An account is given of the development of the SHELX system of computer programs from SHELX-76 to the present day. In addition to identifying useful innovations that have come into general use through their implementation in SHELX, a... more
Map interpretation remains a critical step in solving the structure of a macromolecule. Errors introduced at this early stage may persist throughout crystallographic refinement and result in an incorrect structure. The normally quoted... more
Graphene has been attracting great interest because of its distinctive band structure and physical properties. Today, graphene is limited to small sizes because it is produced mostly by exfoliating graphite. We grew large-area graphene... more
We have developed and implemented a self-consistent density functional method using standard norm-conserving pseudopotentials and a flexible, numerical LCAO basis set, which includes multiplezeta and polarization orbitals. Exchange and... more
Researchers have realized optically and electrically driven mid-infrared (MIR) light-emitting devices in a simple but novel van der Waals (vdW) heterostructure constructed from thin-film black phosphorus (BP) and transition-metal... more
Carbon nanotube science is a new exciting subject for all the carbon community. We now have in hand 1D graphite prototypes opening a new field for basic research and increasing the technological potential of traditional carbon fibers. In... more
We have achieved mobilities in excess of 200,000 cm 2 V −1 s −1 at electron densities of ∼2×10 11 cm −2 by suspending single layer graphene. Suspension ∼150 nm above a Si/SiO2 gate electrode and electrical contacts to the graphene was... more
An algorithm is presented for carrying out decomposition of electronic charge density into atomic contributions. As suggested by Bader [R. Bader, Atoms in Molecules: A Quantum Theory, Oxford University Press, New York, 1990], space is... more
A new mechanism is proposed for exciting the magnetic state of a ferromagnet. Assuming ballistic conditions and using WKB wave functions, we predict that a transfer of vectorial spin accompanies an electric current flowing perpendicular... more
Abstract In spite of intrinsic limitations, neutron powder diffraction is, and will still be in the future, the primary and most straightforward technique for magnetic structure determination. In this paper some recent improvements in the... more
A quantum phase transition from a superfluid to a Mott insulating ground state was observed in a Bose-Einstein condensate stored in a three-dimensional optical lattice potential. With this experiment a new field of physics with ultracold... more
It is generally accepted that the functional compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells is reflected by the differential occurrence of proteins in their compartments. The location and physiological function of a protein are closely related;... more
Graphene - a monolayer of carbon atoms densely packed into a hexagonal lattice - has one of the strongest possible atomic bonds and can be viewed as a robust atomic-scale scaffold, to which other chemical species can be attached without... more
We present in this work a novel application of constant pressure molecular dynamics method (MD) that allows shape variation of MD cells. The new pressostat method, based on metric-tensor flexiblecell algorithm that has patched the... more
We review the recent fast progress in statistical physics of evolving networks. Interest has focused mainly on the structural properties of random complex networks in communications, biology, social sciences and economics. A number of... more
We have fabricated a new type of composite which displays localized sonic resonances at B350-2000 Hz with a microstructure size in the millimeter to centimeter range. Around the resonance frequencies the composite behaves as a material... more
Molecular dynamics simulations based on self-consistent-charge density-functional tight-binding (SCC-DFTB) energies indicate that upon a single molecular TiO 2 impact onto the amorphous TiO 2 surface the resulting structure becomes more... more
A second-generation potential energy function for solid carbon and hydrocarbon molecules that is based on an empirical bond order formalism is presented. This potential allows for covalent bond breaking and forming with associated changes... more
s Abstract Comparative modeling predicts the three-dimensional structure of a given protein sequence (target) based primarily on its alignment to one or more proteins of known structure (templates). The prediction process consists of fold... more
We review the phenomenology of exchange bias and related effects, with emphasis on layered antiferromagnetic (AFM)-ferromagnetic (FM) structures. A compilation of materials exhibiting exchange bias and some of the techniques used to study... more
We have investigated the lowest binding-energy electronic structure of the model cuprate Sr2CuO2Cl2 using angle resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES). Our data from about 80 cleavages of Sr2CuO2Cl2 single crystals give a... more
The density functional theory (DFT) computation of electronic structure, total energy and other properties of materials, is a field in constant progress. In order to stay at the forefront of knowledge, a DFT software project can benefit... more
Consolidated tables showing an extensive listing of the highest independently confirmed efficiencies for solar cells and modules are presented. Guidelines for inclusion of results into these tables are outlined and new entries since July... more
Uniform, spherical-shaped TiO 2 :Eu nanoparticles with different doping concentrations have been synthesized through controlled hydrolysis of titanium tetrabutoxide under appropriate pH and temperature in the presence of EuCl 3 ·6H 2 O.... more
In this paper we report the optical studies of single wall carbon nanotubes dispersed in biomaterials. We have obtained very stable suspensions of SWNTs, which allowed us to get good photoluminescence signal from the individually... more
Consolidated tables showing an extensive listing of the highest independently confirmed efficiencies for solar cells and modules are presented. Guidelines for inclusion of results into these tables are outlined and new entries since... more
Undoped silicon nanowire (Si NW) field-effect transistors (FETs) with a back-gate configuration have been fabricated and characterized. A thick (200 nm) Si3N4 layer was used as a gate insulator and a p++ silicon substrate as a back gate.... more
Titanium oxide nanotubes were fabricated by anodic oxidation of a pure titanium sheet in an aqueous solution containing 0.5 to 3.5 wt% hydrofluoric acid. These tubes are well aligned and organized into high-density uniform arrays. While... more
The design, synthesis and complete characterization of a smart material composed of single-walled nanotubes functionalized with spiropyran-based photo switchable molecules are reported. The chemical complexity of the system requires the... more
A new metal-organic vapor-phase epitaxial (MOVPE) reactor-cell design has been developed to grow on 3-in.-diameter substrates. This was required to produce uniform, fully doped heterostructures needed for array producibility and... more
In this work, we present a theoretical study of the transport properties of two finite and parallel armchair graphene nanoribbons connected to two semi-infinite leads of the same material. Using a single π -band tight binding Hamiltonian... more
In this report we review the fundamentals, applications and future tendencies of dynamic atomic force microscopy (AFM) methods. Our focus is on understanding why the changes observed in the dynamic properties of a vibrating tip that... more
Liposomes, sphere-shaped vesicles consisting of one or more phospholipid bilayers, were first described in the mid-60s. Today, they are a very useful reproduction, reagent, and tool in various scientific disciplines, including mathematics... more
The program system MOLCAS is a package for calculations of electronic and structural properties of molecular systems in gas, liquid, or solid phase. It contains a number of modern quantum chemical methods for studies of the electronic... more
Very stable, high quality electron beams (current ~ 10 kA, energy spread < 1%, emittance ~ 1π mm mrad) have been generated in a laser-plasma accelerator driven by 25 TW femtosecond laser pulses.
A practical method for finding free energy barriers for transitions in high-dimensional classical and quantum systems is presented and used to calculate the dissociative sticking probability of H 2 on a metal surface within transition... more
We review the various ways in which an electron beam can adversely affect an organic or inorganic sample during examination in an electron microscope. The effects considered are: heating, electrostatic charging, ionization damage... more
Electronic structure calculations have become an indispensable tool in many areas of materials science and quantum chemistry. Even though the Kohn-Sham formulation of the density-functional theory (DFT) simplifies the many-body problem... more
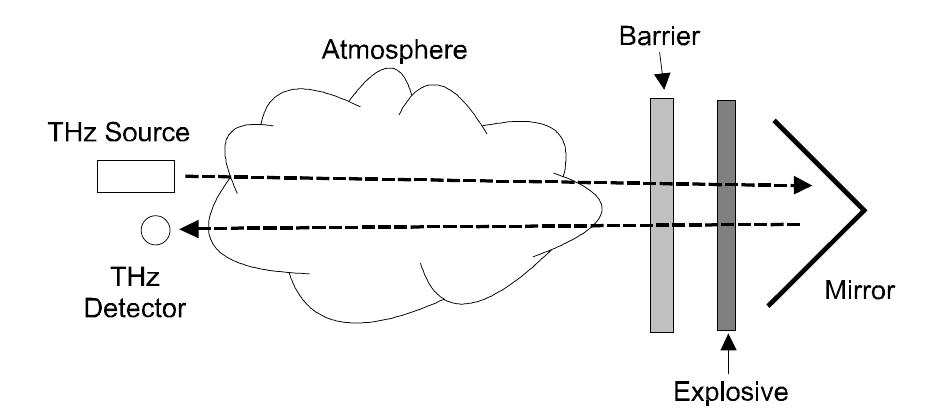
Over the past 5 years, there has been a significant interest in employing terahertz (THz) technology, spectroscopy and imaging for security applications. There are three prime motivations for this interest: (a) THz radiation can detect... more
Electron micrographs showed that dengue virions are characterized by a relatively smooth surface, with a diameter of approximately 500 Å , and an electron-dense are three structural proteins that occur in stoichiometric 1 Department of... more
The polarization behavior of zirconia-yttria solid electrolyte specimens with platinum electrodes has been studied over a temperature range of 400° to 800°C and a wide range of oxygen partial pressures. The complex admittance of these... more



