Results are presented from searches for the standard model Higgs boson in protonproton collisions at √ s = 7 and 8 TeV in the CMS experiment at the LHC, using data samples corresponding to integrated luminosities of up to 5.1 fb −1 at 7... more
We discuss the theoretical bases that underpin the automation of the computations of tree-level and next-to-leading order cross sections, of their matching to parton shower simulations, and of the merging of matched samples that differ by... more
We extend earlier ideas about the appearance of noncommutative geometry in string theory with a nonzero B-field. We identify a limit in which the entire string dynamics is described by a minimally coupled (supersymmetric) gauge theory on... more
MadGraph 5 is the new version of the MadGraph matrix element generator, written in the Python programming language. It implements a number of new, efficient algorithms that provide improved performance and functionality in all aspects of... more
We construct three dimensional Chern-Simons-matter theories with gauge groups U (N ) ×U (N ) and SU (N ) ×SU (N ) which have explicit N = 6 superconformal symmetry. Using brane constructions we argue that the U (N ) × U (N ) theory at... more
In this review we present a thoroughly comprehensive survey of recent work on modified theories of gravity and their cosmological consequences. Amongst other things, we cover General Relativity, Scalar-Tensor, Einstein-Aether, and... more
The World-Wide Web (W 3 ) initiative is a practical project to bring a global information universe into existence using available technology. This article describes the aims, data model, and protocols needed to implement the "web", and... more
This paper presents a new event generator, ALPGEN, dedicated to the study of multiparton hard processes in hadronic collisions. The code performs, at the leading order in QCD and EW interactions, the calculation of the exact matrix... more
We study toroidal compactification of Matrix theory, using ideas and results of noncommutative geometry. We generalize this to compactification on the noncommutative torus, explain the classification of these backgrounds, and argue that... more
We explain how the string spectrum in flat space and pp-waves arises from the large $N$ limit, at fixed $g^2_{YM}$, of U(N) ${\cal N} =4$ super Yang Mills. We reproduce the spectrum by summing a subset of the planar Feynman diagrams. We... more
X -ray radiographic absorption imaging is an invaluable tool in medical diagnostics and materials science. For biological tissue samples, polymers or fibre composites, however, the use of conventional X-ray radiography is limited due to... more
Gigaelectron volt (GeV) electron accelerators are essential to synchrotron radiation facilities and free-electron lasers, and as modules for high-energy particle physics. Radiofrequency-based accelerators are limited to relatively low... more
In high-energy physics, with the search for ever smaller signals in ever larger data sets, it has become essential to extract a maximum of the available information from the data. Multivariate classification methods based on machine... more
We present a novel approach to the detection of weak magnetic fields that takes advantage of recently developed techniques for the coherent control of solid-state electron spin quantum bits. Specifically, we investigate a magnetic sensor... more
In this thesis we present selected results taken from the author's published work . Due to space constraints not all the relevant material is presented and the reader is referred where necessary to extra results in the original papers.... more
We present the latest developments of the MadGraph/MadEvent Monte Carlo event generator and several applications to hadron collider physics. In the current version events at the parton, hadron and detector level can be generated directly... more
We present the first complete next-to-next-to-leading order analysis of the Standard Model Higgs potential. We computed the two-loop QCD and Yukawa corrections to the relation between the Higgs quartic coupling (λ) and the Higgs mass (M h... more
We study the effective field theory of inflation, i.e. the most general theory describing the fluctuations around a quasi de Sitter background, in the case of single field models. The scalar mode can be eaten by the metric by going to... more
It has been shown that a gravitational dual to a superconductor can be obtained by coupling anti-de Sitter gravity to a Maxwell field and charged scalar. We review our earlier analysis of this theory and extend it in two directions.... more
We present a new multi-channel integration method and its implementation in the multipurpose event generator MadEvent, which is based on MadGraph. Given a process, MadGraph automatically identifies all the relevant subprocesses, generates... more
We provide a derivation of holographic entanglement entropy for spherical entangling surfaces. Our construction relies on conformally mapping the boundary CFT to a hyperbolic geometry and observing that the vacuum state is mapped to a... more
We study N = 2 supersymmetric four dimensional gauge theories, in a certain N = 2 supergravity background, called Ω-background. The partition function of the theory in the Ω-background can be calculated explicitly. We investigate various... more
We extract from data the parameters of the Higgs potential, the top Yukawa coupling and the electroweak gauge couplings with full 2-loop NNLO precision, and we extrapolate the SM parameters up to large energies with full 3-loop NNLO RGE... more
We develop a simple description of models where electroweak symmetry breaking is triggered by a light composite Higgs, which emerges from a strongly-interacting sector as a pseudo-Goldstone boson. Two parameters fully characterize these... more
We study the large volume limit of the scalar potential in Calabi-Yau flux compactifications of type IIB string theory. Under general circumstances there exists a limit in which the potential approaches zero from below, with an associated... more
Abstract: We consider all 1/2 BPS excitations of AdS×S configurations in both type-IIB string theory and M-theory. In the dual field theories these excitations are described by free fermions. Configurations which are dual ...
In this paper we present FeynRules, a new Mathematica package that facilitates the implementation of new particle physics models. After the user implements the basic model information ( e.g., particle content, parameters and Lagrangian),... more
We review the landscape of QCD axion models. Theoretical constructions that extend the window for the axion mass and couplings beyond conventional regions are highlighted and classified. Bounds from cosmol- ogy, astrophysics and... more
Uncovering the hidden regularities and organizational principles of networks arising in physical systems ranging from the molecular level to the scale of large communication infrastructures is the key issue for the understanding of their... more
There is growing interest to investigate states of matter with topological order, which support excitations in the form of anyons, and which underly topological quantum computing. Examples of such systems include lattice spin models in... more
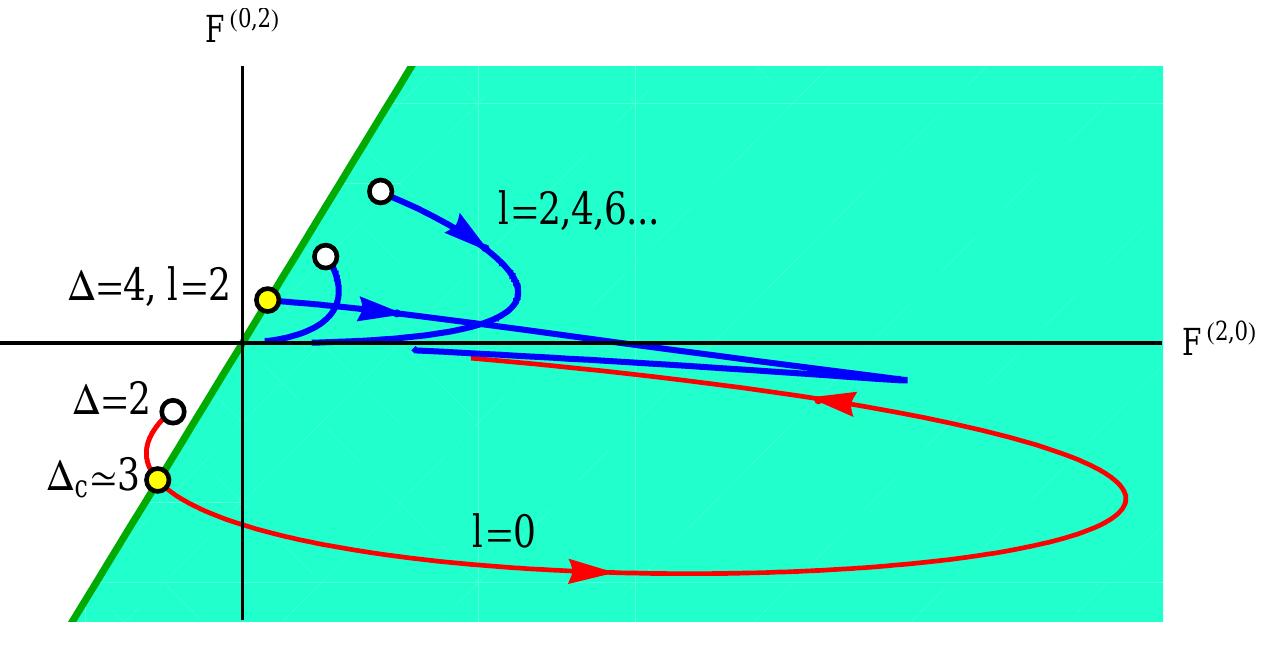
In an arbitrary unitary 4D CFT we consider a scalar operator φ, and the operator φ 2 defined as the lowest dimension scalar which appears in the OPE φ × φ with a nonzero coefficient. Using general considerations of OPE, conformal block... more
The cold dark-matter model successfully explains both the emergence and evolution of cosmic structures on large scales and, when we include a cosmological constant, the properties of the homogeneous and isotropic Universe. However, the... more
A precise measurement of the proton flux in primary cosmic rays with rigidity (momentum/charge) from 1 GV to 1.8 TV is presented based on 300 million events. Knowledge of the rigidity dependence of the proton flux is important in... more
We consider second-order viscous hydrodynamics in conformal field theories at finite temperature. We show that conformal invariance imposes powerful constraints on the form of the second-order corrections. By matching to the AdS/CFT... more
A recurrent idea in the study of complex systems is that optimal information processing is to be found near bifurcation points or phase transitions. However, this heuristic hypothesis has few (if any) concrete realizations where a... more
Applications of Riemannian quantum geometry to cosmology have had notable successes. In particular, the fundamental discreteness underlying quantum geometry has led to a natural resolution of the big bang singularity. However, the precise... more
For any arbitrary algebraic curve, we define an infinite sequence of invariants. We study their properties, in particular their variation under a variation of the curve, and their modular properties. We also study their limits when the... more
The present paper concludes our investigation on the QCD equation of state with 2+1 staggered flavors and one-link stout improvement. We extend our previous study [JHEP 0601:089 (2006)] by choosing even finer lattices. Lattices with N t =... more
We present a maximally supersymmetric IIB string background. The geometry is that of a conformally flat lorentzian symmetric space G/K with solvable G, with a homogeneous fiveform flux. We give the explicit supergravity solution, compute... more
† These two authors contributed equally to this work.
We argue that certain apparently consistent low-energy effective field theories described by local, Lorentzinvariant Lagrangians, secretly exhibit macroscopic non-locality and cannot be embedded in any UV theory whose S-matrix satisfies... more


















