Motorcycle Handling and Chassis Design the art and science
…
498 pages
1 file

Sign up for access to the world's latest research
AI-generated Abstract
The book "Motorcycle Handling and Chassis Design" presents an updated and comprehensive exploration of motorcycle chassis and handling, building on foundational knowledge from the original 1984 publication. It emphasizes the evolution and improvement in motorcycle handling over decades, detailing advancements in chassis design, suspension technologies, and the critical role of tyres and aerodynamics. The text aims to provide readers with not only the theoretical background required for understanding motorcycle dynamics but also practical insights for design, modifications, and setup, encouraging an engaging and thorough study of the subject.
Figures (528)

































































![So where is the benefit in drifting? --- Well, as any drag racer knows maximum traction is achieved whe
the tyre is spinning slightly. In fact the tyre companies tell us that approximately 10 - 20% slip is abot
optimum on tarmac, as shown earlier. So if sufficient power is available to cause this degree of slip th
total friction force on the tyre can be divided between the normal lateral cornering force and that due t
driving force, some of which gets resolved towards the bend centre, thus part of the total cornering forc
is under control of the throttle. Referring to the friction circle in fig. 2.22 this means that the resultar
force moves rearward around the circle. In racing, feel and control over what the tyre is doing can b
enhanced by skilled use of this technique. When cornering in the classic style it is hard to feel the limit c
adhesion and there are minimal control options left to deal with the situation when that limit is exceedec
On the other hand when the bike has been setup with significant drift the rider has more control over th
total tyre force through the throttle. Therefore when he feels that he is about to lose it, he can just clos
sliding at all the lean angle of the combined bike and rider would be 45° , but when sliding at 12° the
required camber angle reduces to 44.4° , hardly a big difference! To return to speedway cornerin
styles, where a more typical slide angle may be, say 50° , then again for the 1G. case the lean angle
reduces to 33°. So we can see that to reduce the lean angle by a significant amount requires a hig]
degree of drifting, more in fact than is usual in road racing.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/63042047/figure_069.jpg)





















































































































































































































































































































































































































































Related papers
Vehicle System Dynamics, 2006
Virtual prototyping is a common practice in the automotive industry but still a developing one for motorcycle companies. Among other advantages such techniques can greatly reduce the development time necessary to validate novel ideas. In that fashion, a motorcycle is modelled as a highly detailed multibody system in order to provide a test-rig for a number of alternative front suspension systems. These systems are compared in terms of kinematics and dynamics to provide improved insight into the aspects that need to be considered when deciding upon the use of an alternative system instead of the conventional forks. Apart from the motorcycle model, a driver model has been developed to allow for the systems to be validated through subjection to a variety of driving manoeuvres during simulations. Some indicative results are shown to prove the performance potential of such systems as compared with the default solution of conventional forks and bring into attention differences between each design philosophy.