![According to the Fowler Nordheim theory (F-N theory, i.e., elastic tunneling through a triangular barrier, with the electron distribution described by Fermi-Dirac statistics [22]), the energy distribution oof the emitted electrons is Jpn(E) « exp((E - E-)/b(F/o!/2))£(E - Ep), where E is the electron energy, E¢ the Fermi energy, @ the work function, F the electric field, and f(E) the Fermi-Dirac distri- bution. We show in Fig. 4(a) a field electron energy spectra obtained on a MWNT film, along with the best fit obtained with the F-N distribution. Obviously, the distribution doesn’t match the measured spectra. The F-N theory predicts exponential slopes or both sides of the distribution which arise from the tail of the Fermi-Dirac distribution and from the increase of the barrier width, respectively.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/51065352/figure_004.jpg)




![Fig. 1. Plot of the profile matching result, refinement without structural model, obtained for the oxide Co, TeOQ,. The satellites (second row of reflection markers) are broadened and have a lorentzian shape with a propagation vector [0 08] with 5 ~ 0.08 (see ext). J. Rodriguez-Carvajal ! On magnetic structure determination by neutron powder diffraction](https://figures.academia-assets.com/42419907/figure_001.jpg)



![Fig. 5. Comparison between the low-angle portions of the neutron diffraction patterns, at 1.5K on D1B, of two different samples of CsMnF,. Two symmetry-unrelated propagation vectors, k, = [0065] and k, = (00 4], are present in both cases. course of analysis from the point of view of the involved physics [29]. Here we shall be inter- ested only in the problem of magnetic structure refinement. The compound was described as a planar ferromagnet [30] and belongs to the space group P4/n. The crystal structure is very simple 29,30] and has MnF, octahedra forming perov- skite layers (of composition MnF,) separated by Cs” ions. There is no Mn—F—Mn superexchange path between layers. Due to the Jahn-Teller effect of Mn*~ and the antiferrodistorsive orbital ordering within the perovskite layers, the in- plane Mn-F—Mn exchange is ferromagnetic and much more intense than the interaction between adjacent layers. The weakness of this later inter- action and, probably, the existence of structural defects perturbs the ferromagnetic ground state causing a more complex magnetic structure. Two different prepared samples [29] have been studied. In fig. 5 a comparison between the low angle portions of their neutron diffraction pat- ferns, at 1.5K on D1B, is presented. One can observe that two symmetry-unrelated propaga- ion vectors, k,=[006] and k,=[004], are present in both cases. From the figure it is deduced that (k,, —k,) and k, are correlated. In fig. 6 is presented the low-angle part of the profile refinement using the above models. The resulting magnetic structure corresponds to a perturbed helix described by the formula given](https://figures.academia-assets.com/42419907/figure_005.jpg)



![Figure 1. (a) [Zn,O] SBU. The carboxylic acid used in the synthesis of (b) MOF-S and (c) MOF-177. The structures of (d) MOF-S and (e) MOF-177.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/41908621/figure_002.jpg)


![Figure 5. Various ligands used in the synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. Figure 4. Two different frameworks formed from Zn(II) and NTB*~ in the different solvent systems. (a) A doubly interpenetrated PdF, struc- ture of [Zn,O(NTB)>],,°3nDEF-nEtOH produced from DEF/EtOH/H,O (5:3:2, v/v) mixture.’* (b) The framework structure of [Zn3(NTB)>(EtOH),],,-4nEtOH produced from EtOH.”](https://figures.academia-assets.com/41908621/figure_005.jpg)



