![it cannot explain the discrepancy between theory and CMS data. Another source of theo- atter curve has been rescaled” in order for its visible integral to coincide with that of the ormer (since in this case we are specifically interested in a shape comparison: in absolute values, the two cross sections differ however by only 2.5%). As one can gather from the plot, the two predictions are close to each other; the FxFx prediction is sightly softer than the unmerged one, but this does not appear to be sufficient to bring it in agreement with the CMS measurement. The variation of the merging scale in a large range (30-155 GeV) does not induce any significant change. It therefore appears that the systematics due to higher-order corrections are fully under control, since scale variations and NLO-merging give consistent results for this observable, and we thus confirm the previous findings that it cannot explain the discrepancy between theory and CMS data. Another source of theo- Figure 12: Transverse momentum of the top quark in tt production. Left panel: comparison between F'xFx-merged (blue) and unmerged (red) predictions; the binning is the same as that of ref. [346]. Right panel: NLO+PS predictions obtained with different PSMCs, compared to the f{NLO result.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/41197946/figure_014.jpg)
![(min; Nmax), eq. (4.12) implies that the © function in eq. (4.11) is identically equal to one. Therefore, GF,,./;,)(Q) is a constant for Q < 30 GeV, equal to the fraction of events which do not have any jet harder than 30 GeV in the relevant pseudorapidity interval: for this reason, gap fractions are not displayed in this range. The quantity p7(j1) in eq. (4.11) can be replaced by a function, defined analogously to what is done in eq. (4.12) in terms of any observable O with mass dimension equal to one; in this way, one constructs a different type of gap fraction, GFo(Q). The transverse momentum of the second-hardest jet [350], and Hy (348, 350] have been considered in the literature; they are rather strongly correlated with p;(j1), and will not be investigated any further here. Figure 13: Gap fraction for the py of the hardest jet, in four different pseudorapidity intervals, as predicted by FxFx-merged, unmerged (labelled AMC@NLO), and MC@NLO simulations. The setup follows closely that of ref. [350]. See the text for details. ‘igure 13: Gap fraction for the p; of the hardest jet, in four different pseudorapidity](https://figures.academia-assets.com/41197946/figure_015.jpg)










![Table 5: Sample of LO and NLO total rates for the production of heavy quarks and/or jets, possibly within cuts, at the 13-TeV LHC; we also report the integration errors, and the fractional scale (left) and PDF (right) uncertainties. Processes d.1 and d.2, as well as processes involving at least a top pair, are computed in the five-flavour scheme. Processes that explicitly involve b-quarks in the final state are calculated in the four-flavour scheme. For processes d.3-d.6 we require 2 (or 4) b-jets in the final state with |7| < 2.5. For processes d.1—d.6, we require the (b)-jets to have p, > 80 GeV, with at least one of them with p; > 100 GeV. Calculations of cross sections at the NLO for this class of processes are available in the literature as well as in public codes: from the seminal results for the hadroproduction of a heavy quark pair [282-286], to their NLO+PS implementation in MC@NLO [169] and POWHEG [287], to ttj [288] (also including top decays [254,289] and parton shower effects [290]), to the computation of ttj7 [291]. Merged NLO+PS results for tt plus jets are also available [188,292,293]. NLO results for three jets [294], four jets [73], and up to five jets [295,296] have been published. Two- and three-jet event generation is available in POWHEG [297,298]. Calculations for bbbb [299,300], ttbb [301-303], and tttt [304] production have appeared in the literature.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/41197946/table_005.jpg)







































![Figure 6: Interactions induced by the chromomagnetic operator. The same issue happens for a graviton interacting with four gauge bosons. A full validation of the MADGRAPH 5 implementation the FEYNRULES RS model against the MADGRAPH 4 [66] implementation has been performed. 6.4 Chromo-magnetic operator](https://figures.academia-assets.com/41204818/figure_006.jpg)

