adriatic - Balkan Region, 2019
Monitoring is important for assessing the stability of the ground and for confirming the validity of the design during the construction and operation of structures. The ideal monitoring system for projects in Rock and Geotechnical Engineering would be able to monitor the behavior of small to extensive areas continuously and automatically with high accuracy. In addition, the costs would be low and the system would be easy to handle. Satellite technology has the potential to realize the above monitoring system by combining it with conventional geotechnical instruments. In this paper, satellite technology for displacement monitoring, i.e., GPS and SAR, is firstly outlined and then the concept of spatiotemporal continuous displacement monitoring is introduced. The use of both satellite technology and geotechnical instruments is effective for geotechnical monitoring. Practical applications of GPS for landslide monitoring and collaborative researches using DInSAR with Balkan countries are described.
Natural Hazards, 2016
Landslides are common phenomena that occur worldwide and are a main cause of loss of life and damage to property. The hazards associated with landslides are a challenging concern in many countries, including Italy. Over the last 15 years, an increasing number of applications have aimed to demonstrate the applicability of images captured by space-borne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) sensors in slope instability investigations. InSAR (SAR interferometry) is currently one of the most exploited techniques for the assessment of ground displacements, and it is becoming a consolidated tool for Civil Protection institutions in addressing landslide risk. This paper presents a subset of
Environmental Earth Sciences, 2015
The objective of this study was to evaluate and predict land movement by integrating geodetic, geophysical and meteorological data in a landslide area. Specifically, electrical resistivity tomography surveying, Global Navigation Satellite System and terrestrial laser scanning techniques were integrated to monitor a landslide. The study area lies to the southeast of the town of Taşkent in southern Turkey, close to Balcılar in the Central Taurus mountain chain. Landslides result in considerable damage to structures, farmland and the environment in this area; therefore, it is important to characterise the size, extent and timing of past land movements in order to mitigate damage from future landslides. Analysis presented in this paper shows that the greatest land movements in the region occur in spring, when average motions can be up to 1.5 m per month. It is demonstrated that integrated techniques provide a better means for monitoring landslide processes and gathering data for predictions of future movements. Mapping landslide movements by integrating geophysical and geodetic observations can provide a meaningful evaluation of a landslide and its dynamics.
Proceedings of the 4th Regional Symposium on Landslides in the Adriatic - Balkan Region, 2019
Monitoring is important for assessing the stability of the ground and for confirming the validity of the design during the construction and operation of structures. The ideal monitoring system for projects in Rock and Geotechnical Engineering would be able to monitor the behavior of small to extensive areas continuously and automatically with high accuracy. In addition, the costs would be low and the system would be easy to handle. Satellite technology has the potential to realize the above monitoring system by combining it with conventional geotechnical instruments. In this paper, satellite technology for displacement monitoring, i.e., GPS and SAR, is firstly outlined and then the concept of spatiotemporal continuous displacement monitoring is introduced. The use of both satellite technology and geotechnical instruments is effective for geotechnical monitoring. Practical applications of GPS for landslide monitoring and collaborative researches using DInSAR with Balkan countries are described.
CATENA
Differential Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (DInSAR) techniques have been repeatedly proved as an effective tool for monitoring built environments affected by geological hazards. In this paper, it is described how the Coherent Pixel Technique (CPT) approach has been successfully applied to assess the response of an unstable slope to the different phases of remedial works following a landslide event. The CPT technique was performed on 59 COSMO-SkyMed images (May 2011-August 2016) centered on the Quercianella settlement (a small hamlet of Livorno municipality, Tuscany, Italy), where the reactivation of a dormant shallow slide had occurred in March 2011 and, hereafter, a geotechnical intervention, designed with the aim of mitigating the risks, has been conducted from August 2013 lasting thirteen months. The time series of CPT results show a deformation pattern characterized by sudden accelerations (up to 21 mm in few months) in correspondence of the beginning of the interventions, during which the area has been excavated to install a drainage well, followed by mild decelerations and resulting from the stabilization of the area after the conclusion of the works. In particular, the integration of ground-based subsurface monitoring (inclinometers and piezometers) and DInSAR superficial data have provided consistent results for landslide characterization and helped in defining the state of activity and the areal distribution of the sliding surface. Moreover, the performance of remedial works installed in the landslide-affected area has been observed, showing the stabilization in the upper part of the hamlet and the still ongoing movement in the lower part. The combined monitoring system led 2 also the geotechnical company in charge to design further stabilization works as to preserve buildings and roads in the still moving area. Therefore, the integration of remote sensing techniques and in situ instruments represents a timely and cost-efficient solution for monitoring intervention works, opening new perspectives to engineering design for the stabilization of unstable slopes.
Proceedings of the 4th Regional Symposium on Landslides in the Adriatic - Balkan Region, 2019
Monitoring is important for assessing the stability of the ground and for confirming the validity of the design during the construction and operation of structures. The ideal monitoring system for projects in Rock and Geotechnical Engineering would be able to monitor the behavior of small to extensive areas continuously and automatically with high accuracy. In addition, the costs would be low and the system would be easy to handle. Satellite technology has the potential to realize the above monitoring system by combining it with conventional geotechnical instruments. In this paper, satellite technology for displacement monitoring, i.e., GPS and SAR, is firstly outlined and then the concept of spatiotemporal continuous displacement monitoring is introduced. The use of both satellite technology and geotechnical instruments is effective for geotechnical monitoring. Practical applications of GPS for landslide monitoring and collaborative researches using DInSAR with Balkan countries are described.
Proceedings of the 4th Regional Symposium on Landslides in the Adriatic - Balkan Region, 2019
Monitoring is important for assessing the stability of the ground and for confirming the validity of the design during the construction and operation of structures. The ideal monitoring system for projects in Rock and Geotechnical Engineering would be able to monitor the behavior of small to extensive areas continuously and automatically with high accuracy. In addition, the costs would be low and the system would be easy to handle. Satellite technology has the potential to realize the above monitoring system by combining it with conventional geotechnical instruments. In this paper, satellite technology for displacement monitoring, i.e., GPS and SAR, is firstly outlined and then the concept of spatiotemporal continuous displacement monitoring is introduced. The use of both satellite technology and geotechnical instruments is effective for geotechnical monitoring. Practical applications of GPS for landslide monitoring and collaborative researches using DInSAR with Balkan countries are described.
2011
Natural phenomena especially that cause hazard for human beings, like landslide, have turned the efforts of the researchers to study the mitigation of risk as possible. The professional planning for monitoring the landslide reflects adequate alarm systems to assess the imminent danger and reduces the harmful product of the hazard on the human's lives and the social economic. Global position system have transformed the survey work from the traditional surveying work into applications that have been applied in many critical phenomena, because of the high accuracy in the monitoring of the earth deformation activities in addition to the high productivity. Main body structure of this paper aims to spot the light on specific techniques used in practice to monitor the landslides, bearing in mind the unnecessary for the direct sight between the static or moving stations. Also, in most of monitoring techniques the bad weather condition and scope of survey doesn't effect on the required accuracy such as like, GPS with InSAR, GPS stations and inclinometers, GPS with TDR, FS and RTK, and Static DGPS.

Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
 Adnan Ibrahimović
Adnan Ibrahimović