![Figure 25. The X-ray structures of NOTT-200 (left) and NOTT-201 (right).°” The Hyppz~* dications in the channel B of NOTT-200 can be completely exchanged with Li* ions in the channel C of NOTT-201. Color code: In, violet; Li, green; C, gray; N, blue; O, red; H, white. Among heterocyclic azolate-based frameworks, Mn-BTT, Mn3[(Mn,Cl)3(BTT)3(CH30H) 0], exhibited the highest sur- face area, H, uptake capacity, and isosteric heat of Hy adsorp- tion.** The X-ray crystal structure indicates that the chloride- centered square-planar [Mn,Cl]’* units are linked with eight trigonal planar BTT?~ ligands to form the anionic, three-dimens- ional sodalite-type framework. The solvent molecules occupy the sixth coordination site on each Mn7* ion, while charge balance is provided by Mn complexes. The desolvated Mn-BTT, which contains open metal sites, exhibited a BET surface area of 2100 m* g ', excess (total) H adsorption capacity of 5.1 wt % (6.9 wt %) at 77 K and 90 bar, and high zero-coverage isosteric heat of H, adsorption, 10.1 kJ mol’. On the contrary, [Mn(DMF)g]3[(Mn4Cl)3(BTT)s(DMEF) 3], which is the iso- morphous framework where all Mn** ions are coordinatively saturated with DMF molecules shows much lower zero- coverage enthalpy of H) adsorption, 7.6 kJ mol '. It adsorbs only total 3.9 wt % of Hy at 77 K and SO bar. These values indicate strong H) adsorption sites are available in Mn-BTT, which do not exist in [Mn(DMF).]3[(Mn,Cl)3(BTT)<- (DMBP),]2. The neutron powder diffraction study reveals that this is directly related to H, binding at coordinatively unsaturated Mn” centers with a distance of 2.27 A. The isostructural sodalite frameworks, HCu[(Cu,Cl)3(BTT)s]+3.SHCl (Cu-BTT)*”* and Fe3[(Fe4Cl)3(BTT)g(MeOH),], (Fe-BTT),””! also showed high zero-coverage H binding enthalpy, 9.5 and 11.9 kJ mol (, respectively. The strongest binding site is located just 2.47 and](https://figures.academia-assets.com/41908621/figure_026.jpg)






![Figure 32. SNU-3 with embedded Pd nanoparticles. (a) FE-TEM image, (b) X-ray photoelectron spectrum, (c) EPR spectrum (powder, measured at 173 K), and (d) IR spectrum, for 3 wt % PdNPs@[SNU-3]°***(NO* )o.54. Reproduced with permission from ref 134. Copyright 2009 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/41908621/figure_033.jpg)



![Figure 37. (a) Structure of IRMOF-77. Atom colors: blue tetrahedron, Zn; purple, I; orange, Pd; red, O; blue sphere, N. (b) Synthesis and representative structure of MOF-253. Post synthetic insertion of PdCl, into free bpy ligand sites. Atom colors: orange, yellow, green, red, blue, and gray spheres represent octahedral Al, Pd, Cl, O, N, and C atoms, respectively. Reproduced with permission from ref 329 and 330. Copyright 2010 American Chemical Society. Figure 38. Schematic representation of generating open metal sites in the ligand part: postsynthetic reaction of [Zn.(TCPB)(DPG)] with succinic anhydride followed by the Cu chelation.**"](https://figures.academia-assets.com/41908621/figure_037.jpg)
![Figure 36. Schiff base complexes used in the synthesis gf (a) [Zn;(OH)>(L“),]-2DME,°*** (b) [Cu,(pzde),L(H,0)]- 4H,0,°* (« [Ln,(L™'),(DMF)(H,O);]-4DME-10H30 (Ln = Er, Lu),*”* and (d) [(ZnBr2)3(AIL)3], [Pdg(AIL3)g](NO3) 12.”](https://figures.academia-assets.com/41908621/figure_038.jpg)


![Figure 40. Reaction of Zn,O(BDC); with Cr(CO)g to generate Zn4O- [(BDC)Cr(CO)3]3, followed by photolysis under N> or H) to afford Zn,O[(BDC)Cr(CO),(N3)]3 and ZngO[(BDC)Cr(CO)>(H>)]3.””](https://figures.academia-assets.com/41908621/figure_041.jpg)



![Figure 44. (a) The N, isotherms of IRMOF-3 at 77 K, after SCD activation (top), after the exchange with CHCl, followed by evacuation at 25 °C (middle), and conventional activation at 100 °C (bottom). (b) The N> isotherms of IRMOF-16 at 77 K, after SCD activation (top) and after exchange with CHC], followed by activation at 25 °C (bottom). Reproduced with permission from ref 339. Copyright 2009 American Chemical Society.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/41908621/figure_045.jpg)