![[able 2: Number of subprocess directories, number of integration channels for the initial run (“survey”) f the event generation, size of the directory after one run generating 10,000 events, and run times for enerating 10,000 events, comparing MADGRAPH/MADEVENT4 output (“MG 4”) with grouped subpro- ess output (“MG 5”). For all processes, p = j = g/u/t/e/¢/d/d/s/s, I+ = e+/p*. The run times for -, 1- and 2-jet processes are for a Sony VAIO TZ laptop with 1.06 GHz Intel Core Duo CPU running Jbuntu 9.04, gFortran 4.3 and Python 2.6, while the 3-, 4- and 5-jet run times (marked by *) are for a 28-core computer cluster with Intel Xeon 2.50GHz CPUs. pp — Wt + 5] is not possible to run with VIADGRAPH/MADEVENT 4.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/41204818/table_002.jpg)





![preserved V = 4 supersymmetry.) Each chiral multiplet consists of a two-component Ma- jorana fermion and a complex scalar. We will now recall how to obtain the Chern-Simons term by a mass deformation of this configuration [7]. There are several possible mass deformations. Separating the D5-branes from the D3-branes in the directions 78 corre- sponds to a standard complex mass parameter in the superpotential, which is inherited from the four-dimensional NV = 1 theory. The separation in the 5 direction corresponds to a real mass term of equal magnitude but opposite sign for the fundamental chiral and anti-fundamental chiral multiplets. Figure 3: The web deformation of the intersecting NS5-D5 configuration, as seen in the 59 plane. anti-fundamental chiral multiplets.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/43070133/figure_001.jpg)







































































![Figure 8.4: The FI space of the C?/Z3 theory. (a) The three chambers of the moduli space. The blue lines correspond to the FI parameter values that result, after RG flow, in the non-conformal theory in Figure[8.3] (b) The FI path dual to the B-field period is plotted in orange for the fixed FI parameter k, which is the dual to the Kahler modulus in each chamber.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/33997497/figure_012.jpg)









![Table 4: Cross sections for the ten SPS points and the contributions, in %, from different sub- dominant channel is gluon fusion, with gg annihilation contributing to less than 10% of production where the processes in column 4 are excluded, and (anti)squark-(anti)squar Prospino 2 [71, 72, 73]. processes for each point. In the process definitions, ¢ = tiz,.r,dz,r. For gg and tt* production, the the numbers. The exceptions are point 2 and 5, respectively, where we have separated the gg and q@ channels by the “+” sign. The last two columns show the contributions from associated gluino-(anti)squark k production where the processes in column 5, 7 and 8 are excluded. The NLO cross sections are calculated using Figure 14: Hr distribution for SPS points la, 2, 3, 5 and 9. The peak or peaks of the distribution is correlated with the masses of the produced SUSY particles.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/41204574/figure_010.jpg)





![Table 5: The positions of the peaks in the Hr distributions and the masses of the particles mainly produced, as well as the LSP, for the SPS points la, 2, 3, 5 and 9. though there might still be effects from interference or Breit-Wigner curve distortions in some parameter regions). However, if we want to study angular distributions where spin correlations might be important, the gluino decay should be done in Mad] kind of refinements, efficiency will start to become an important factor. Fivent. For this It is therefore better to use different treatments for the different parameter points, in order to make an optimized choice for which processes to include at each point. So this should be seen rather as a preparatory study for such a more elaborate analysis.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/41204574/table_005.jpg)










![Figure 30. (Color online).Scaling of nearest neighbour entanglement of the ground state of the transverse Ising Hamiltonian on a chain (from [663]). The inset at top right shows the nearest neighbour entanglement, while the main figure shows its derivative, plotted against the parameter X. In the main figure (top right inset), say at \ = 1 (say at A = 1.25), the curves from the top are respectively for 7, 9, 11, ..., 41 sites (the quality of the figure improves in the online version). Bottom left inset: The position Ayin of the minimum of 0)C1 in the main figure changes with the total number of sites. The current inset shows the plot of the logarithm of A;in — 1 against the logarithm of the total number of sites (denoted in this figure as In).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/69199186/figure_032.jpg)
![Figure 31. Dynamical phase transitions: a “river” of separable states between the two regions of control parameter space where nearest neighbour entaglement is non-zero in an asymmetric XY model in a time-dependent transverse field. (from [655]). Entanglement (logarithmic negativity) is plotted against the initial transverse field (a) and (real) time (¢). A similar behaviour is absent in magnetization [655].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/69199186/figure_033.jpg)
![Figure 2. Schematic pictures of optical lattice potentials; a) 2D square lattice of quasi 1D traps; b) 3D simple cubic lattice (from [33]).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/69199186/figure_002.jpg)

![Figure 1. Distribution of atoms among lattice sites vs. momentum distribution of atoms released from an optical lattice. (a): low lattice potential: the largest interference peak is at zero momentum. The system is a superfluid with fluctuating number of atoms per site. (b): high lattice potential case where a perfect Mott state with exactly one atom per site is achieved — the momentum distribution is blurred (from [33]).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/69199186/figure_001.jpg)
![Figure 4. Overlapping MI phases for the Bose-Hubbard model in an optical cavity (from [173]](https://figures.academia-assets.com/69199186/figure_004.jpg)
![Figure 6. Quantum phase diagrams of Fermi-Bose mixtures in an homogeneous optical lattice as functions of jz? and a = V/U, for pf = 0.4 and t/U = 0.02. Roman numbers denote the total number of particles that form the composite and a bar means that the composite is formed by bosonic holes rather than bosons. (a) Diagram of composites where the filled small (blue) dots symbolize fermions, large (red) dots symbolize bosons and empty (red) dots, bosonic holes. The subindex A (R) indicates attractive (repulsive) composites interactions. (b) Detailed quantum phase diagram of fermionic composites. The subindices denote here different phases: DW (density wave), FL (fermi liquid), SF (superfluid) and FD (fermionic domains). The strongly correlated phases for small but finite t are surrounded by characteristic lobes [183], beyond which bosons become superfluid. Therefore, there are thin regions of bosonic superfluid between the various composite phases (from ys](https://figures.academia-assets.com/69199186/figure_006.jpg)
![Figure 7. Theoretical prediction of Bose-Anderson glass in a 1D optical lattice; top: superfluid fraction as a function of disorder Vi (thickline), respectively quasi-disorder V2 (thinline); middle: disordered speckle potential (thickline), and quasi-disordered (thinline) potential formed by incommensurable superlattices; bottom: occupation numbers of the ground state in the presence of disorder (black dots), and quasi-disorder (open dots) (from [68]).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/69199186/figure_007.jpg)
![Figure 8. Numerically simulated dynamical transition to the Bose glass state; first (in inset) a superfluid at high value of lattice potential is formed, and then (in the main figure) the disorder is turned on gradually. Condensate (solid line) and superfluid (dashed line) fractions tend to zero (from [68]).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/69199186/figure_008.jpg)
![Figure 9. Contour plot of the square of the largest coefficient, C?,,,, of the expansion of the state of the system described by a Bose-Hubbard model in the number basis, as a function of disorder A and on-site interaction V, in units of the hopping energy J. The results correspond to exact diagonalization of a one-dimensional system with 8 sites and 8 bosons (from [69]. Note that V accounts for U and J for t in the figure). The labels identify the predicted different phases: superfluid, Mott insulator, Bose glass (BG), and Anderson localization (AL).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/69199186/figure_009.jpg)

