Lee J. Skandalakis Surgical Anatomy and Technique
…
696 pages
1 file

Sign up for access to the world's latest research
AI-generated Abstract
The paper discusses the surgical anatomy and techniques associated with various procedures, with particular emphasis on the anatomy of the scalp, including its vascular, lymphatic, and nerve supplies. It presents detailed insights into the blood supply of the scalp, highlighting the important arterial branches and their anastomoses, as well as the implications for surgical procedures. Additionally, the paper outlines techniques for surgical interventions, positioning, and considerations necessary for effective outcomes.
Figures (683)










































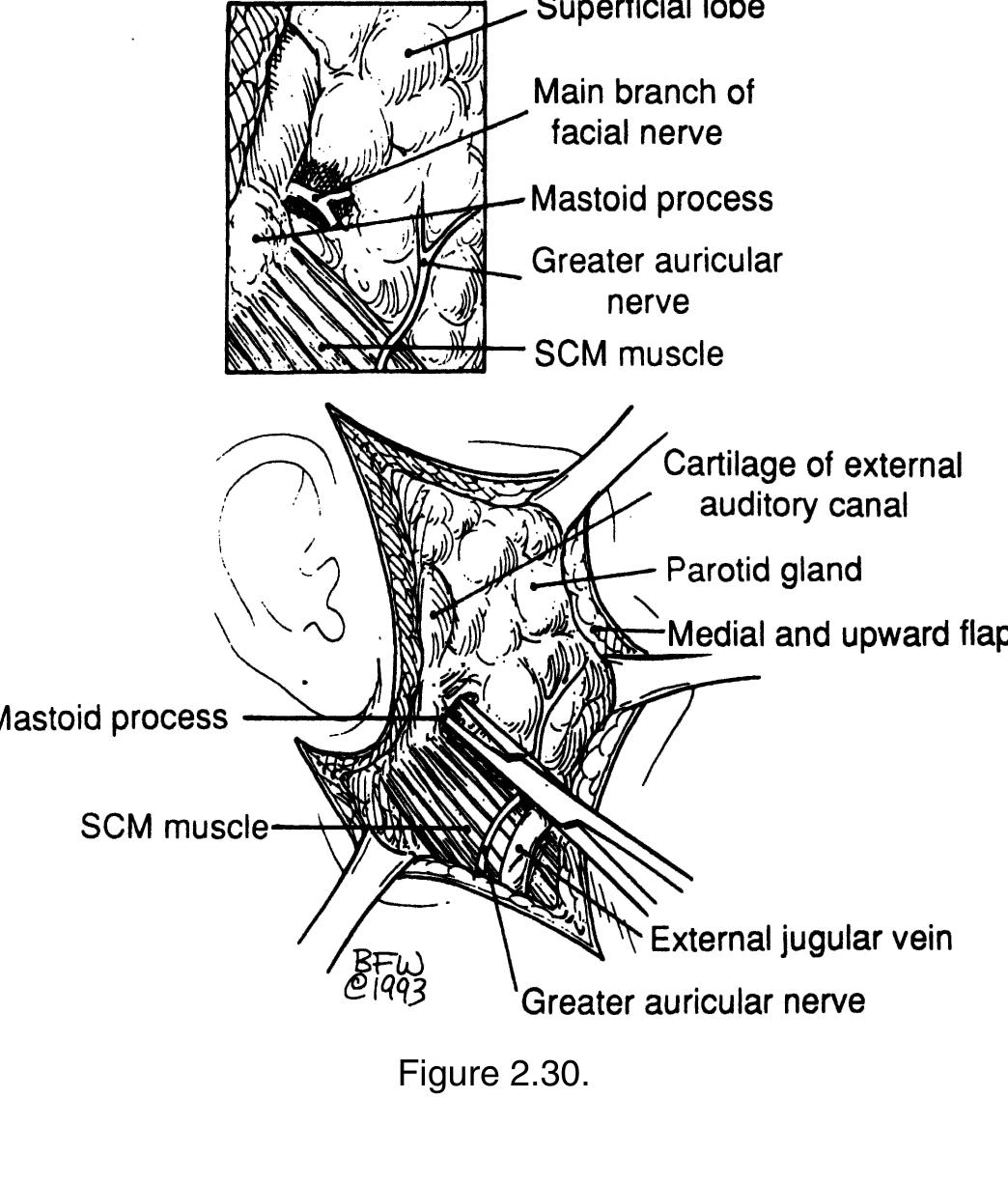




























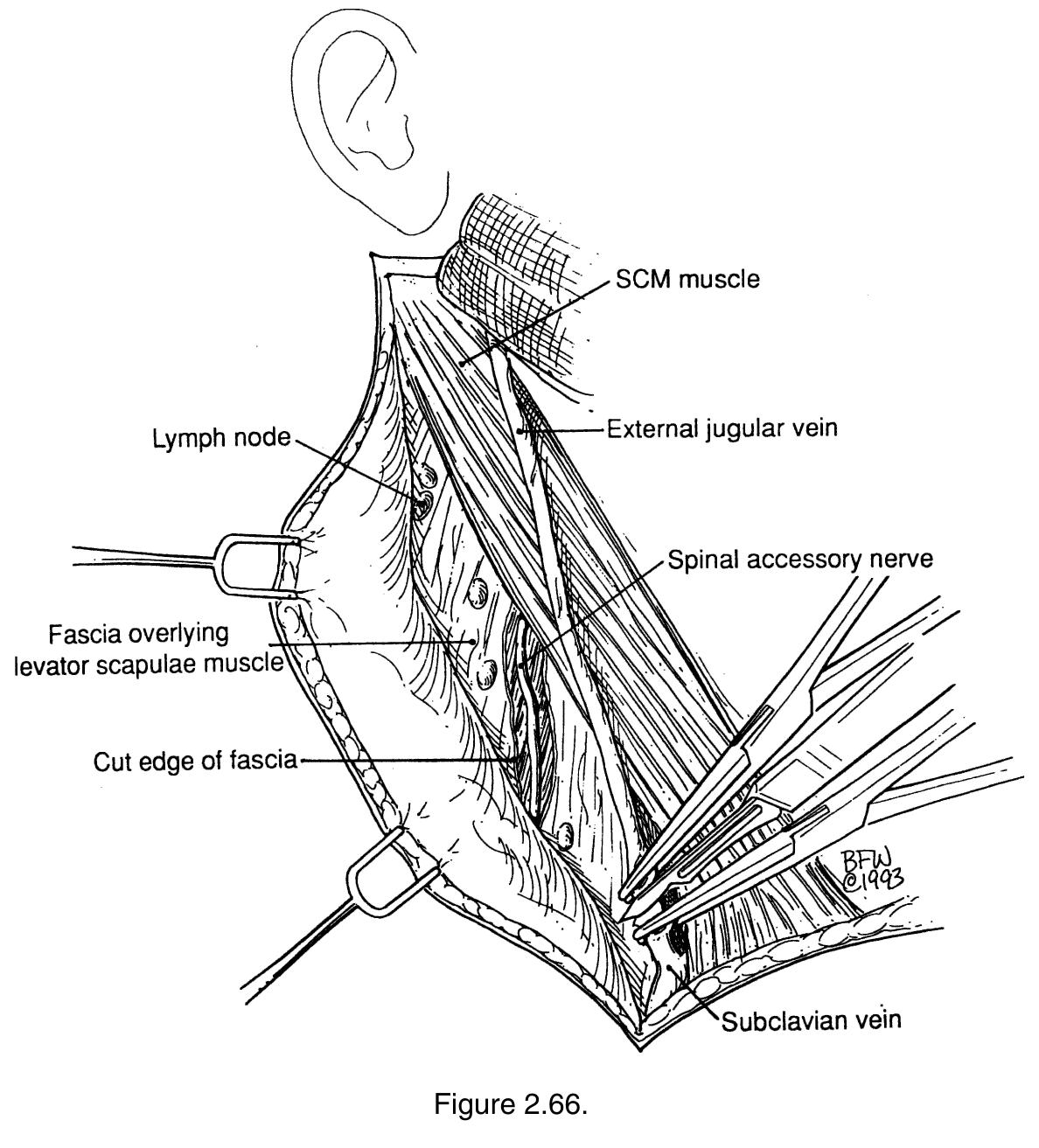