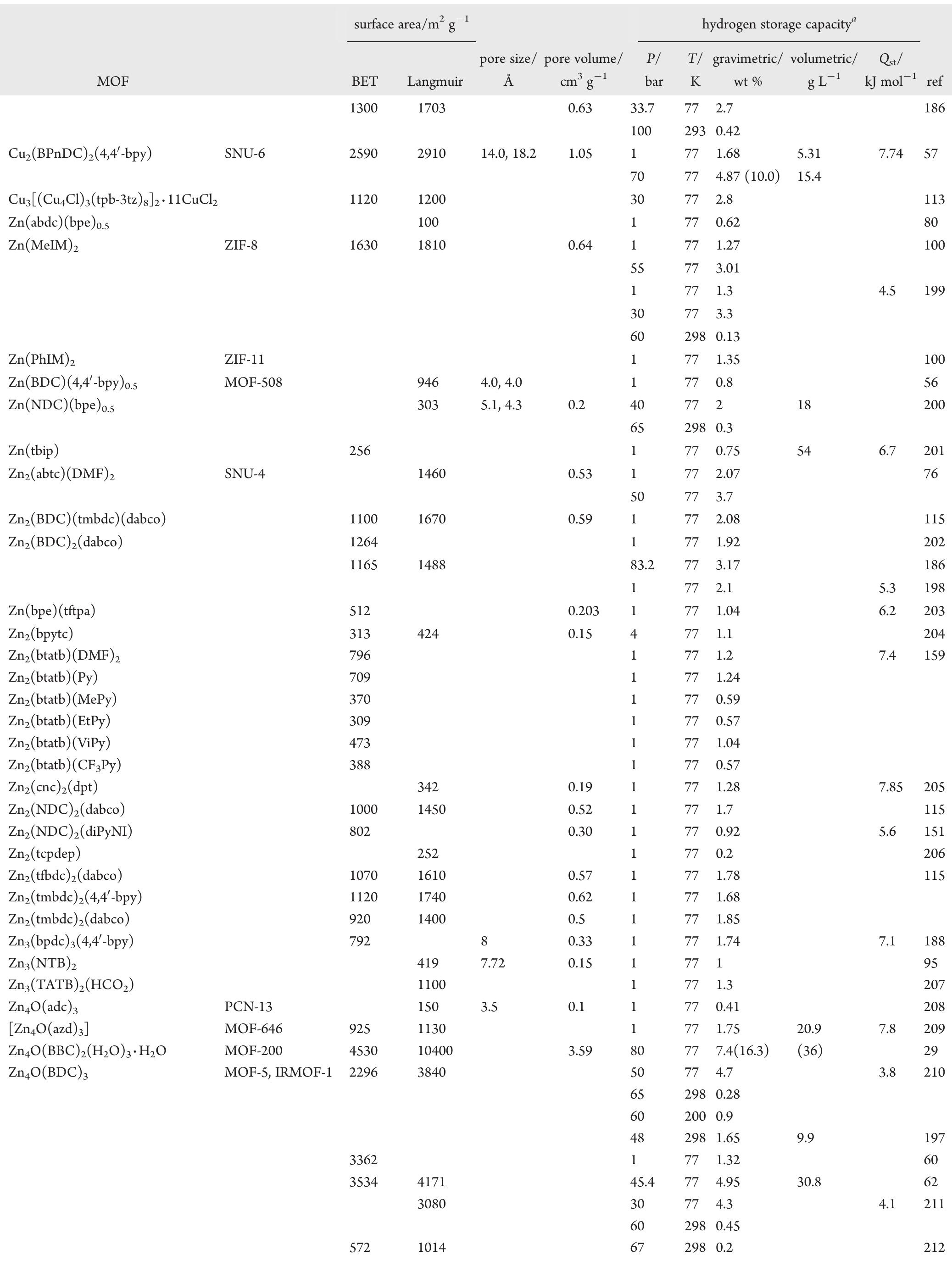













![Table 11. Hydrogen Uptake Properties of a Series of MOFs (IRMOF-3, UMCM-1-NH,, and DMOF-1-NH,) upon Post- synthetic Modification'”” fewer than 0.2 molecules of Hp per formula unit of MOF at 298 K due to the aggregation of Cr atoms. Gentle photolysis conditions enabled substitution of a single CO ligand per metal by Nz and H; to give Zn,O[(bdc)Cr(CO) (N>) ]3 and Zn4O[(bdc)Cr(CO)>- (H2)]3 (Figure 40), respectively, which was characterized by infrared spectroscopy. Considering the H, binding energy for [(C6H6)Cr(CO)2(H2)] and [(CsHsMe)Cr(CO)(H2)], the H, binding energy for Zn,O[(bdc)Cr(CO),(H,)]; was ex- pected to be 60—70 kJ mol” 1.”](https://figures.academia-assets.com/41908621/table_016.jpg)





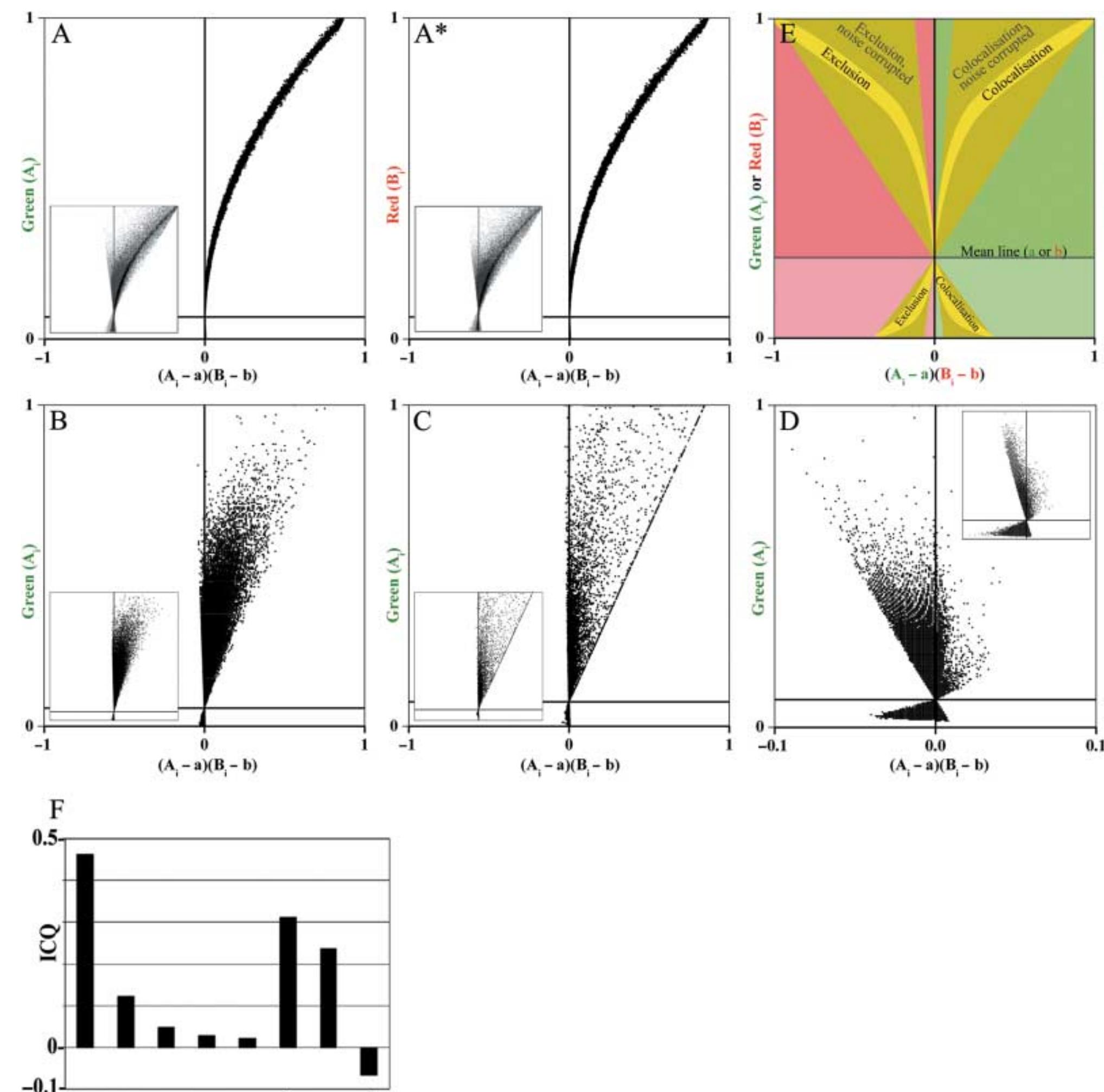
![Fig. 5. Colocalization analysis with JACoP; Pearson and Manders, scatter plots and correlation coefficients. Scatter plots (A—D) correspond to the colocalization events as shown in Fig. 4. (E) Model scatter plot explaining the effects of noise and bleed-through. (F) Pearson’s and Manders’ coefficients in the different colocalization situations. A complete colocalization results in a pixel distribution along a straight line whose slope will depend on the fluorescence ratio between the two channels and whose spread is quantified by the Pearson’s coefficient (PC), which is close to 1 as red and green channel intensity distributions are linked (F, a,, black bar). (B) A difference in fluorescence intensities leads to the deflection of the pixel distribution towards the red axis. Note that the PC diminishes even if complete colocalization of subcellular structures is still given (F, b, black bar). (C) In a partial colocalization event the pixel distribution is off the axes and the PC is less than 1 (F,c, black bar). (D) In exclusive staining, the pixel intensities are distributed along the axes of the scatter plot and the PC becomes negative (F, d, black bar). This is a good indicator for a real exclusion of the signals. (E) The effect of noise and bleed-through on the scatter plot is shown in the general scheme. (F) The influence of noise on the PC was studied by adding different levels of random noise (n1-n4)* to the complete colocalization event (A = n0, no noise). (F) Note that the PC (black bar) tends to O when random noise is added to complete colocalizing structures. The inset (A*) in (A) shows the scatter plot for the n2 noise level. Note that all of the mentioned colocalization events (A—D) may only be detected faithfully once images are devoid of noise. (F) Manders’ coefficients were calculated for (A—D). The thresholded Mander’s tM, (cross-hatched bars) and tM, (diagonal hatched bars) are shown. Compare complete colocalization (a, ), complete colocalization with random noise added (a,,;—a,,4), and complete colocalization with different intensities (b), partial colocalization (c) and exclusion (d). Note that the original Manders’ coefficients are not adapted to distinguish between these events, as they stay close to 1 for all situations (not shown). *Signal-to-noise ratios are: n] = 12.03 dB, n2 = 6.26 dB, n3 = 4.15 dBandn4 = 3.52 dB.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/76163092/figure_005.jpg)