![Figure 11. Experimental signatures of the MI—Bose glass transition: Broadening of the excitation spectrum as disorder (s2) grows. One observes discrete linbes in the gapped MI, and significantly broadened and structureless spectrum in the BG phase (from [35]).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/69199186/figure_011.jpg)
![Figure 12. Density profiles (absorption images) of quasi 1D BEC released from the combined harmonic trap plus random speckle (left column), and from the combined harmonic trap, optical lattice, and random speckle (right column). The second row shows the column density and the third row shows the result of the numerical simulation (from [73]).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/69199186/figure_012.jpg)
![Figure 13. Calculated condensate wavefunction for a BEC in a combined potential formed by harmonic trap, and two incommensurate standing waves. The sequence (a)—(c) shows the effects of the increasing nonlinearity (i.e., increasing the number of atoms) (from [73]).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/69199186/figure_013.jpg)
![Figure 14. Numerically calculated dynamical transition from the Fermi liquid to the Fermi glass of fermionic composites (fermion + bosonic hole composites) in a 2D lattice with N = 10 x 10 sites. In (a), the decrease of the variance of the number of fermions per lattice site is shown as a function of the amplitude of the disorder. In (b), the probability of having one composite at each lattice site in the absence of disorder is given, and (c) gives the same as (b) after adiabatically ramping up the disorder (from [87]).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/69199186/figure_014.jpg)
![Figure 15. Numerically calculated dynamical transition from the Fermi domain to the Fermi glas of fermionic composites (one fermion and zero boson) in a 2D lattice with N = 10 x 10 sites. In (a the decrease of the variance of the number of fermions per lattice site is plotted as a function of th amplitude of the disorder. In (b), the probability of having one composite at each lattice site in th absence of disorder is given, and (c) gives the same after adiabatically ramping up the disorder (from [87]).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/69199186/figure_015.jpg)
![Figure 16. Schematic predicted phase diagram of (a) fermion plus bosonic hole composites and of (b) fermion plus boson composites [87]).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/69199186/figure_016.jpg)



![Figure 20. (a) Enumeration of intertrimer (intratrimer) nearest neighbours; (b) Classical 120‘ Néel state with left chirality. 5.4.1 The quantum magnet Hamiltonian. The spinless interacting Fermi gas in the trimerised kagomé lattice is described by the following extended Fermi- Hubbard Hamiltonian where (a,b) denotes nearest neighbors, a = {a,7} with a referring to intra-trimer indices and 7 num bering the trimers. The tg, and Ug», take the values t and U for intratrimer, and t’ and U’ for intertrimer couplings, ng = fi fa and fa is the fermionic annihilation operator. The sites in each trimer are enumerated as in Fig. 20{a). We denote t he 3 different intra-trimer modes by f = (f1,;+ foit fs.) /V3 (zero momentum mode), and FO = (fia + 2+ fou + 22.f34)/V3 (left and right chirality modes), where z4 = exp(+277/3). In the limit of weak coupling between trimers, the extended Hubbard Hamiltonian for the problem of t on a triangular lat fT11} tice with couplings that depend on the bond directions [63] wo fermions per trimer becomes equivalent to a quantum magnet 110)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/69199186/figure_020.jpg)

![Figure 22. Scheme of the proposed experimental set-up. Each arrow depicts a wave vector of a standing wave laser. The three vertical planes intersect at an angle of 120°. Dark (dark blue in the online version) spots in the right kagomé figure indicate the potential lattice minima (from [111]}). Here we focus on control of interactions and recent proposals based on ultracold bosonic or fermionic atoms [64], cold gases of polar molecules [I15], and trapped ions [495)/496|[497]. Realizations of frustrated models in ultracold atomic systems requires either the creation of a lattice with appropriate geometry, or the control of the effective atomic interactions. Geometry of the lattice, as we already mentioned, can be engineered using superlattice techniques (see Fig. details in the case of kagomé lattices). 22 and Ref. [111] for the](https://figures.academia-assets.com/69199186/figure_022.jpg)
![where H;,, and H,., represent respectively the internal and external dynamics of molecules. Haq is the Hamiltonian for dipole-dipole interactions between two molecules. The rotational excitation of each molecule is described by the Hamilto- nian In Ref. [115], the authors start with two polar molecules, trapped in an optical lattice. The outermost shell of an electron of a heteronuclear molecule represents the spin-1/2 system. The total Hamiltonian of a pair of heteronuclear molecules trapped in an optical lattice is given by](https://figures.academia-assets.com/69199186/figure_023.jpg)
![where b,; annihilates a boson in a hyperfine state mp =o at site 7, n; denotes the number of particles at site i and F; = eset ol T o0'bo; is the spin operator at site 7 (Too being the usual spin matrices for a spin-1 particle) and < ij > denotes pairs of nearest neighbours in the lattice. The first two terms in the Hamiltonian represent 6.3.2 Bose-Hubbard model for spin 1 particles. The derivation of the Bose-Hubbard Hamiltonian for ultracold spinor gases is performed in the same way as in the scalar case. One has to add to the scalar Bose-Hubbard model the spin dependent part of the interaction. Following the identities given in the previous part of the section, the Bose-Hubbard Hamiltonian for spin 1 particles is obtained straightforwardly [119]:](https://figures.academia-assets.com/69199186/figure_024.jpg)

![Figure 24. (Color online.) Sketch of the phase diagram, obtained by applying the variational principle in the Az, A4 phase space (for Ao = 0) to mean field, Néel, and dimer states with one atom per site. The scale is set by letting A1 = A3 = 1. Néel-type states are never favorable over nematic states. The ferromagnetic region (gray) was obtained numerically by imaginary time evolution of MPS (and comparing the results from runs with D = 1 and D = 5) in a chain of 50 sites with open boundary conditions [300]. (Note that here D is the dimension of the ancillary system that is used in the MPS method.) Of course, on the line (Aq = 0, A2) ferromagnetic states give always ground states. Dashed lines indicate the regions where the type of mean field state with lowest energy changes qualitatively. The red (dashed-dotted) line gives the values of (A2, A4) which can be obtained by changing the spin-independent scattering length co = (3g4 + 4g2)/7 through optical Feshbach resonances. [175\[177]. Black and white circles indicate a change of co of 10% and 100%, respectively.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/69199186/figure_026.jpg)


![Figure 27. (Color online, see [135]). Optical lattice setup for U(2) gauge fields: Red and blue open semi-circles (closed semi-circles) denote atoms in states |gi) and |g2), respectively (\e1) and |e2)). Left) Hopping in the x-direction is laser assisted and allows for unitary exchange of colors; it is described by the same unitary hopping matrix Uz, for both |g;) and |e;) states. Hopping along the y-direction is also laser assisted and attains “spin dependent” phase factors. Right) Trapping potential in y-direction. Adjacent sites are set off by an energy A due to the lattice acceleration, or a static inhomogeneous electric field. The lasers 1; are resonant for transitions |g1;) < |e2;), while Qe; are resonant for transitions between |e1;) < |g2i) due to the offset of the lattice sites. Because of the spatial dependence of 21,2 (running waves in + direction) the atoms hopping around the plaquette get the unitary transformation U = Ul (m U2 Uy(m + 1)UL, where U,.(m) = exn(2zim, diaglai.ao]). as indicated in the left Gieure (from [135l).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/69199186/figure_029.jpg)
![Figure 28. (Color online). The Hofstadter “moth” spectrum. Forbidden eigenenergies € are plottec versus a; = pi/qi,€ [0, = 0.5] (¢ = 1,2), where gq; < 41 and ai ¥ az (from [135]).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/69199186/figure_030.jpg)