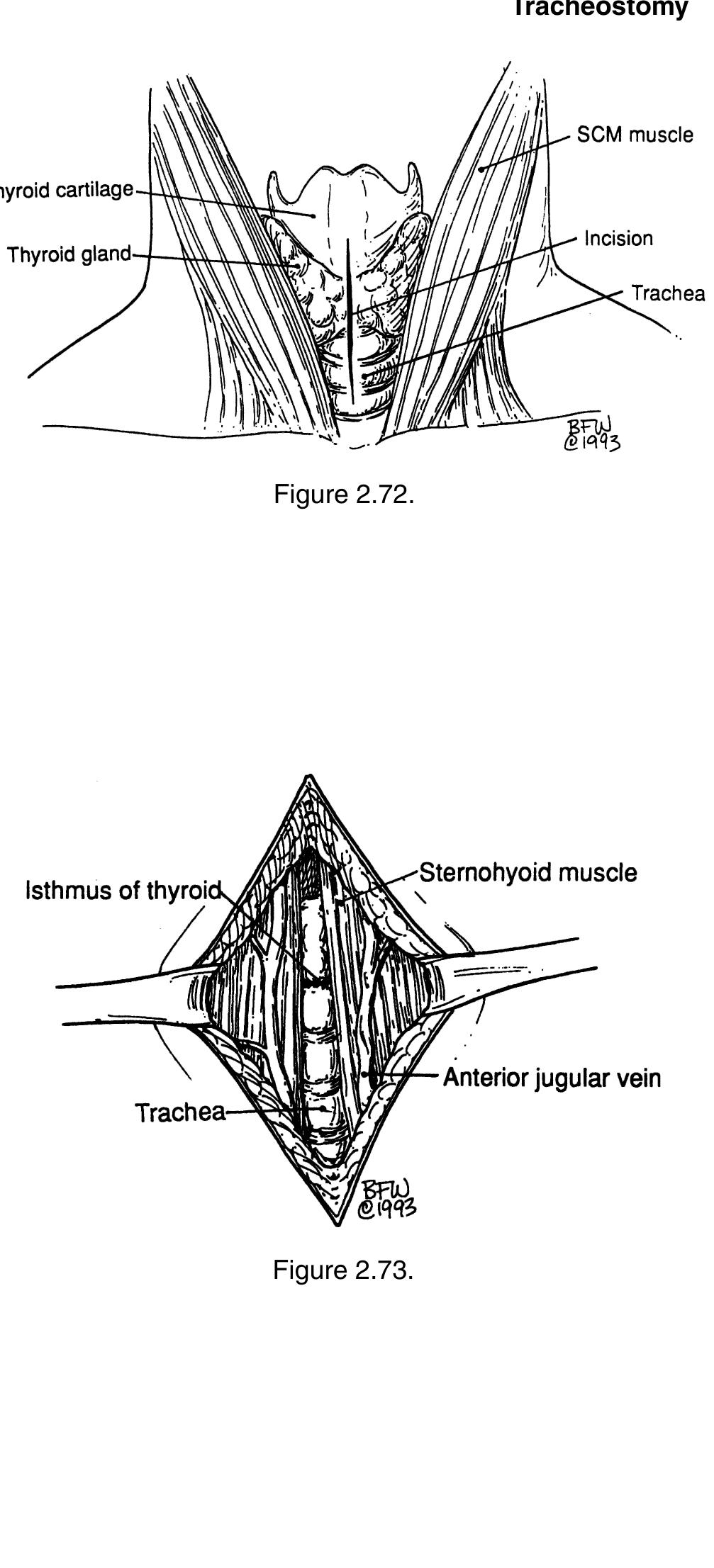






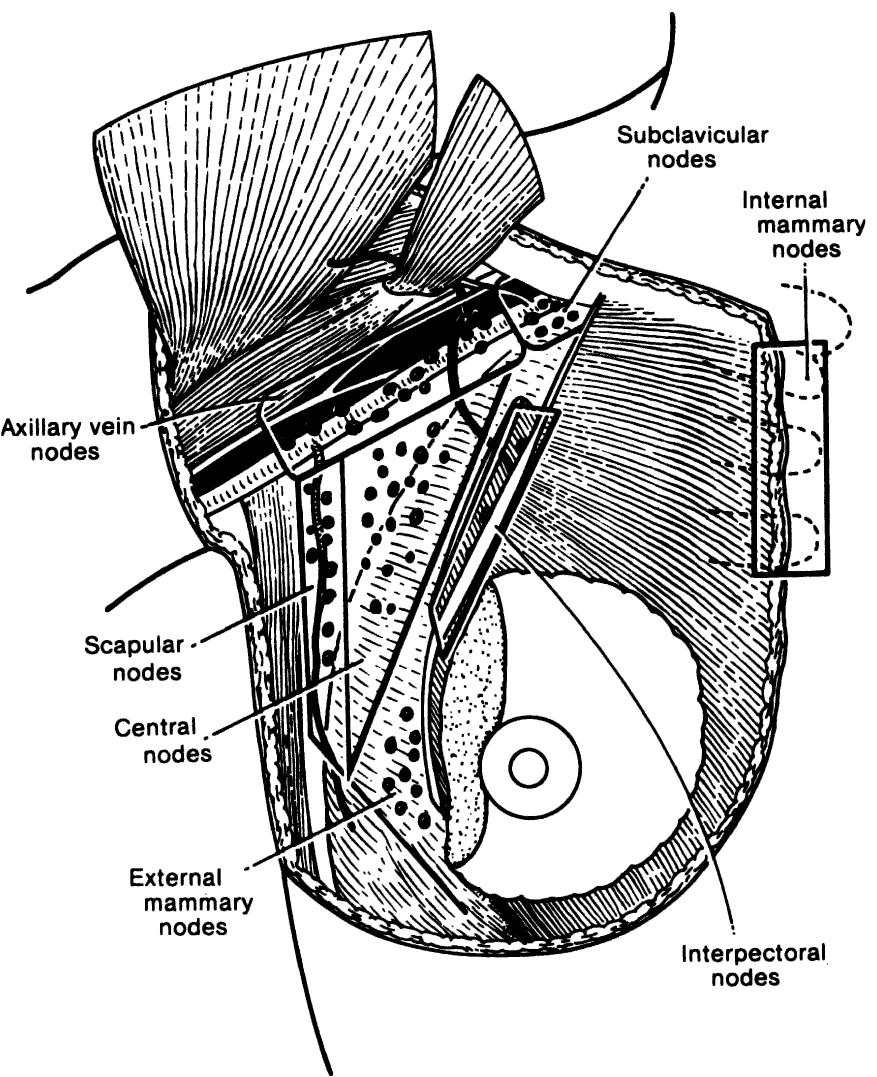























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































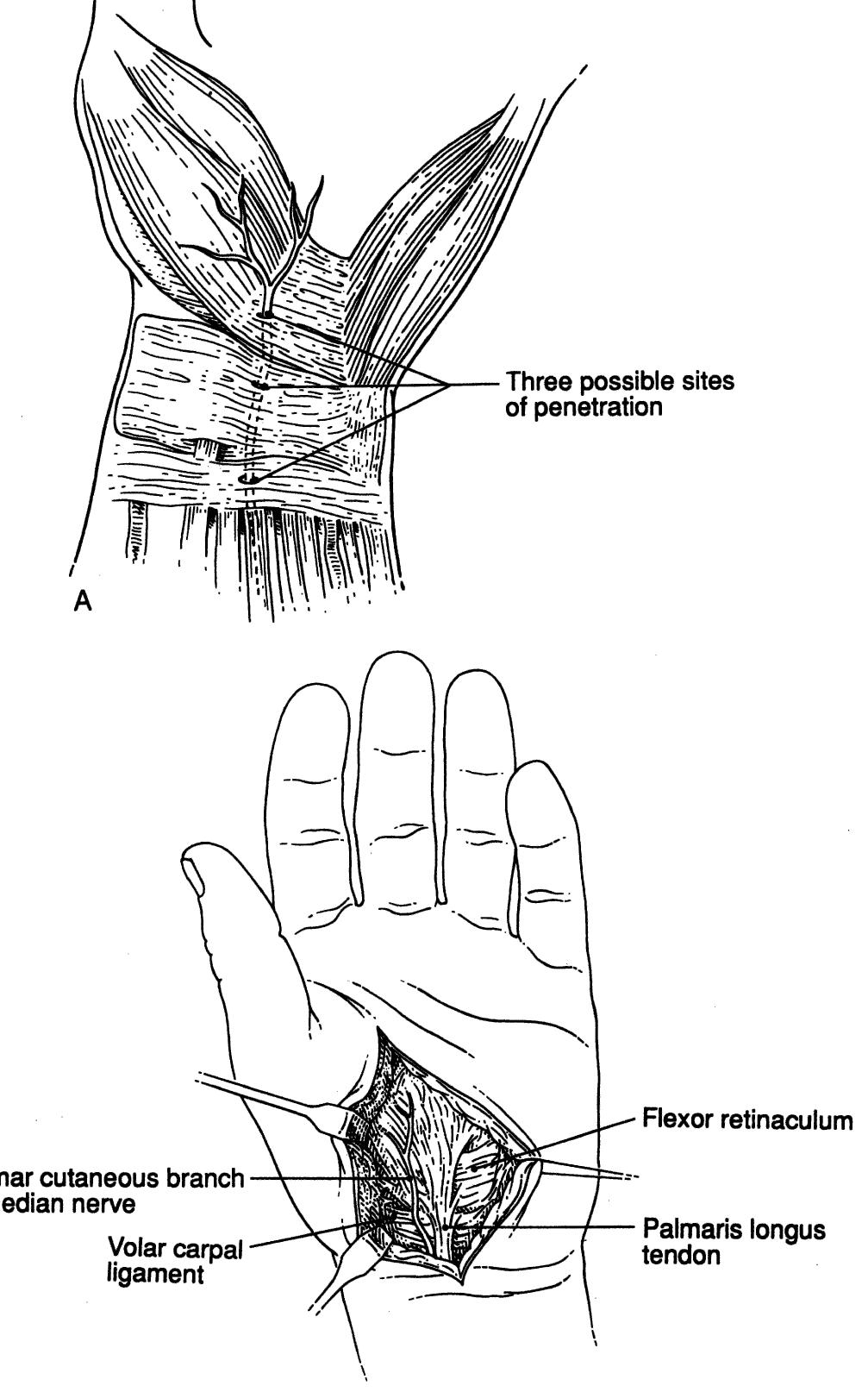







Key takeaways
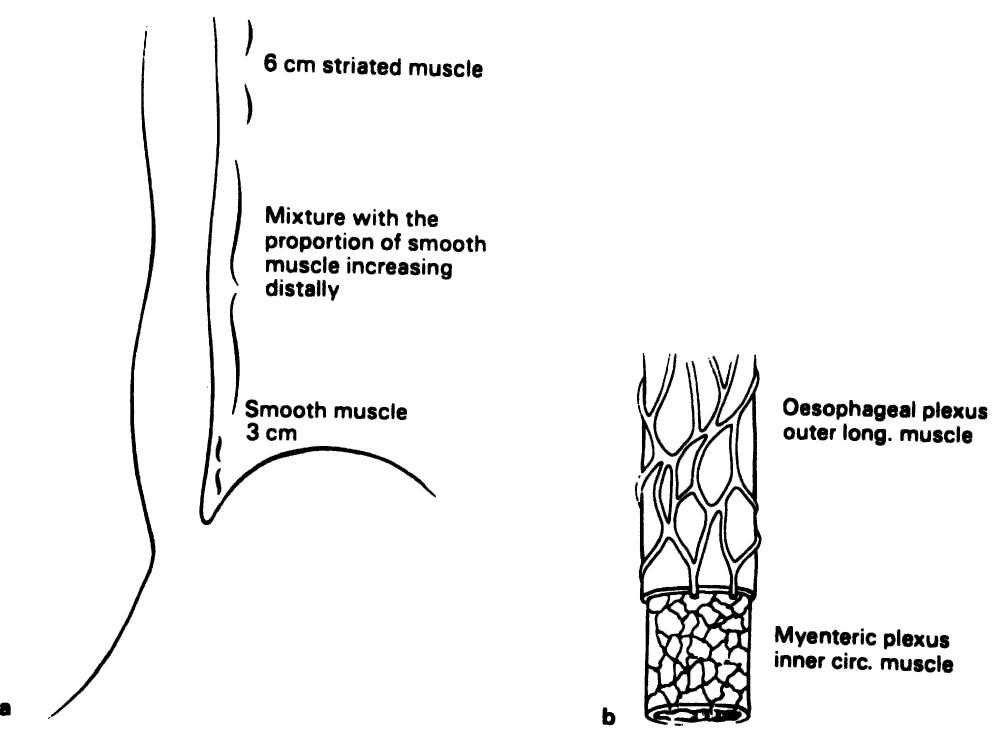
- The nerve may pass anterior or posterior to the artery, or between its branches (Fig. 2.16 ).