![Scheme 1. Synthesis of building block A: a) toluene/DMF, [Pd(PPh;),], 85°C; b) 1) LDA, —78°C to room temperature; 2) Bu;SnCl, —78°C to room tem- perature, THF; c) Toluene/DMF, [Pd(PPh;),], 70°C; d) 1) nBuLi, —78°C; 2) Bu;SnCl, —78°C to room temperature, THF. LDA: lithium diisopropyl- amide.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/49965831/figure_002.jpg)

![Scheme 3. Synthesis of OFbTs: a) toluene/DMF, [Pd(PPh;),], 85°C. pling reactions for the synthesis of F7Th12 and F9Th16](https://figures.academia-assets.com/49965831/figure_004.jpg)
![Figure 2, MALDI-TOF mass spectra ((M+H]*) of oligomers F7Th12, F9Th16, and F13Th24 with anthracene-1,8,9-triol as matrix. The molecular structures of OFbTs were validated by ‘HNMR spectroscopy, gel-permeation chromatography (GPC), and matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time- of-flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry (MS), and ele- mental analysis. Molecular weights measured by GPC (weight-average molecular weight M,cpc) and MS (M,.us) along with calculated ones (M.ai-q) are listed in Table 1. The M,ms of all oligomers determined by means of MALDI- Ww,](https://figures.academia-assets.com/49965831/figure_005.jpg)
![Figure 3.'H NMR spectrum of F13Th24 in C,D,Cl, at 20°C, 50°C, and 80°C, with a concentration of 8.5x10~* molL”! (6.0 mgmL'). [a] Measured by MALDI-TOF MS. [b] Measured by GPC with PS as standard. [c] Measured by DSC with second heating at 10°C min '. [d] From refer ence [27].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/49965831/figure_006.jpg)






![[a] Measured in chloroform at a concentration of 10° and 10°° molL”! for absorption and PL, respectively. [b] Band gap calculated from absorptior edge. [c] Measured by cyclic voltammetry. [d] From reference [27]. Table 2. Absorption (Anaxabs) and PL (AmaxpL) maxima of OFbTs in chloroform solution and film state, and energy levels of OFbTs.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/49965831/table_002.jpg)





![Fig. 4. The density phase transition curve of MD simulation. The phase transition of ZrO, is very complicated, but it is a good choice for MD algorithm checking. With a heat- ing rate of 10 from 2100 to 3000 K, the phase transition from tetragonal to cubic is simulated successfully by a MD process starting with a tetragonal sample. The variations of the density are plotted in Figure 4. Note that a similar curve has been given in Ref. [17] where the pressure was controlled by a scaling of the MD cell, which could not be verified to yield the correct NPT ensemble. Figure 5 depicts the variations of the effective axial ratio of (a+ b)/2c. From the phase diagrams, transition from tetrago- nal to cubic can be identified easily. In Figure 5, due to the initialization of tetragonal phase, the axial ratio (0.922)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/45335064/figure_006.jpg)









![FIG. 6. Structure of a directed graph when the giant strongly connected component is present (see the text). Also, the structure of the WWW (compare with Fig. 9 of Ref. fi). If one ignores the directedness of edges, the network consists of the giant weakly connected component (GWCC) — actually, the usual percolating cluster — and disconnected components (DC). Accounting for the directedness of edges, the GWCC contains the following components: (a) the gi- ant strongly connected component (GSCC), that is, the set of vertices reachable from its every vertex by a directed path; (b) the giant out-component (GOUT), the set of vertices ap- proachable from the GSCC by a directed path (includes the GSCC); (c) the giant in-component (GIN), contains all vertices from which the GSCC is approachable (includes the GSCC); = (d) the tendrils (TE), the rest of the GSCC, ie. the vertices which have no access to the GSCC and are not reachable from it. In particular, this part includes something like “tendrils” A but also there are “tubes” and numerous clusters which are only “weakly” connected. Note that our definitions of the GIN and GOUT differ from the definitions of Refs. [f]{61): the GSCC is included into both GIN and GOUT, so the GSCC is the interception of the GIN and GOUT. We shall show in Sec. that this definition is natural.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/31480387/figure_006.jpg)