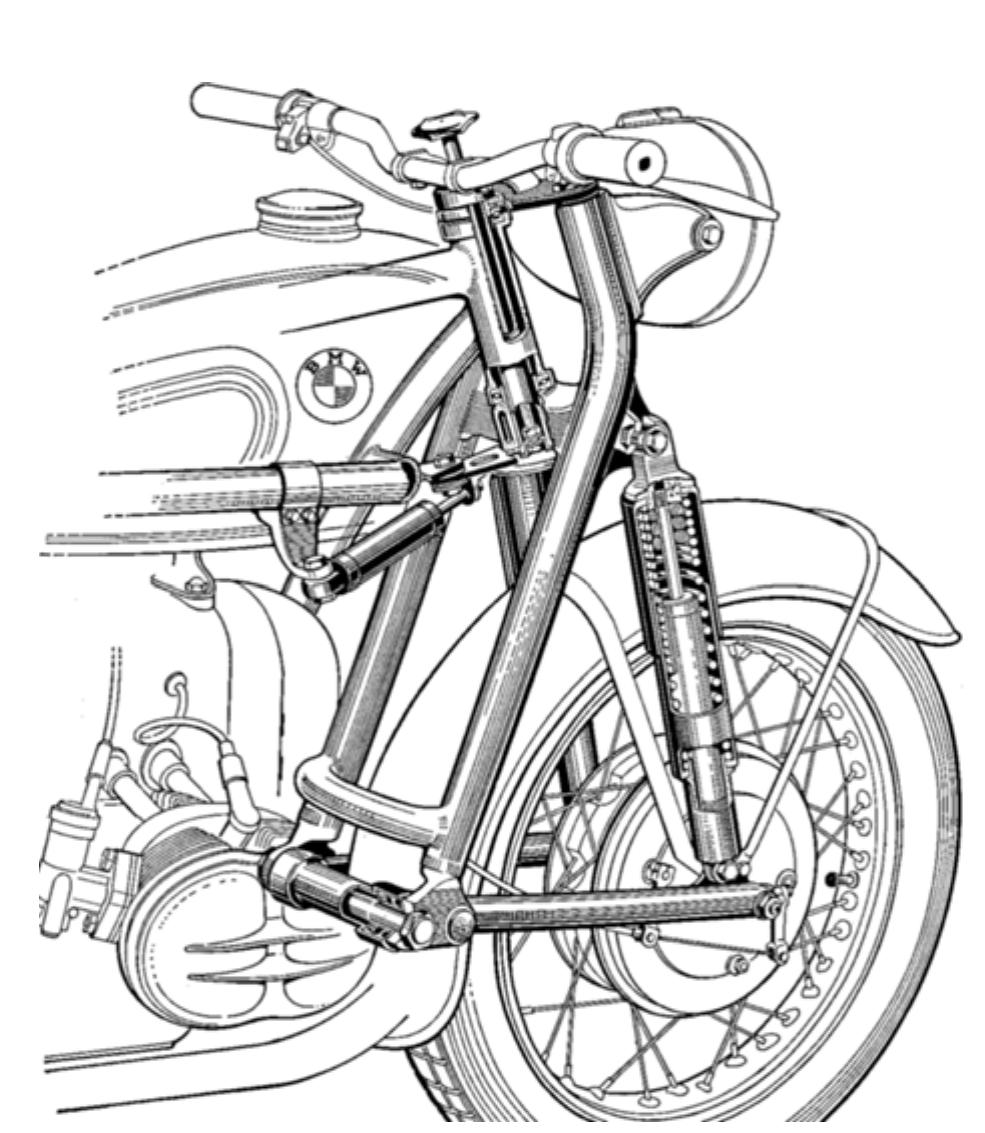
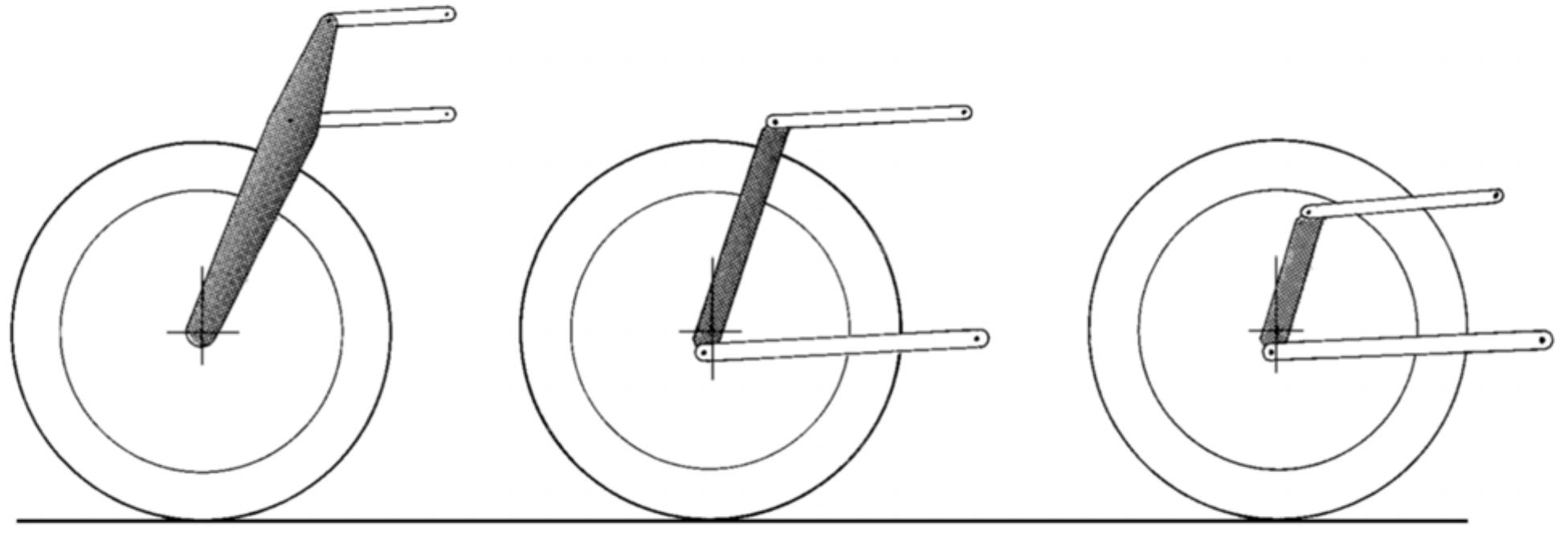
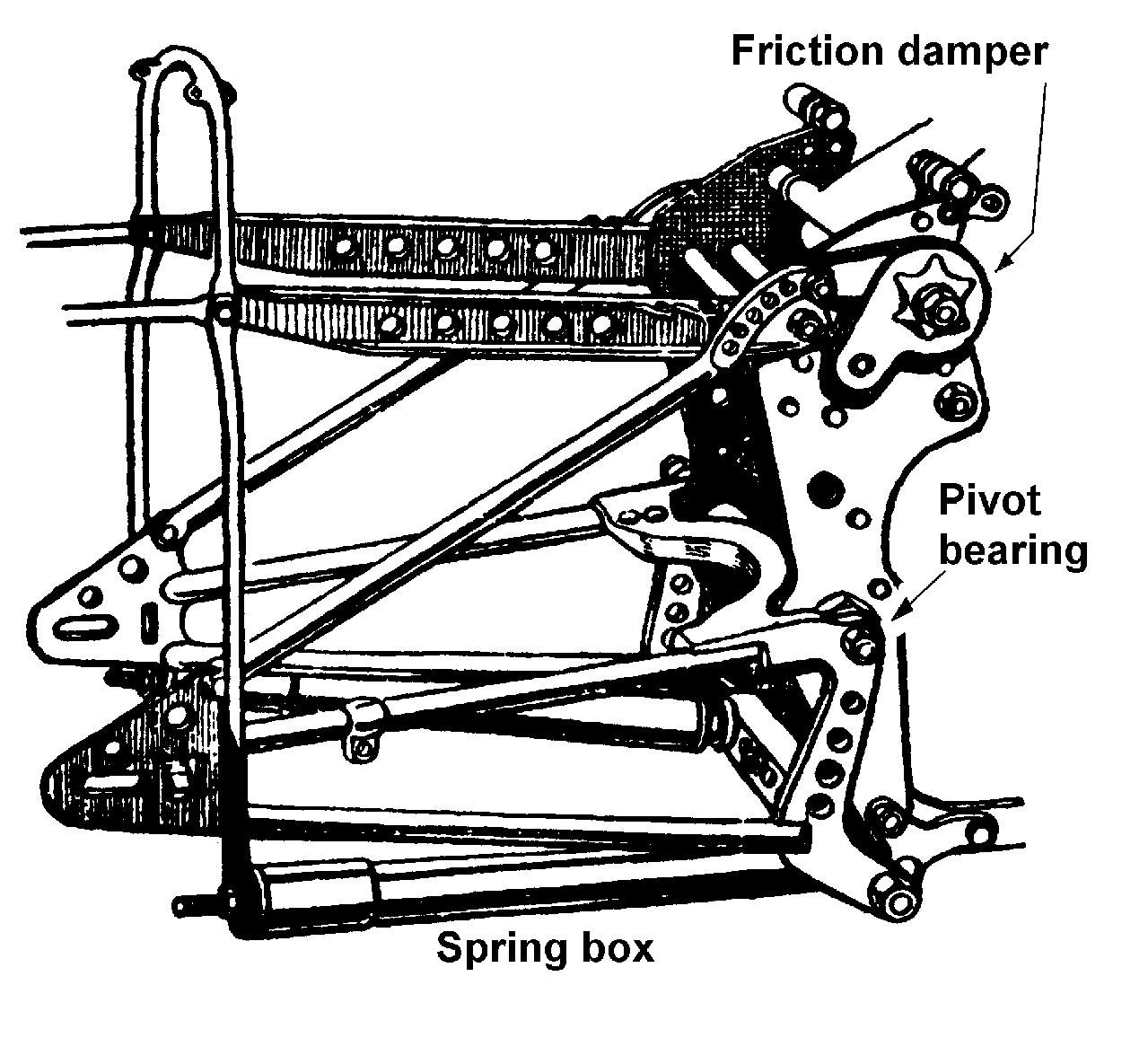
The project aims at design and development of a front suspension system, alternative to conventional fork type motorcycle suspension. The project also aims at in-depth analysis of both the systems and also the feasibility of the same under various riding conditions in the country. Telescopic forks are the default choice of front suspension for motorcycles for designers. Even after decades of decades of development, the problems associated with sliding fork design still persist. The sliding forks represent a sliding prismatic joint. As in the case of every other sliding prismatic joint, the inherent friction between the sliding surfaces cannot be eliminated completely. Thus the response of the system under relatively small excitation is very less. The next major factor associated with this type of design is the requirement of highly stiff mount points for the suspension. Due to the large length of the forks the load is transferred to some high point on the frame. This automatically puts some limitation in the frame design like the height or length of the frame. Also due to the high leverage, the frame has to be designed to handle the magnified road load. This is achieved by using much stiffer frame. Stiff frame means either more weight or more cost, both factors which are adverse for designers. The forks can easily bend in lateral direction. This will lead to misalignment between front and rear wheel, and also change the contact area between the tire and road surface. In order to avoid this, high levels of stiffness has to be achieved at forks. This will lead to additional weight of forks and hence increase the unsprung mass. The fork type suspension has got the major disadvantage of nose dive. This will result in the rider slapping against the tank under hard braking. Also the fork being a