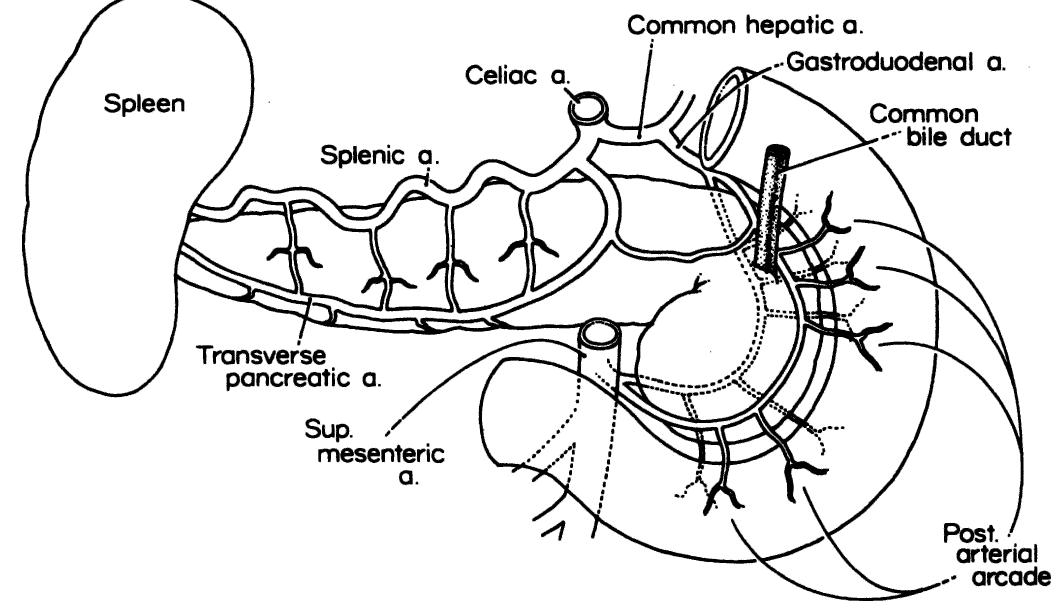
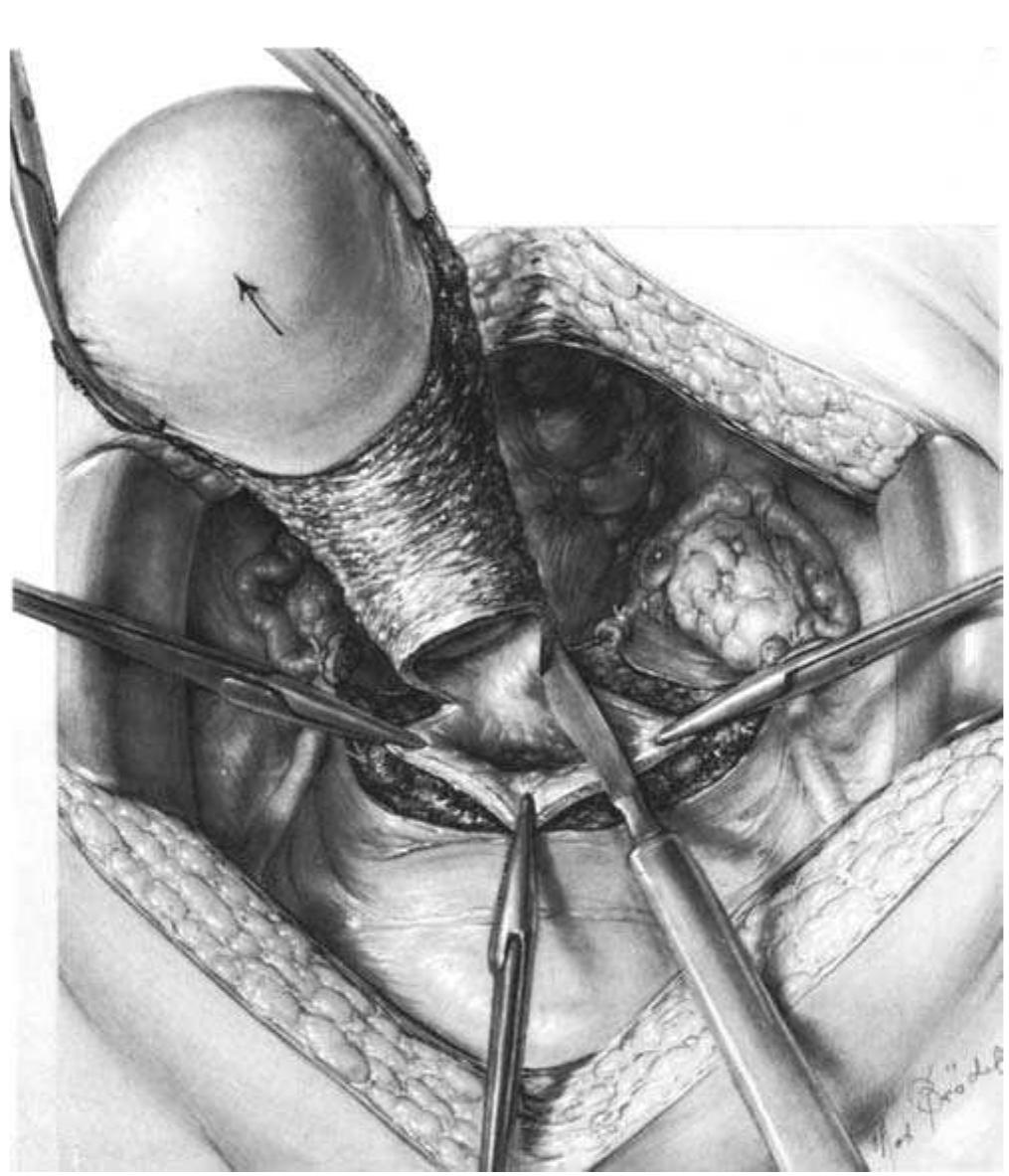
- The ligament contains the following structures: left gastric artery and vein; hepatic division of left vagus trunk; lymph nodes; occasionally, both vagal trunks; occasionally, branches of the right gastric artery and vein; the left hepatic artery when it arises from the left gastric artery (in 23 percent of cases).