![FIG. 8. Typical food web. Cannibalism and mutual eat- ing are widespread. Additionally, in Ref. [19], the stability of food webs against random or intentional removal of vertices was considered. The results were typical for scale-free net- works (see Sec. [x1 C).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/31480387/figure_008.jpg)
![FIG. 9. The distribution of the numbers of connections (degrees) of words in the word web in a log-log scale (i264. Empty and filled circles show the distributions of the number of connections obtained in Ref. (hq) for two different meth- ods of the construction of the Word Web._The solid line is the result of theory of Ref. (h27] (see Sec. where the pa- rameters of the Word Web, namely, the size t + 470000 and the average number of connections of a node, k(t) ~ 72, were used. The arrows indicate the theoretically obtained point of crossover, Keross between the regions with different power laws, and the cutoff keuz due to the size effect. For a better comparison, the theoretical curve is displaced upward to ex- clude two experimental points with the smallest & (note that the comparison is impossible in the region of the smallest k where the empirical distribution essentially depends on the definition of the Word Web).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/31480387/figure_009.jpg)
![FIG. 10. Small-world networks in which the ae from a regular lattice to a random network is realized. (a) The original Watts-Strogatz model with the rewiring of links L1]. (b) The network with the addition of shortcuts fedisq](https://figures.academia-assets.com/31480387/figure_010.jpg)



![FIG. 13. Spreading of diseases in “small-world” networks 35). The average fraction of infected nodes, ni/L, vs. the elapsed time from the instant when the first vertex “fell ill”. It is possible to consider various problems for these networks lad fas} fi6g). In Refs. firdio3), percolation in them was studied (for infinitely large networks). Dif- fusion in the WS model and other related nets was con- sidered in [164].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/31480387/figure_014.jpg)





![Vertices of this simple network are born without incoming edges, so the boundary condition for this equation is The master equation approach (69) is very efficient for problems of the network evolution. Indeed, the linear discrete difference equations that arise (usually of first order) can be easily solved, e.g., using Z-transform. Let us describe the degree distributions for networks with preferential linking of a more general type than in Sec. Let us discuss the general case. The structure of the master equation for the in-degree distribution of individ- ual vertices, p(q, s, t), may be understood from the follow- ing. The probability that a new edge comes to a vertex s equals [¢(s, t) + am]/[(1+ a)mt]. Here, a= A/m. The probability that a vertex s receives exactly | new edges of the m injected is B. Master equation approach The parameter A = ma plays the role of additional attractiveness of vertices. The resulting in-degree distri- bution does not depend on the place from which new edges go out. If, in particular, each new vertex is the source of all the m new edges (see a citation graph in Fig. (9), then k(s,t) = q(s, t)-++m, and the degree of each vertex is fixed by its in-degree. If, in addition, we set A=™M, i.e., a = 1, then new edges are distributed with probability proportional to k(s,t), and we come to the BA model.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/31480387/figure_020.jpg)



![FIG. 24. Log-linear plot of the y exponents of all the networks reported as having power-law (in-, out-) degree distributions (i-e., scale-free networks) vs. their sizes. The line y ~ 1+log,, t/2.5 is the estimate of the finite-size boundary for the observation of the power-law degree distributions for y > 2. Here 2.5 is the range of degrees (orders) which we believe is necessary to observe a power law. The dashed line, 7 = 3, is the resilience boundary (see Sec. x1). This boundary is important for networks which must be stable to random breakdowns. The points are plotted using the data from Tab. i Points for y. and +; from the same set of data are connected. The precision of the right points is about +0.1 (?) and is much worse for points in the grey region. There exists a chance that some of these nets are actually not in the class of scale-free networks. The oints: 1i and lo are obtained from in- and out-degree distributions of the complete map of the nd.edu domain of the WWW ;__ 12’ and lo’ are from in- and out-degree distributions of the pages of the WWW scanned by Altavista in October of 1999 90]; 10” is the yo value from another fitting of the same data by; li” is +; for domain level of the WWW in spring 1997 1171); 2 is y for the inter-domain level of the Internet in December 1998 [5]; 2’ is y for the network of operating AS in one of days in December 1999 bd; 3 is y for the router level of the Internet in 1995 [fh]; 3’ is y for the router level of the Internet in 2000 104]; 4i is 7; for citations of the ISI database 1981 — June 1997 ; i’ is the result of the different fitting of the same data Pd); 4i” is another estimate obtained from the same data p4, ; 4j is y: for citations of the Phys. Rev. D 11-50 (1975-1994) P74: 4j' is the different fitting of the same data [99]; 4j" is another estimate from the same data paps; 4j’" is y; for citations of the Phys. Rev. D (1982-June 1997) |[l00]; _5a is the 7 exponent for the collaboration network of movie actors ; 5a’ is the result of another fitting for the same data (Log: 5b_is y for the collaboration network of MEDLINE IEF 5b’ is y for the collaboration net collected from mathematical journals fil; 5b” is y for the collaboration net collected from neuro-science journals (ia); 6i0 is ¥i = Yo for networks of metabolic reactions 11]; 7 is y of the network of protein-protein interactions (yeast proteome) if it is treated as undirected bali); 8 is y of the degree distribution of the word web in the range below the crossover point Tr 9 is y of large digital electronic circuits fi2q; 10 is 7; of the telephone call graph ise | (the out-degree distribution of this graph cannot be fitted by a power-law dependence); 11 is ¥ of vertices in the web of human sexual contacts (133.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/31480387/figure_024.jpg)
![FIG. 25. Scheme of the growth of the network with a mix- ture of the preferential and random linking (compare with the schematic Fig. bj] for the WWW growth). At each time step, a new vertex with n incoming edges is added. Simultaneously, the target ends of m new edges are distributed among vertices according to a rule of preferential linking, and, in addition, the target ends of n, new edges are attached to randomly chosen vertices. The source ends of each edge may be anywhere. One _ may consider more complex growing networks fi75fi 76). We will demonstrate that scale-free nets may be obtained even without “pure” preferential linking. It is convenient to consider incoming edges here, so we use the following notation for in-degree, g = k;.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/31480387/figure_025.jpg)