![Figure 32. Schematic representation of the gate operation. Solid and dashed lines represent potentials felt by the atoms in the different internal states, respectively. By shifting the potentials. the pair of atoms in the middle experiences a collisional shift (from [31])](https://figures.academia-assets.com/69199186/figure_034.jpg)








![in this paper we consider a class of 1/2 BPS states that arises very naturally in the study of the AdS/CFT correspondence for maximally supersymmetric theories. These states wre associated to chiral primary operators with conformal weight A = J, where J isa yarticular U(1) charge in the R-symmetry group. For small excitation energies J < N shese BPS states correspond to particular gravity modes propagating in the bulk [I]. As yne increases the excitation energy so that J ~ N one finds that some of the states can »e described as branes in the internal sphere [2] or as branes in AdS [3]. These were called “giant gravitons”. As we increase the excitation energy to J ~ N? we expect to ind new geometries. The BPS states in question have a simple field theory description in erms of free fermions [4] (see also [5}). In a semiclassical limit we can characterize these states by giving the regions, or “droplets”, in phase space occupied by the fermions. We ‘an also picture the BPS states as fermions in a magnetic field on the lowest Landau evel (quantum Hall problem). In this paper we study the geometries corresponding to hese configurations. These are smooth geometries that preserve 16 of the original 32 supersymmetries. We are able to give the general form of the solution in terms of an squation whose boundary conditions are specified on a particular plane. We can have two sypes of boundary conditions corresponding to either of two different spheres shrinking on this plane in an smooth fashion. This plane, and the corresponding regions are in lirect correspondence with the regions in phase space that were discussed above. Once she occupied regions are given on this plane, the solution is determined uniquely and the ‘en (or eleven) dimensional geometry is non-singular and does not contain horizons. Figure 1: Droplets representing chiral primary states. In the field theory description these are droplets in phase space occupied by the fermions. In the gravity picture this is a particular two-plane in ten dimensions which specifies the solution uniquely. In (a) we see the droplet corresponding to the AdS x S ground state. In (b) we see ripples on the surface corresponding to gravitons in AdS x S. The separated black region is a giant graviton brane which wraps an S® in AdS; and the hole at the center is a giant graviton brane wrapping an S® in $°. In (c) we see a more general state.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/40001952/figure_001.jpg)
![Figure 2: Plane wave configurations correspond to filling the lower half plane. This can be understood from the fact that the plane wave solution is a limit of the AdS x S solution. ae u.—tCO — “ variables. Our approach leads to a simple way of constructing non-singular geometries. We have also performed a similar analysis for the M-theory case, which corresponds to giant gravitons in AdS, x S” or AdS7 x S*. In this case we have similar droplets, and the 11 dimensional geometry is obtained after solving a three dimensional Toda equation. In this case we could only solve the equations explicitly in very simple examples. We also consider the M-theory plane wave. In this way we could find geometries that are dual to the BMN matrix model [13]. In particular, we find more evidence that the M5 brane emerges as a state of the BMN matrix model [I4].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/40001952/figure_002.jpg)
![[his equation is analyzed using techniques similar to the ones developed in {25} {19} [20]. Jne first writes the ten dimensional spinor as a product of four dimensional spinors and spinors on the spheres. Due to the spherical symmetry the problem reduces to a four limensional problem involving a four dimensional spinor. One then constructs various orms by using spinor bilinears. These forms have interesting properties. For example, we ‘an construct a Killing vector, which we assume to be non-zero. This is the translation renerator, A — J. There is another interesting form which is a closed one form. This ‘an be used to define a local coordinate y. This coordinate y is rather special since one ‘an show that y is the product of the radii of the two S%s. By analyzing the Killing pinor equations one can relate the various functions appearing in the metric to a single unction. This function ends up obeying a simple differential equation. We present the letails of this analysis in appendix A. The end result is: where 7 = 1,2 and x3 is the flat space epsilon symbol in the three dimensions parameter- ized by y, %1,%2. We see that the full solution is determined in terms of a single function z. This function obeys the linear equation](https://figures.academia-assets.com/40001952/figure_003.jpg)












![Figure 1: The thermal rest mass (or energy) Myes; and the kinetic mass Min of a quark immersed in the NV =4 plasma at temperature T, as functions of the zero-temperature mass m, with all masses measured in units of Am(T) = svAT. At m = 0.92 Am(T), the location of the D7-brane jumps discontinuously to the horizon [41-44].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/1513060/figure_001.jpg)






