- The portal vein lies behind the pancreas and in front of the inferior vena cava, with the common bile duct on the right and the common hepatic artery on the left.
- In this ligament, the proper hepatic artery lies to the left of the common bile and hepatic ducts and anterior to the portal vein.
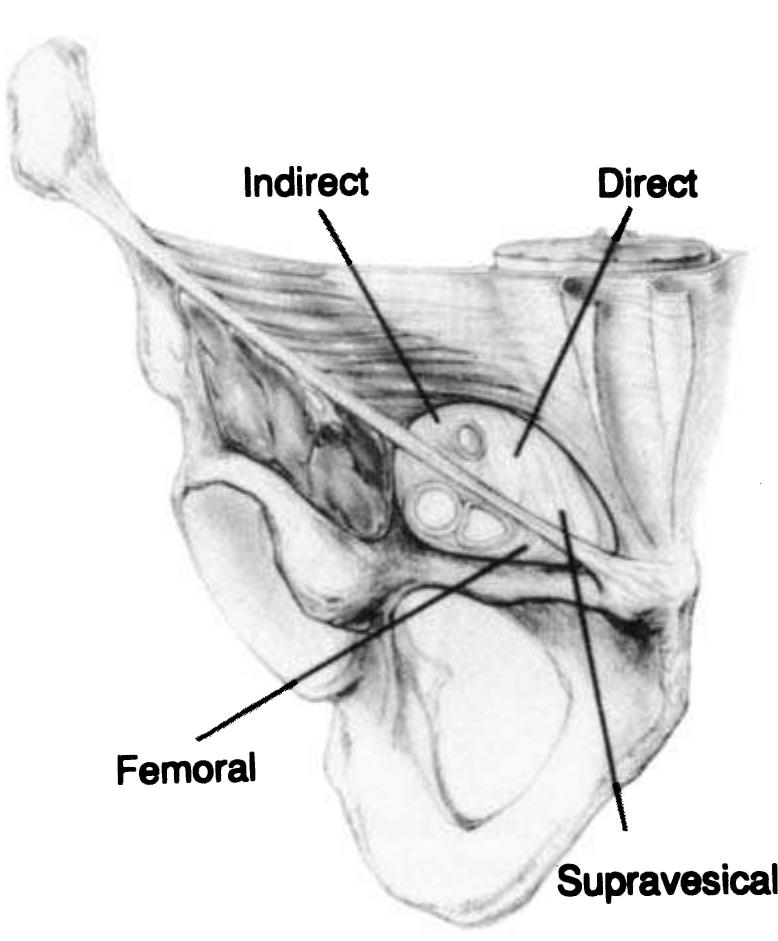
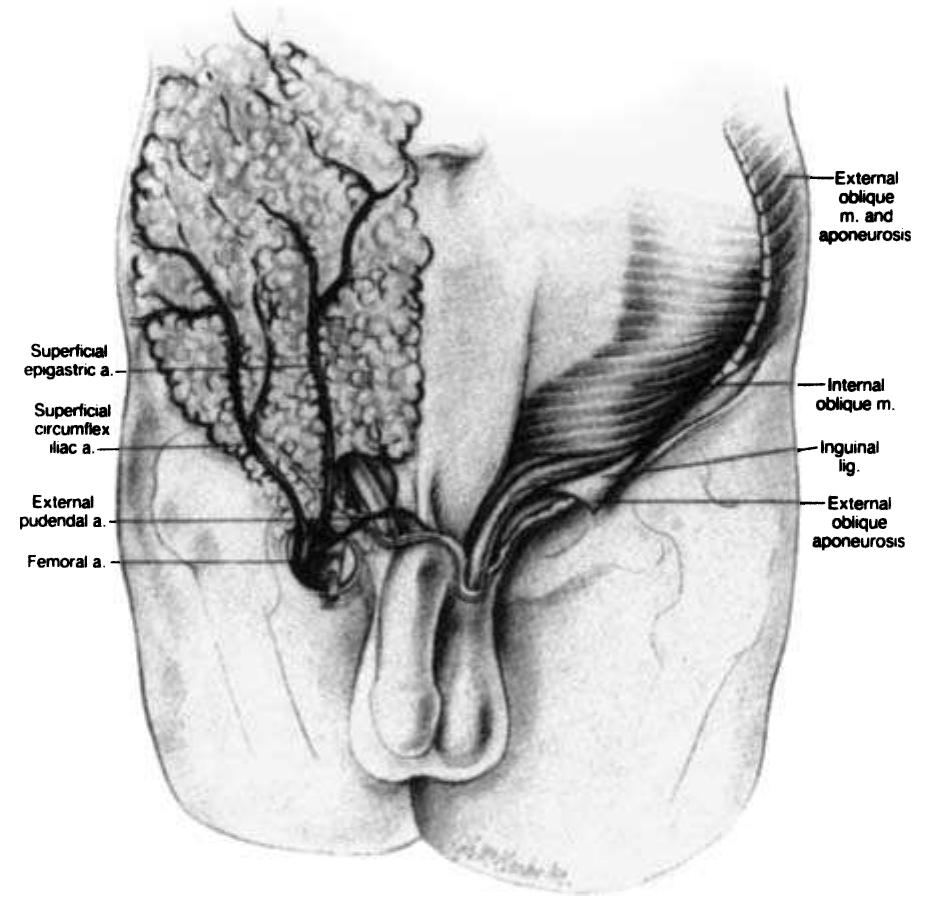
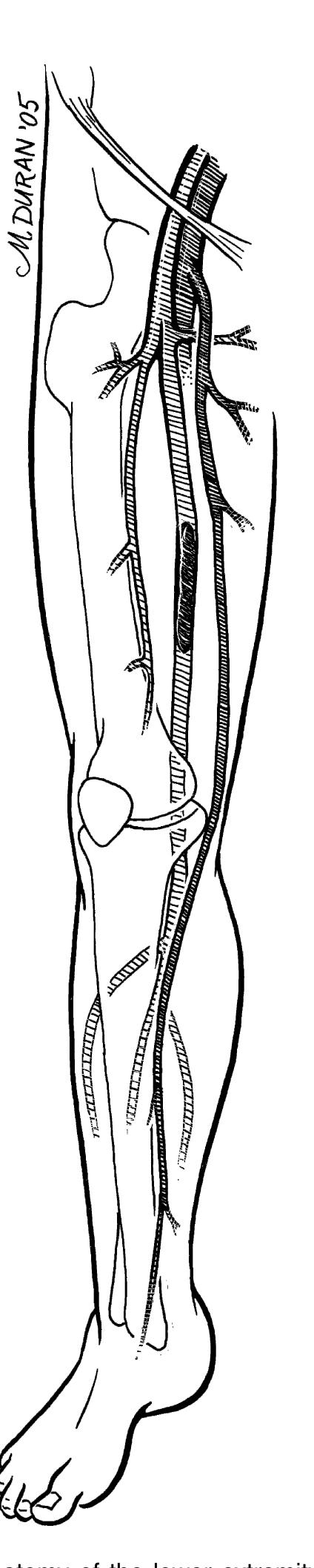
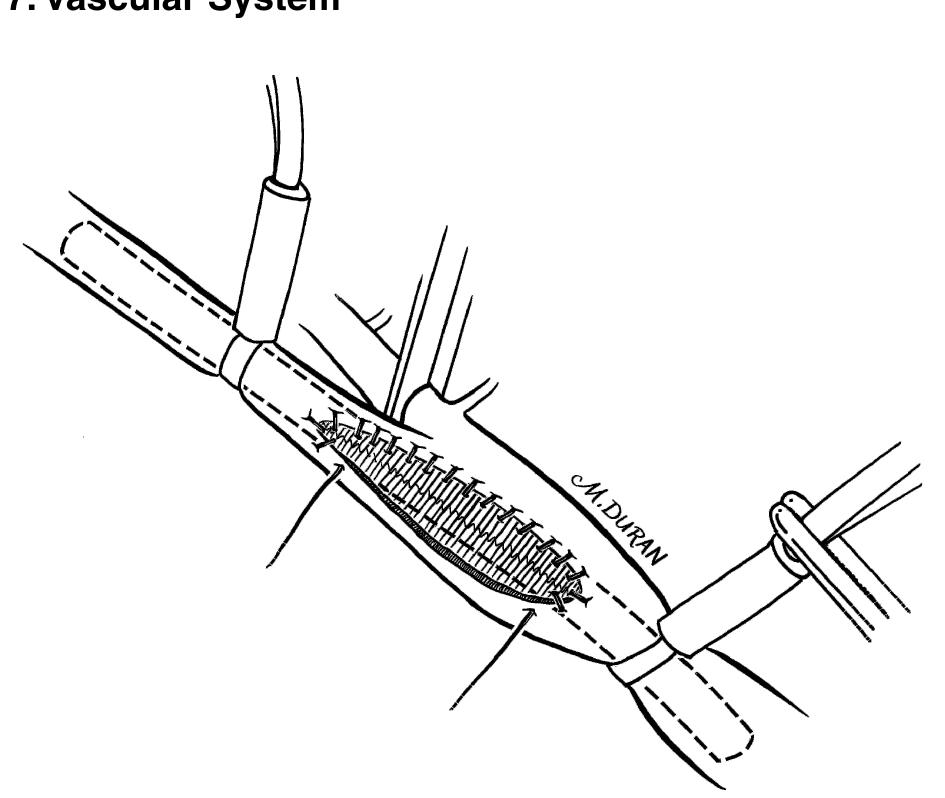
- The external iliac artery becomes the common femoral artery as it emanates from a point under the middle of the inguinal ligament.
Related papers
Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 1991
Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery, 2012
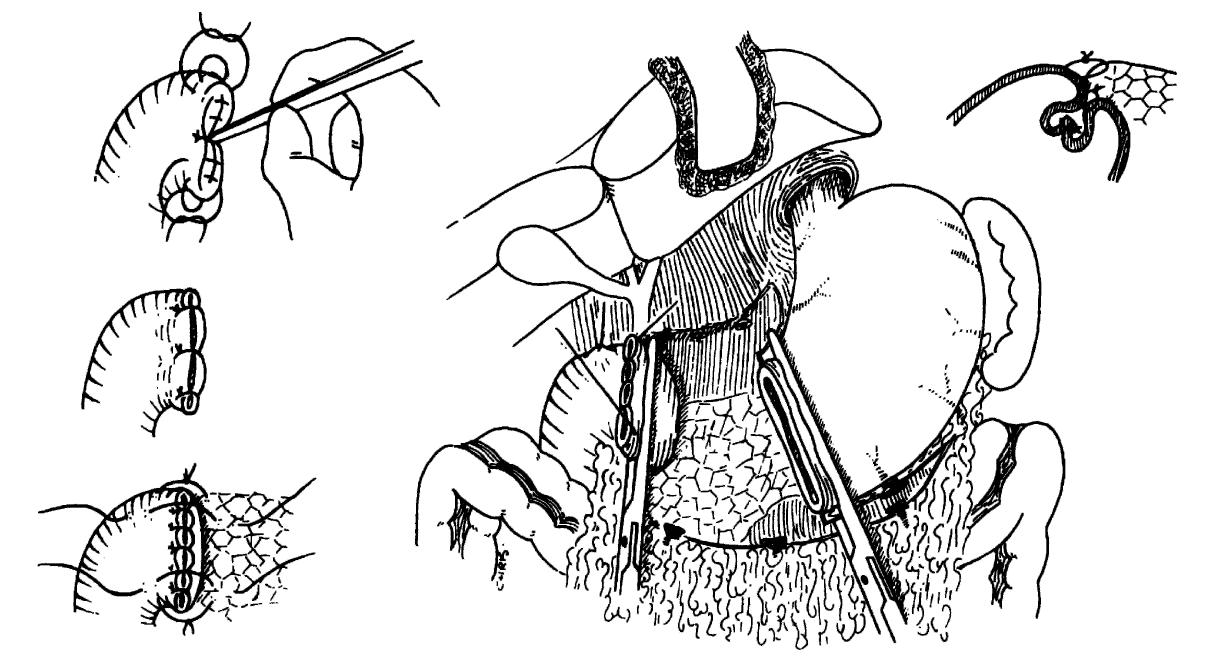
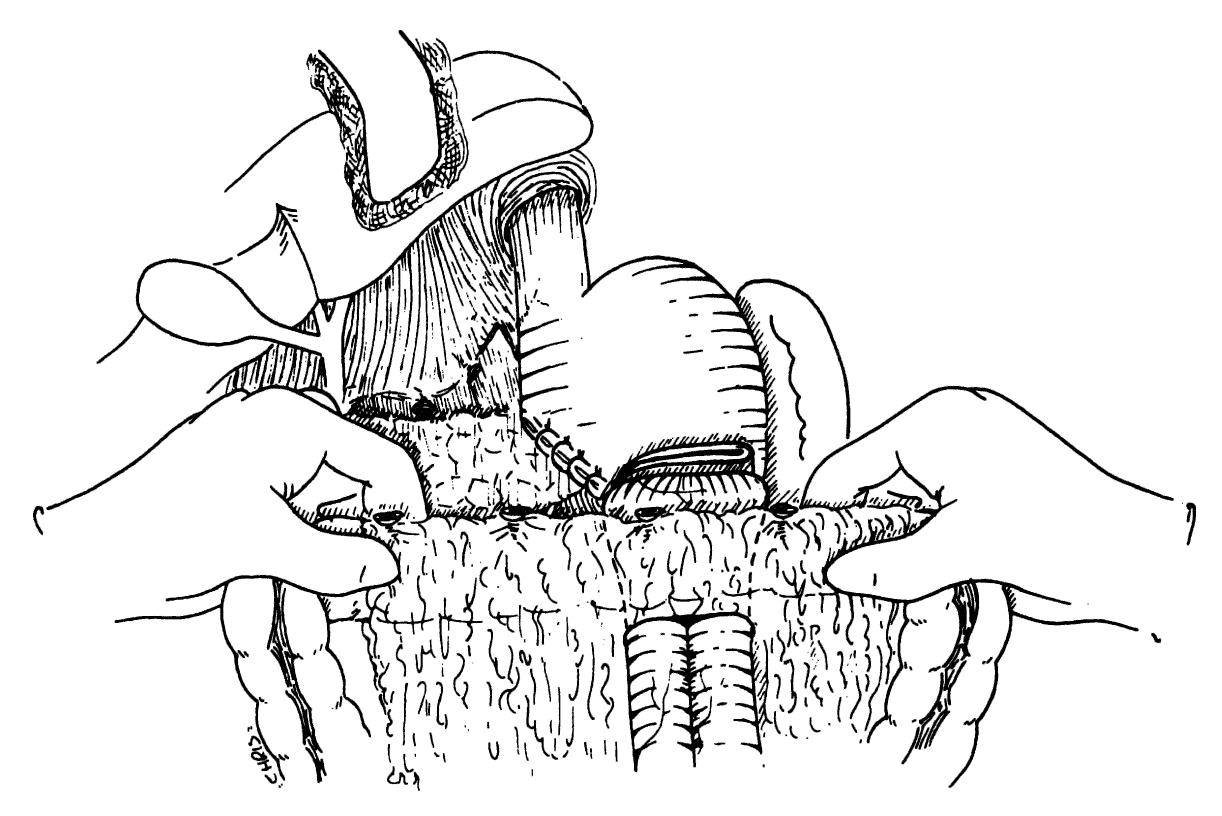
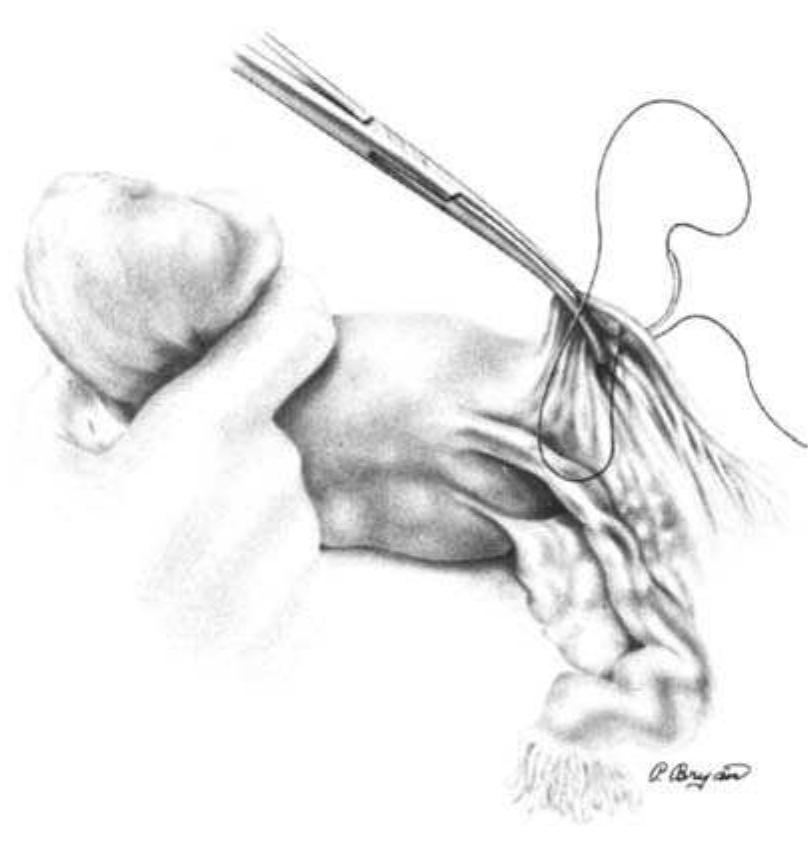