![FIG. 30. 6 exponent of the average degree vs. the aging exponent a of the network with aging of vertices. The points are obtained from the simulations fir). The line is the result of the calculations. The inset shows the analytical solution in the range —5 <a <1. Note that 6 — 1 when a > —co. From Eq. (70), one obtains the solution «(€, 3). Substi- tuting it into the O equality in Eq. ( or, equiva- lently, into So d¢K(C) = 2, we get a wranseendental equa- tion for G. The renulting exponents, 0 < @ < 1 and 2<y< o, are shown in Figs. Bd and Bi] ray.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/31480387/figure_031.jpg)

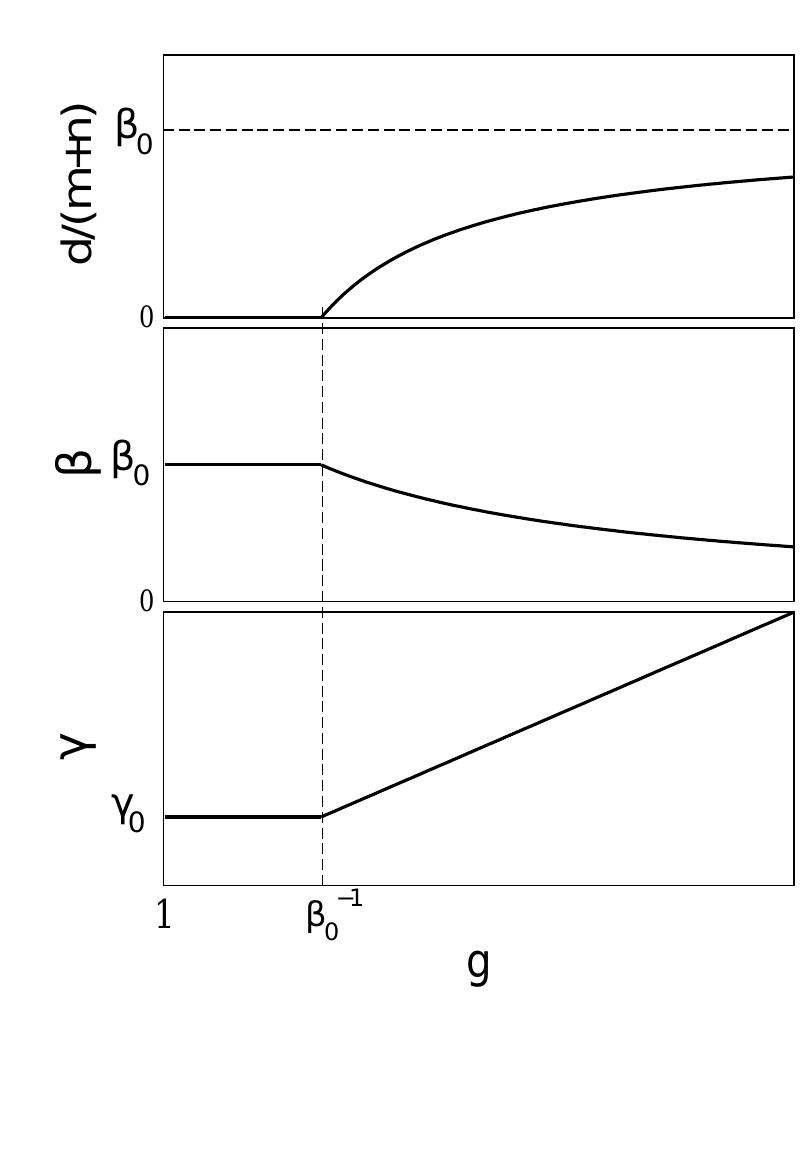
![FIG. 33. Schematic plot of the degree distribution of the network with one_vertex, the fitness of which exceeds the threshold value fi73. The peak is due to edges “condensed” on the strong vertex. A hump at the cutoff of the continuum part_of the distribution is a trace of initial conditions (see Sec. and Ref. (lied). FIG. 32. “Condensation” of edges. Fraction of all edges, d/(m +n), captured by a single strong vertex at long times and the scaling exponents ( and ¥ vs. relative fitness g of the strong vertex The network contains only one “strong” vertex. The condensation occurs above the threshold value ge = 1/80 = y-—1> 1. Here Go and yo are the corre- sponding exponents for the network without a strong vertex. d/(m+n)[g — co] — Bo and B[g — oo] = 0.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/31480387/figure_034.jpg)









![FIG. 42. Anomalous percolation in the growing network. (a) The giant connected component size W vs. the rate b of the creation of new edges in the growing network (see Eq. ({57)). (b) The average size 3 of a finite connected compo- nent vs. b (see Eqs. (isd) and (i59)) [203]. The region of anomalous percolation threshold b. = 1/8 is shown.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/31480387/figure_044.jpg)
![TABLE I. Sizes and values of the y exponent of the networks or subgraphs reported as having power-law (in-, out-) degree distributions. For each network (or class of networks) data are presented in more or less historical order, so that the recent exciting progress is visible. Errors are not shown (see the caption of Fig. ba). They depend on the size of a network and on the value of y. We recommend our readers to look at the remark at the end of Sec. vod before using these values. 'The data for the network of operating AS was obtained_for one of days in December 1999. The value of the 7 exponent was estimated from the degree distribution plot in Ref. 1104] . 3The network of protein-protein interaction is treated as undirected. ‘The value of the 7 exponent for the word web is given for the range of degrees below the crossover point (see Fig. bp. >The out-degree distribution of the telephone call graph cannot be fitted by a power-law dependence (notice the remark in Sec. (VF). °In fact, the data was collected from a small set of vertices of the web of human sexual contacts. These vertices almost surely have no connections between them. “These food webs are truly small. In Refs. baba} degree distributions of such food webs were interpreted as exponential-like.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/31480387/table_001.jpg)


![Figure 3. (a) External quantum efficiency (EQE) for the new perovskite, dye sensitised and organic (OPV) results in this issue (* asterisk denotes normalized values; others are absolute values); (b) corresponding current density-voltage (JV) curves. 3. DISCLAIMER Table IV also reports two new results for concentrating modules and submodules, with performance based on out- door measurements. A landmark 40.4% efficiency has been measured in outdoor testing by NREL for a 287-cm* split- spectrum concentrator submodule fabricated by the Univer- sity of New South Wales (UNSW), using commercial GalnP/GalnAs/Ge and Si cells manufactured by Spectrolab and SunPower, respectively. A new record of 36.7% is re- ported for an 830-cm” photovoltaic module using a four cell stack [24]. The module was fabricated and measured at the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems (FhG-ISE).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/43090489/figure_003.jpg)