![Figure 1. Upper limits on the spin-independent (SI) elastic dark matter-nucleon cross-section as a function of mass of the dark-matter particle. The figure is reproduced from [113].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/64072079/figure_001.jpg)
![ass of the disk is estimated as Mg = Mx + Megas, where M,. and Megas are the total mass in stars nd gas, respectively. M., is estimated as M, = Y,,L, where L is the total disk luminosity and Y,, is a onstant mass-to-light ratio. Mgas is given by 1.4Myy, where Mjy is the total estimated mass of neutral ydrogen and the factor 1.4 is the standard correction to account for helium and metals. The black solid ne shows an unweighted linear fit to the points with stellar mass estimated in the I-, H-, and K’-bands he B-band data are not included in the fit because this band is not a robust indicator for the stellar 1ass. The slope of this straight line is b = 3.98 £0.12. Figure 2. Baryonic Tully-Fisher Relation (BTFR): total baryonic disk mass of galaxies against the rotation velocity V.. Circles and squares represent the data derived from [138] (red), [139] (black), [137,142] (green), [140] (light blue) and [141] (dark blue). The black solid line shows an unweighted linear fit. The figure is reproduced from [125].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/64072079/figure_002.jpg)
![Salpeter . where Y; is the mass-to-light ratio provided by the Salpeter IMF and x ~ 3/4 Figure 3. Mass-Discrepancy Acceleration Relation (MDAR), where the galaxy mass discrepancy, the squared ratio between the observed velocity V and the velocity due to baryons Vj, is plotted against the Newtonian centripetal acceleration gn = Ve/ R derived from the observed baryonic surface mass density. The black dots show several hundreds of individual resolved measured points from the rotation curves of almost one hundred spiral galaxies. The figure is reproduced from [149]. the squared ratio between the observed velocity V and the velocity due to baryons V,, is plotted For both the BTFR and the MDAR, the scatter depends on the value of the adopted mass-to-light ratio [146]. Specifically, the intrinsic scatter in both relations is minimized by the same mass-to-light ratio, consistent with SPS models [146]. Intriguingly, when we use MOND (Section 5.1) to describe the rotation curves [146,147], the required mass-to-light ratio approximately coincides with the best mass-to-licht ratio predicted bv the SPS model based on a scaled Salneter IMF [148]](https://figures.academia-assets.com/64072079/figure_003.jpg)
![Figure 4. Radial Acceleration Relation (RAR), the observed centripetal acceleration versus the Newtonian acceleration due to baryonic matter alone. The blue color-scale rectangles show 2694 individual measured points from the rotation curves of 153 SPARC galaxies. The red solid line is the fitted RAR given by Equation (4), whereas the black dotted line represents the one-to-one relation, for comparison. The figure is reproduced from [129].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/64072079/figure_004.jpg)
![Figure 5. Rotation curve (left panel) of UGC 5750 (the LSB galaxy, showed in the right panel). The data of the rotation curve are obtained with the integrated field Ha spectroscopy (squares) [197], long slit optical observations of the Balmer transition (circles) [193,198], and radio observations of the 21 cm atomic hydrogen spin flip transition (stars) [199]. The isothermal sphere with a core (CIS) profile (solid line) fits the data. r,(zero) and r-(max) are the values of the core radius obtained from the fit in the no disk and maximum-disk case, respectively; the solid line is the case of no disk. Neither the NFW profile (dashed line), whose parameters are fixed and given by the ACDM cosmology, nor the singular isothermal sphere (SIS) profile can describe the dark-matter halo of this LSB galaxy. The figure is reproduced from [200]. The NFW density profile is too steep to fit the observations in the innermost regions of the dwarf and LSB galaxies [140,190]: the observations favor a density profile with a core [191-196]. Figure 5 shows an example of how well a density profile with a core (black solid line) fits the measured rotation curve of the LSB galaxy UGC 5750. Neither the NFW profile (long-dashed line) nor the singular isothermal sphere (SIS, dotted line) can fit the measured rotation curve.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/64072079/figure_005.jpg)
![Figure 13. The giant plane of Andromeda (GPoA) and the Andromeda (M31) disk (solid black ellipse at the center) as viewed from the Sun. The orientation and the width of the best-fit satellite plane are indicated by the dashed and dotted lines, respectively. The colored triangles, red upward (blue downward) for receding from (approaching towards) an observer at rest with respect to the host galaxy, indicate coherent kinematics of the co-orbiting satellites. The satellites that are not part of the GPoA are plotted as open triangles whose orientations, upward for receding, indicate their line-of-sight velocities. The grey area corresponds to the region outside the Pan-Andromeda Archaeological Survey. The figure is reproduced from [325]. by the dashed and dotted lines, respectively. The colored triangles, red upward (blue downward)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/64072079/figure_013.jpg)
![Figure 12. Edge-on view of the vast polar structure (VPOS) (solid black line at the center). The orientation and the width of around the Milky Way and the disk the best-fit satellite plane are indicated by the dashed and dotted lines, respectively. The colored triangles, red upward (blue downward) for receding from (approaching towards) an observer at rest with respect to the host galaxy, indicate coherent kinematics of the co-orbiting satellites. The satellites with no proper motion measurements are plotted as crosses. The grey area corresponds to the region 4 -12° from the Milky Way disk which is obscured by galactic foreground. The figure is reproduced from [325]. by the dashed and dotted lines, respectively. The colored triangles, red upward (blue downward)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/64072079/figure_012.jpg)
![Figure 21. The current constraints on QCD axions and ALPs. The yellow band represents the various models of QCD axions. The constraints from the Sun and the Horizontal Branch stars are the regions above the corresponding lines. The regions ruled out by various experiments are indicated by the colored areas. The figure is reproduced from [113]. Figure 21. The current constraints on QCD axions and ALPs. The yellow band represents the various](https://figures.academia-assets.com/64072079/figure_021.jpg)
![Figure 6. Projected velocity dispersion profile of the eight brightest dwarf satellites of the Milky Way. The red lines represent the best fit of the dark-matter density distribution with a core, while the blue ones derive from a cuspy profile. The long-dashed and dotted lines show the isothermal and power law models, respectively. The figure is reproduced from [51,207]. dark matter, such as NGC 1052-DF2 and NGC 1052-DF4 [220-225], can challenge the standard CDM paradigm. Specifically, galaxies such as DF2 and DF4 appear to be at 2.60 and 4.1¢ tension with the standard model, respectively: according to ACDM simulations, the probability of finding DF2-like galaxies at a distance 11.5 Mpc from the observer is at most 10~*; this proba at a distance 20.0 Mpc [188]. However, more accurate dynamical models can substantially alleviate this tension [226-228]. In addition, a recent analysis [229 rather 20 Mpc, as previously estimated; the closer distanc the galaxy mass. Similarly, properly taking into account t of the small sample of globular clusters of DF2 suggests t the distribution of the mass-to-light ratios of dwarf galaxi are still consistent with the universal mass profile of the e increases to 75% t hat its mass-to-ligh’ Local Group dwarf bility drops to 4.8 x 1077 suggests that the distance to DF2 is 13 Mpc he dark-matter content of he uncertainty on the velocity measurements ratio is at the low end of es [230], but its velocity dispersion and mass galaxies [51].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/64072079/figure_006.jpg)
![Figure 7. Left panel: Projected dark-matter distribution (600 kpc ona side) of a 10!2 Mg dar -matter halo from the ELVIS ACDM simulations [56]. The number of small subhalos strongly exceeds the number of known Milky Way satellites (missing satellites problem; Section 3.3). The circles high ight the nine most massive subhalos. Right panel: Spatial distribution of the closest nine of the 11 most luminous (classical) satellites of the Milky Way (the diameter of the outer sphere is 300 kpc). For these satellites, the central mass inferred from stellar kinematics is a factor of ~5 lower than the mass predicted for the central regions of the subhalos highlighted in the left panel, preventing the association of the classical satellites to the most massive subhalos of the dark-matter halo of Milky Way-like galaxies (too-big-to-fail problem; Section 3.4). The figure is reproduced from [115].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/64072079/figure_007.jpg)
![Figure 8. Abundance matching (AM) relations from the models by Behrooz [268], Garrison-Kimmel GK14 [269], Garrison-Kimmel GK16 [267], Moster [270], and Brook [271]. The solid lines show the models in a region of the parameter space where observational data are available; the dashed lines show the extrapolation of the models where the observational information is missing. The orange shaded area show the 1¢ log-normal scatter around the model GK16. The figure is from [272]. mechanism in the models make the estimation of the stellar mass uncertain and, consequently, the AM relation less constrained: for example, a stellar mass M., ~ 10° Mo would correspond to Mhalo ~ 10? Mo for the Behroozi model, but to Mnalo ~ 5 X 10? Me for the Brook model. These differences translate into an additional uncertainty on the number of low-mass satellites in the Local Group. This uncertainty is further increased by the fact that this halo mass, Mnalo © 10°Mo, is close to the mass scale, +108 M, below which star formation is expected to be suppressed.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/64072079/figure_008.jpg)
![Figure 9. Mean number of satellite galaxies with mass larger than a given stellar mass threshold, Neats (> M,.), as a function of the threshol dark-matter halo with virial mass Mpaio = d mass, M,, around a Milky Way-sized galaxy hosted by a 1.4 x 10!2 Mo, as predicted by various AM models applied to the dark-matter-only Caterpillar simulations. The colored dashed lines indicate the predictions of the AM models shown in Figure 8; the so inclusion of reionization that suppresses t the prediction of 37-114 satellites with ste id lines show the predictions of the same models after the he formation of low-mass galaxies. The grey box represents lar luminosity L, > 103Lo by [273], derived by combining several toy models applied to dark-matter-only simulations with the sample of dwarfs corrected for completeness, observed by the Sloan cumulative stellar mass function (derived Digital Sky Survey. For comparison, the complementary from V-band luminosities, assuming a mass-to-light ratio equal to 1 Mo /Lo) of the 40 known satel with a black dashed line. The figure is rep present in the label of the ordinate axis of ite galaxies of the Milky Way with M, > 10° Mo is shown roduced from [272]. Here, we corrected the misprint that is the original figure.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/64072079/figure_009.jpg)