lengthy space occupying member puts limitation for the designer in optimising the suspension parameters and wheelbase. The current project aims in developing a system that can overcome the aforementioned disadvantages. The design is basically based on usage of swing arm type suspension at the front accompanied by linkages to deliver the required motion with least possible complexity and parts.
American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics eBooks, 2008
The ENGG 3100 proceedings are a collection of papers written by undergraduate students enrolled in the ENGG3100 Design III course offered by the School of Engineering, University of Guelph during the Winter 2007 term. The Design III course is the third in a four courses design sequence that all students studying Engineering at Guelph must take regardless of their Engineering speciality. The course prepares students for open ended design projects by guiding them through the design process using an active learning approach. Each student works as part of a group of 4 students on one of several pre-selected design projects. These projects typically cover all of the Engineering fields offered by the School of Engineering. Students are engaged in the design process using lectures, weekly meetings with highly experienced teaching assistants and course instructors. Students also get feedback on their design after submitting two design reports for evaluation and making two presentations to the entire class.
De Formula Student competitie is een competitie waaraan universiteiten vanuit de hele wereld deelnemen. In 2004 heeft het Formula Student Racing Team Eindhoven (FSRTE) voor het eerst deelgenomen in klasse 3. In deze klasse wordt het ontwerp beoordeeld. In 2005 heeft het FSRTE voor de 2 e keer meegedaan en dit keer in klasse 2 met een onafgebouwde wagen. Het doel voor 2006 is om deel te nemen met een rijdende auto in klasse 1. In deze klasse kan daadwerkelijk worden geraced met de zelfgebouwde eenzitter. Het maximale vermnogen ligt hierbij op 65 kW.