![*Effic. = efficiency. ®(da) = designated illumination area; (ap) = aperture area. °One sun corresponds to direct irradiance of 1000 Wm”. 4Not measured at an external laboratory. °Spectral response reported in Version 36 of these tables. ‘Measured under a low aerosol optical depth spectrum similar to ASTM G-173-03 direct [61]. °Spectral response and current-voltage curve reported in Version 44 of these tables. Spectral response and current-voltage curve reported in present version of these tables. ‘Measured outdoors at 883.7 Wim? direct irradiance, pressure-corrected airmass of 2.5 and cell temperature referenced to 25°C. 'Recalibrated from original measurement. ‘Referenced to 1000 Wim> direct irradiance and 25 °C cell temperature using the prevailing solar spectrum and an in-house procedure for temperature translatic 'Measured under IEC 62670-1 reference conditions following the current IEC power rating draft 62670-3. ™Geometric concentration. Table IV. Terrestrial concentrator cell and module efficiencies measured under the ASTM G-173-03 direct beam AM1.5 spectrum at a cell temperature of 25 °C.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/43090489/table_004.jpg)























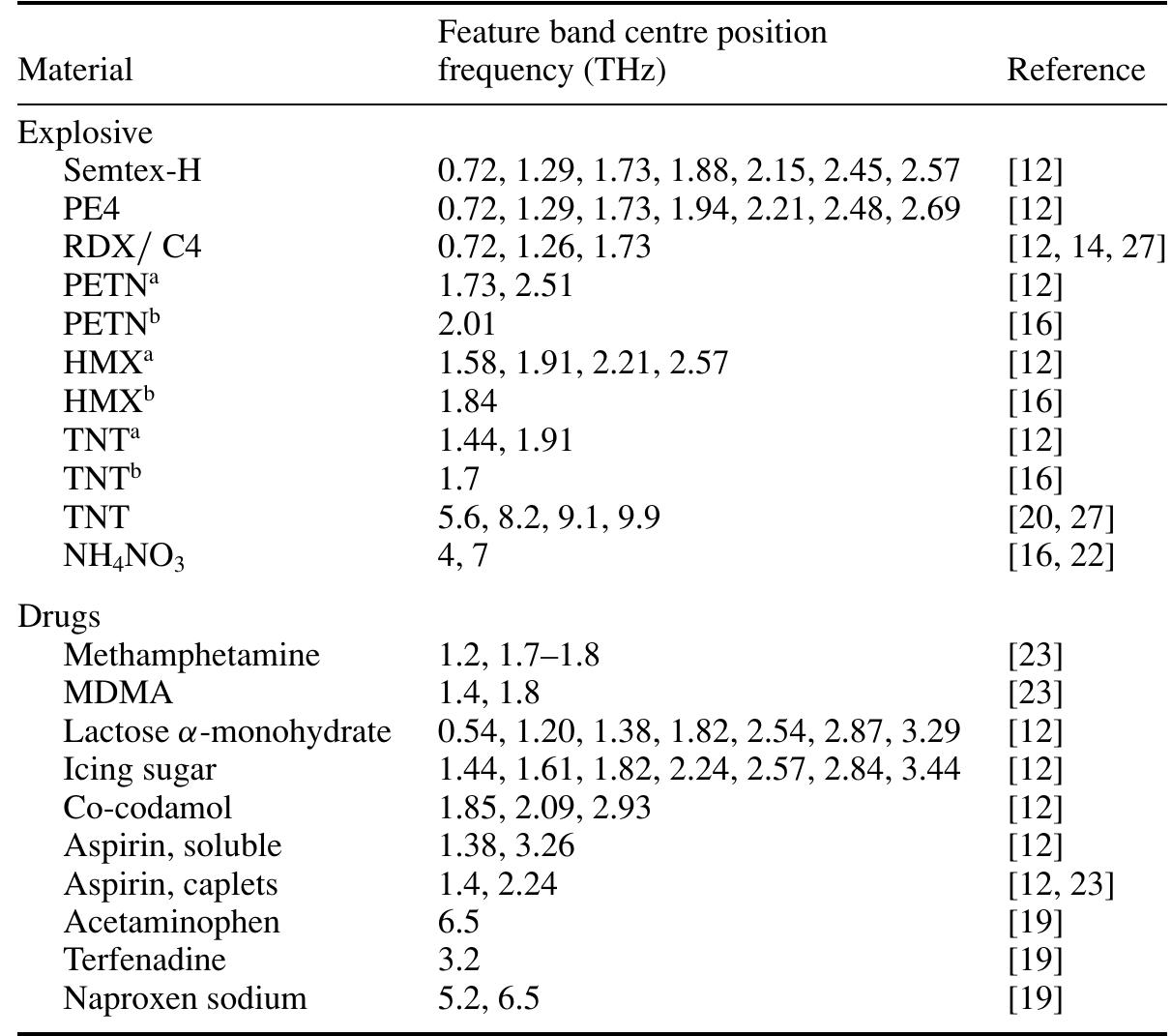
![Figure 1. (a) THz absorption spectra from [13]. (b) Comparison study of transmission spectra of RDX using THz-TDS and FTIR (Fourier transform infrared) spectroscopy with data from [13, 14]. The dashed line is RDX from [13]. The other curves are from [14] where the bottom curve is RDX measured by THz-TDS, the solid curve is RDX measured by FTIR, and the top curve is C4 measured by THz-TDS). The sharp features in C4 (THz-TDS) are remnants of water. Note that the absorption features at 0.8, 1.5, 2.0, 2.2 and 3 THz are exhibited in both the datasets. The spectral feature at 1.1 THz is not present in both datasets.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/33672423/figure_001.jpg)
![Figure 2. (a) THz spectra of ammonium nitrate (1 mm thick sample). The dotted line corresponds to measured data of [22]. The dashec line is from [16]. (b) Extended transmission spectra [22] out to 21 THz with nominal sample thickness listed.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/33672423/figure_002.jpg)
![Figure 3. Atmospheric transmission bands in the terahertz range of frequencies (after [8]).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/33672423/figure_003.jpg)