![Figure 10. Complementary cumulative subhalo mass function of the Milky Way satellites in a sphere of radius 280 kpc centered on the Gal axy. The mass function is derived from either the My — M200 AM relation (left panel) or the (SFR) — M299 AM relation (right panel). The peak masses before the infall are taken as the subhalos masses M299. The names of the individual galaxies used to build the complementary cumulative subhalo mass functions are indicated in the plots. The median relations are shown as blue solid lines, whereas the 4 +68% confidence intervals are delimited by the blue dashed lines. The green lines have the same meaning as the blue lines, but they also include the sample of ultra-faint dwarf galaxies of [178]. The grey shaded areas represent the variation of the complementary cumulative subhalo mass functions resulting from ten dark-matter-only “zoom-in” simulations of the Milky Way in the ACDM model. The red shaded areas have the same meaning as the grey shaded areas, but they include a model for the stellar disk of the Milky Way. The figure is from [257]. Here, we corrected the misprint that is present in the label of the ordinate axis of the original figure. Figure 10 shows the complementary cumulative subhalo mass function of a complete volume-limited sample of the bright Milky Way satellites within 280 kpc from the Galaxy center In the left panel, the subhalo mass function is derived from the M. — M209 AM relation, whereas the right panel shows the subhalo mass function based on the (SFR) — M299 AM relation [257] The complementary cumulative subhalo mass function based on the M,, — M299 relation (left panel) shows the existence of the MSP for masses Mx99 < 2 x 10?Mo: there are not enough quenched satellites, such as Sculptor and Leo I, in the Milky Way to be consistent with the predictions of the ACDM model. On the contrary, the complementary cumulative subhalo mass function based on the (SFR) — Moo9 AM relation (right panel) suggests that no MSP exists for masses above M99 ~ 10? Mo](https://figures.academia-assets.com/64072079/figure_010.jpg)
![Figure 11. Circular velocity profiles of simulated dark-matter subhalos compared to measured velocity dispersions of Milky Way dSph satellites to illustrate the too-big-to-fail problem in the Milky Way. Similar tensions are suggested by photometric observations alone. The systems of galaxies surrounding both M94 and M101 appear to contain galaxies that are substantially less massive than expected in the CDM framework. M94 is a group with a central Milky Way mass galaxy that displays only two satellites, each with mass M, < 10° Mo, instead of the ~10 satellites expected for similar systems [298]. The luminosity function of the galaxies of the M101 group is similar to the luminosity function of the Milky Way system, suggesting a similar lack of intermediate-mass galaxies [299]. In the ultra-faint dwarf galaxy regime, the M101 group also appears to exacerbate the MSP (see Section 3.3), by containing only half of the satellites of the Milky Way system [300].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/64072079/figure_011.jpg)
![Figure 22. Dark-matter halos in the FDM scenario. Left panel: dependence of the dark-matter density profile on the mass of the boson compared with the NFW profile. Here 1122 is the boson mass in unit of 10-22 eV. Right panel: an image displaying the soliton in the center of a galaxy with an interference pattern surrounding it. The figure is reproduced from [499]. Figure 22. Dark-matter halos in the FDM scenario. Left panel: dependence of the dark-matter density](https://figures.academia-assets.com/64072079/figure_022.jpg)
![Figure 14. The Centaurus A satellite plane (CASP) and the Centaurus A disk (dark grey circle at the center) as viewed from the Sun. The orientation and the width of the best-fit satellite plane are indicated by the dashed and dotted lines, respectively. The colored triangles, red upward (blue downward) for receding from (approaching towards) an observer at rest with respect to the host galaxy, indicate coherent kinematics of the co-orbiting satellites. The grey area show the volume outside the survey. The figure is reproduced from [325]. Milky Way. From our position, the CASP is seen almost edge-on and 14 out of 16 satellites that have line-of-sight velocity measures, are found to be co-rotating in the plane [324] (Figure 14). by the dashed and dotted lines, respectively. The colored triangles, red upward (blue downward)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/64072079/figure_014.jpg)
![Figure 15. Allowed parameter space of the currently most popular dark-matter candidates. The bottom axis shows the characteristic free-streaming wavenumber of the model, which is set in the primordial Universe. The top axis shows the corresponding halo mass, and the y-axis shows the characteristic interaction or decay rate which quantifies the evolutionary effects of dark matter. ADM, BEC, and FDM stand for Asymmetric Dark Matter, Bose-Einstein Condensate, and Fuzzy Dark Matter, respectively. The figure is from [370]. Ld 4 Figure 15 shows the allowed regions in the I — kg, parameter space for different dark-matte undidates. Deviations from the CDM paradigm arise when the gravitational collapse of dark matter hibited or modified above a characteristic comoving wavenumber. This wavenumber translates int characteristic halo mass below which the number of halos is reduced. Alternatively, the deviatior an be driven by the interactions of the dark matter particles with the Standard Model particle woughout the evolution of the Universe. Both effects can erase existing structures or change th elocity distributions of the dark matter particles and the densities of their structures. For WIMP hose decoupling temperature varies from 15 MeV to 1500 MeV and ky; ~ Ipc”! for my = 100 Ge ne gets a minimum halo mass of the order of ~[10~8-10~7] Mo. Sterile neutrinos, which are a wart ark-matter (WDM) candidate with mass ranging from 0.4 to 10° keV, have ky, ~ 0.5(my/keV) Mpc” hich translates into a minimum halo mass in the range Mhalo ~ [10-¢-10" | Mo. Similarly, gravitinc ad to Mpaio ~ [107 !7-10'4] Mo while their mass is set by the supersymmetry breaking scale which 1 the range 100 eV to 100 TeV. Fuzzy Dark Matter models also erase structures below the de-Brogl: avelength of the particle, of the order of the kiloparsec, which leads to a minimum halo mas Lalo ~ 101° © fora particle mass ~10-~ eV.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/64072079/figure_015.jpg)
![Figure 16. The allowed parameter space for sterile neutrinos obtained from the X-ray emission. The colored regions are 1, 2 and 30 confidence levels. Numbers from 1 to 9 mark the center of the 2¢ region detections obtained using nine galaxy clusters [386]. The lines show constraints at the 90% confidence level from Chandra [381], Suzaku [383] and dwarf galaxies dataset [382]. The stars represent several models of sterile neutrino. The figure is reproduced from [385]. setto My > /OU eV [o/o] Dy ftting the Lyman -a forest In quasar spectra. viore recent analyses of the Lyman-a forest and of the Milky Way satellites have increased the bound to several keV [374-377]. One of the most stringent bounds on the mass of WDM particles comes from the high-resolution HIRES/MIKE spectrographs: my, > 4.65 keV [378]. The most promising candidate of WDM is sterile neutrino, with mass ms, which is mixed with an ordinary neutrino [379,380]. For small mixing angles such as sin? 20 ~ 10~7, the total amount of sterile neutrinos is only a small fraction of the ordinary neutrinos. In Figure 16, we give a visual representation of the allowed parameter space for sterile neutrinos in the plane sin? 26 — m;. The claimed detections are based on the so-called 3.55 keV line emission, which is attributed to the decay of dark-matter particles, and are obtained by using Chandra X-ray observations of galaxies in the Local Group [381], studies on dwarf galaxies [382], and Suzaku observations of the Perseus galaxy cluster [383]. These investigations imply a sterile neutrino of mass ~7 keV and sin? (20) = [2,20] x 10-1". In contrast to these results, the full-sky Fermi Gamma-ray Burst Monitor data [384] do not reveal any significant signal for sterile neutrino decay lines in the energy spectrum, and improve previous upper limits by an order of magnitude (for a comprehensive review of sterile neutrino we refer the reader to [385]). The colored regions are 1, 2 and 30 confidence levels. Numbers from 1 to 9 mark the center of the](https://figures.academia-assets.com/64072079/figure_016.jpg)
![Figure 17. Left panel: comparison of the linear matter power spectrum as a function of wavenumber in the WDM and CDM scenarios. The solid black line shows the CDM model. The dot-dashed lines represent the WDM power spectra for different values of the particle mass. Right panel: density profiles of CDM and WDM halos with mass: M = 10? Mo. The black line shows the CDM profile; the red, green, blue, cyan, and magenta lines show the WDM profiles for particle mass 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1.0, and 1.25 keV, respectively. The solid colored lines show the case where there are no thermal relic velocities; the dot-dash lines denote the case where it is assumed the existence of a relic thermal velocity distribution for the WDM particles. In the panel, it is indicated the scale radius of the halo for the various WDM particle mass considered. The figure is reproduced from [371]. = V In addition, the gravitational collapse leads to a cuspy halo profile with a lower central concentration compared to CDM halos [371]. This feature is shown in the right panel of Figure 17, where the NFW profile (black solid line) is compared with the cuspy WDM density distribution (solid colored lines) for a halo with a mass of M = 10? Mz. Moreover, the existence of a relic thermal velocity distribution for the WDM particles may convert the cusp in the density profile into a core (dot-dashed colored lines), providing a solution to the CCP [395]. Nevertheless, the cores appear to be smaller than required to explain the data on LSB galaxies [396,397].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/64072079/figure_017.jpg)
![Figure 18. Inner density profile of a dark-matter halo with Mpaio = 0.9 x 10!° Mz in collisionless CDM and in SIDM for different values of 7/m. The figure is reproduced from [414].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/64072079/figure_018.jpg)
![Figure 19. Observed rotation curves of four disk galaxies. Solid red lines indicate the total rotation curves for SIDM with 7/m = 3 cm?/ g which include contributions from the dark-matter halo (solid blue), stars (magenta dashed), and gas (magenta dot-dashed). The corresponding CDM halos (dashed blue) and SIDM halos (blue stars) neglecting the baryons are also shown. The concentration parameters C299 are indicated in terms of the standard deviation from the median cosmological concentration of halos of mass M09. The figure is reproduced from [410,429]. = In addition, if baryonic effects are taken into account by the Jeans method, SIDM may solve the issues related to the disk-halo conspiracy [428] (see Section 3.1), i.e., it can reproduce diverse inner rotation curves from a single value of 7/m for galaxies with similar maximum rotation speed Vmax [429,430] (see Figure 19). Collisionless CDM, even with baryonic feedback, does not solve this issue because of the large dark-matter density in the central region. Thanks to the smaller dark-matter density provided by the SIDM scenario, the baryons are more effective at setting Vmax.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/64072079/figure_019.jpg)
![Figure 20. Parameter space spanning the mass my, of the SIDM particle and the vector mediator mass my with self-coupling a, = «a = 1/137. Regions preferred by dwarfs (red), LSB spiral galaxies (blue) and galaxy clusters (green), each at 95% confidence level, are indicated. Combined 95% (99%) region is shown by the solid (dashed) contour. The region estimated to be excluded by the Bullet Cluster (other observed merging clusters) lies below the dot-dashed (long-dashed) curve. The figure is reproduced from [427].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/64072079/figure_020.jpg)
![Figure 23. Left panels: best-fit models (blue lines) of the velocity dispersion profile in the FDM scenario for a sample of Milky Way dwarf satellites. Right panels: corresponding core radius-mass relation for each dwarf galaxy sampled from the posterior distribution. The figures are from [502].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/64072079/figure_023.jpg)
![Figure 24. Dependence of the cut-off of the halo mass function on the mass of an FDM particle, and comparison with the CDM model. The figure is reproduced from [508].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/64072079/figure_024.jpg)
![constrained by the dSphs galaxies (colored data points) and by the more massive galaxies in the THINGS catalogue (black lines) [619]. Figure 25. Galaxy rotation curves from the THINGS catalogue fitted with MOG. The best fits are shown as black lines. The figure is reproduced from [603].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/64072079/figure_025.jpg)