Background: Total scalp avulsion is a rare and devastating event. Microsurgical replantation is the sole method to achieve an ideal cosmetic outcome. In the literature, most studies have reviewed limited sample sizes. Most authors report better outcomes when a greater number of microvascular anastomoses are used. This strategy remains controversial, as some authors have suggested that one artery may be sufficient. Methods: From 2005 to 2008, seven patients who sustained scalp avulsion underwent microsurgical replantation. All of the vascular anastomoses were made with a branch of the superficial temporal artery. We did not use vein grafts. The ischaemia time was 4e16 h. Results: In six cases, a single artery and one to two veins were anastomosed; in another case, two arteries and three veins were anastomosed. Six of the seven scalp replantations were successful and achieved normal hair regrowth. In five of the six successful cases, we performed a single-artery anastomosis. Conclusion: Scalp avulsion is rare around the world but occurs relatively frequently in our country due to the lack of safe and secure working conditions in agriculture and industry. In cases where multiple arterial anastomoses are not possible, the present findings suggest that one branch of the superficial temporal artery may be sufficient to reperfuse the replanted scalp and achieve excellent aesthetic results.
Injury, 1993
The freafmenf of choice for the avulsed scalp is microvascular replanfafion. Affer replanfafion there are numerous arterial anasfomoses, with venous congestion. UstMlly an effort to establish it&w through fwo arferial anasfomoses is made. We elected to anasfotnose one artery and mulfipk veins in each of our pafienfs. We present three consecufive successful replanfafions of total scalp au&on, using only one arterial anasfomosis, and mulfiple veins. Surprisingly, fwo of the patients regained their abilify to elevate fheir eyebrows actively.