Frame is very important part of bikes, as all the important accessories are mounted on the frame. The frame need to be very strong, stiff and light in weight, which is obtained by combining different materials and optimizing its shapes. The strength of frame construction is correct design of a frame because it is the most important part that ensures safe riding. This project deals with the design of bike frame. The modeling of bike frame is done in solid works and analysis of frame is done using the ansys work bench software. This project gives us the stress, strain, displacement values of particular bike frame on load condition.
The objective of the 2008 IPFW SAE Mini-Baja "Team Innovations" is to design, fabricate and test a new vehicle suspension design utilizing electronic semi-active suspension control. This vehicle will be used in competition at the 2008 SAE Mini-Baja Competition in Edwards, Illinois, and will therefore be designed in accordance with the 2008 Mini-Baja Rules and Regulations. By implementing this new suspension system, the team hopes to gain a significant competitive edge at the competition, and improve IPFW's ranking from previous competition years. Upon completion of this project, the team hopes to have gained real-world multidisciplinary design experience.
Attributing Design Identity, Identifying Design Identities, 2020

Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
Related papers
Engineering Failure Analysis, 2010
2010 IEEE International Conference on Control Applications, 2010
Bicycle design history and systems of mobility, 2017
Applied Acoustics, 2006
Physical Modelling for Architecture and Building Design, 2019
Proceedings of the Canadian Engineering Education Association, 2015
International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology, 2020
 Philippe Thiriet
Philippe Thiriet