![Although rotation curves are well accommodated in f(R)-gravity, there is a lack of studies of pressure-supported systems such as dwarf galaxies. Nevertheless, due to the similarities between the gravitational potential in f(R)-gravity and in MOG (see Equation (24) in Section 5.2), one may expect to encounter difficulties similar to MOG to explain the dynamics of dwarf galaxies, and to provide a solution to the CCP. It is worth mentioning that the possibility that these systems might not be in dynamical equilibrium in the context of these theories may invalidate the constraints [657-659]. ay: W nT 1 . CrP ft TRnN ee 1 wa va 1 ee a ee 1 v7](https://figures.academia-assets.com/64072079/figure_027.jpg)
![Table 1. Summary of whether alternative dark matter (DM) and gravity models either solve or do not display the challenges of the CDM model discussed in this work. Here, we refer to a problem as “solved” when the model does not currently display major tensions with the observations. The ability of the models to explain the large-scale structure of the Universe is also included. WDM, SIDM, ALPs, and FDM, discussed in Section 4, allow the existence of a dark-matter core in dwarf galaxies, hence, providing, in principle, a solution to the CCP. Moreover, WDM and FDM show a cut-off in the matter power spectrum that suppresses the formation of halos below a given mass threshold [395,475]. However, WDM does not alleviate any of the CDM issues at galactic scale when the constraints from the Lyman-a forest or the gravitational lensed quasars are taken into account. The cores in the WDM halos are indeed too small to solve the CCP, although they might contribute to fix the TBTF problem. It thus remains unclear whether WDM models may represent a viable solution [372]. SIDM solves the CCP, but its ability to solve the MSP and PSP requires further investigations that take into account the baryonic feedback. QCD axions are highly motivated dark-matter candidates from the perspectives of both particle physics and cosmology. However, whether they can solve the small-scale issues of CDM has not been properly investigated yet, because the role of the quantum nature of hermalizing QCD axions on cosmic small scales demands a more rigorous theoretical framework. Finally, FDM also encounters its own difficulties. The boson mass, ~10722 eV, required to explain the dynamics of the dwarf galaxies and to solve the CCP and the MSP is almost two orders of magnitude ower than the boson mass, ~7 x 10~2! eV, needed to account for the Lyman-e« data [511]. Nevertheless, he debate is far from being settled [493]. Uncertainties on the thermal histories and the underlying reionization model may invalidate these constraints [515,666] Although the CCP and MSP may usually be solved in paradigms beyond the standard model of](https://figures.academia-assets.com/64072079/table_001.jpg)


![Then, the integral can be evaluated approximately as [37]:](https://figures.academia-assets.com/38519061/figure_003.jpg)