Microsurgery, 1993
A successful replantation of a totally avulsed scalp. including both eyebrows, with only one arterial and one venous anastomosis to the superficial temporal vessels is described. Apart from a small partial skin necrosis of the right eyebrow, the entire transplant survived. Subsequently, the patient required only minor additional skin grafting, correction of scars hair micrografts. Replantation of the total scalp based on two or more vessels has previously been recommended and reported elsewhere. In the present case, complete survival of the scalp on only one artery and one vein was demonstrated, indicating that replantation should be considered even if available vessels for anastomosis are minimal. 8 1993 Wiley-uss. Inc. with a skin expander, and reconstruction of the eyebrow with MCROSUROERY 1 4-1SS3 Es wird die erfolgreiche Replantation cines komplett ausgerissenen Skalps einschlieSlich beider Augenbrauen iiber eine Anastomosierung der A. und V. superficialis temporalis vorgestellt. AuOer einer kleinen Teibkrose der Haut im Bereich der rechten Augenbraue blieb das gcaamte Transplantat vital. Im weiteren Verlauf m t i g t e die Patientin lediglich geringfiigige ZuSiItzliche Hauaransplante, eine Narbenkorrektur mittels Hautexpander und die Rekonstruktion einer Augenbraue mit Minihaamansp lantaten. Die Replantation des gesamten Skalps iiber zwei oder meh GeFaSe wurde bereits friiher empfohlen und auch an anderer Stelle berichtet. Im vorliegenden Fall wurde gezeigt, das der Skalp in toto vital blieb bei nur einer Anastomose einer einzigen Arterie und einer einzigen vene. somit konnte ndchgewiesen werden, das eine Replantation unbedingt ins Auge gefaRt werden SOU, selbst wenn nur spiirliche Gefiiiiverhiiltnisse zur Anastomosierung vorhanden sind.
Plastic Surgery, 2010
Surgical and …, 1992
The arrangement and structure of the fascial layers of the scalp were studied in 48 red neoprene latex-injected cadavers with the aid of an operating microscope. The galea aponeurotica was continuous with a superficial temporal fascia. Deep to the galea, the subaponeurotic connective tissue was bilaminar. There was an outer, vascular, areolar layer, and an inner, avascular, membranous layer. Underlying the temporalis muscle, the pericranium was thinner and more adherent than elsewhere with no subpericranial tissue.
European Journal of Plastic Surgery, 1997
The authors report their experience in successful reimplantation of avulsed scalp in two patients with one arterial and one venous anastomosis to the superficial temporal vessels. In both cases a double vein graft, harvested from the dorsum of the hand, was interposed between the pedicle of the scalp and the recipient temporal vessels to avoid tension after trimming of the damaged segments. Scalp replantation based on two or more vessels has previously been reported in the literature. In the present cases, the complete survival of the scalp on only a single vascular pedicle suggests that replantation should be considered also when the available vessels for the anastomosis are few. Moreover, even if these reconstructions are lengthy, a prolonged ischemic interval does not appear to be a significantly limiting factor for the success of the revascularization. The cosmetic and psychological success of these cases lend support to the idea that one should always attempt a microvascular replantation of avulsed scalps.
Clinical Anatomy, 2010
Microsurgery, 2012
Background: Soft tissue defects of the scalp may result from multiple etiologies and can be challenging to reconstruct. We discuss our experience with scalp replantation and secondary microvascular reconstruction over 36 years, including techniques pioneered at our institution with twin-twin scalp allotransplant and innervated partial superior latissimus dorsi (LD) for scalp/frontalis loss. Methods: A retrospective review of all patients presenting with scalp loss requiring microvascular reconstruction at a single center was performed from January 1971 to January 2007. Medical records were reviewed for age, gender, defect size/location, etiology, type of reconstruction, recipient vessels used, vein grafts, and complications. Results: Thirty-three patients were identified; mean age was 33 years (range, 7-79). Mean scalp defect size was 442 cm 2 (range, 120-900 cm 2). Thirty-six microvascular reconstructions were performed; of these, 10 scalp replants and 26 microvascular tissue transfers. Of these 26, 17 were LD based (partial superior LD with and without reinnervation, LD combined with serratus, LD combined with parascapular, LD combined with split rib, LD only) and 2 free scalp allotransplant among others. The superficial temporal artery and vein was used as recipient vessels in 70% of cases. Overall, microvascular success rate was 92%; complications occurred in 14 cases, nine major (tumor recurrence [n 5 2], partial flap loss [n 5 2], replant loss [n 5 3, size <300 cm 2 ], hematoma [n 5 2]) and five minor (donor site seroma /hematoma [n 5 3], flap congestion [n 5 1], superficial wound infection [n 5 1]). Conclusions: Every attempt should be made at scalp replantation when the patient is stable and the parts salvageable. Larger avulsion defects had higher success rates after replantation than smaller defects (<300 cm 2), with the superficial temporal artery and vein most commonly used for recipient vessels (P 5 0.0083). Microvascular tissue transfer remains a mainstay of treatment for scalp defects, with LD-based flaps, demonstrating excellent versatility for a range of defects. V V
2019
The facial artery (a branch of the external carotid artery) is the main artery of the face. It gives rise to seven branches viz. inferior labial, superior labial, inferior alar, superior alar, lateral nasal and angular arteries, which are variable. This study included a dissection of twenty embalmed adult cadaveric head and neck specimens. The parameters of origin, branching patterns, termination and variations were analysed and compared with sex and laterality. The facial artery followed the standard anatomical description of origin in 84.62 % of the sample. Variations: (i) origin as a linguofacial trunk in 12.82 % and (ii) high origin in 2.56 % was observed. Male specimens displayed a higher number of linguofacial trunk origins (7.69 %). The branching patterns of the facial artery was classified into six types, with subtypes for Types 1 and 2. Subtype 1-A (standard anatomical description with early termination) occurred in most of the sample (46.15 %). Males were found to have more variations in branching patterns than females (48.72 % and 41.03 % respectively). Termination of the facial artery was as follows: inferior labial artery (5.13 %), superior labial artery (10.26 %), inferior alar artery (10.26 %), superior alar artery (46.15 %), lateral nasal artery (5.13 %), and angular artery (20.51 %). A single case (2.56 %) of an abortive artery was noted. Statistical analysis showed that sex was independent of each parameter observed in this study. Anatomical knowledge of the facial artery is of importance to clinicians and surgeons during procedures such as musculomucosal, island flaps and aesthetic dermatology.

Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
Related papers
Annals of Plastic Surgery, 2011
Journal of Craniofacial Surgery, 2019
Surgery Today, 1994
Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 2009
Cureus, 2020
Current Concepts in Plastic Surgery, 2012
Bangladesh Journal of Anatomy, 2014
Morphologie, 2019
Journal of Neurosurgery, 1978
Revista Brasileira de Cirurgia Plástica (RBCP) – Brazilian Journal of Plastic Sugery, 2020
Frontiers of neurology and neuroscience, 2008
Journal of Neurosurgery, 1976
Journal of Neurosurgery, 2006
International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 2019
British Journal of Plastic Surgery, 1995
Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy, 1999
Skull Base, 2007
International Journal of Advanced Research, 2016
Neurosurgery Clinics of North America, 2009
Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy, 2010
 Sharen Selvadurai
Sharen Selvadurai