How does the existence of case systems, and strict word order patterns affect the learnability of a given language? We present a series of connectionist simulations, suggesting that both case and strict word order may facilitate syntactic... more
Connectionist psycholinguistics: The very idea
Psycholinguistics refers to the empirical study of the human language processing system, typically using behavioral experiments. This chapter considers attempts to capture psycholinguistic data using connectionist models . We primarily... more
Because I don't know what a cultural imaginary is, nor how to put (or find) something in one, I propose instead to provide a brief, general account of what, when we think and write about, and thereby determine, the characteristics of... more
A s y m bol is a pattern (of physical marks, electromagnetic energy, e t c . ) which denotes, designates, or otherwise has meaning. The notion that intelligence requires the use and manipulation of symbols, and that humans are therefore... more
For the least the last 10 years, there has been growing interest in, and growing evidence for, the intimate relations between more abstract or higher order cognition-such as reasoning, planning, and language use-and the more concrete,... more
This article presents a model of long term forgetting based on 3 ideas: (a) Memory for a stimulus can be described by a population of accessible traces; (b) probability of retrieval after a delay is predicted by the proportion of traces... more
In 4 experiments, rats were given intermixed or blocked preexposure to an array of landmarks that subsequently defined the location of a hidden goal in a Morris pool task. Previous research has shown that intermixed preexposure to pairs... more
According to , the analogy space:time::vision:audition is seductive but misleading:
We discuss three aspects of research on perceptual organization: emergence, epiphenomenalism, and experimentation.
Previous studies have shown that change detection performance is improved when the visual display holds features (e.g., a colour and an orientation) that are grouped into different parts of the same object compared to when they are all... more
In this article, we propose that adolescents' online interactions are both a literal and a metaphoric screen for representing major adolescent developmental issues, such as sexuality and identity. Because of the public nature of Internet... more
Because causal relations are neither observable nor deducible, they must be induced from observable events. The 2 dominant approaches to the psychology of causal induction-the covariation approach and the causal power approach-are each... more
In this chapter, we describe four psychological phenomena that offer clues to how untutored people infer causal relations. We contrast the predictions for these phenomena, all involving asymmetries in causal inferences, according to two... more
Five experiments investigated transfer from multiple analogs to a superficially dissimilar target problem. When subjects explicitly compared the analogs and then immediately attempted to solve the target problem in the context of a single... more
This article proposes that learning of categories based on cause-effect relations is guided by causal models. In addition to incorporating domain-specific knowledge, causal models can be based on knowledge of such general structural... more
Theories of analogical reasoning differ in the roles they ascribe to pragmatic factors as a source of constraints on analogical mappings. The multiconstraint theory as instantiated in the ACME model claims that pragmatic constraints... more
The use of analogy in human thinking is examined from the perspective of a multiconstraint theory, which postulates 3 basic types of constraints: similarity, structure, and purpose. The operation of these constraints is apparent in... more
Theories of analogical reasoning have assumed that a 1-to-1 constraint discourages reasoners from mapping a single element in 1 analog to multiple elements in another. Empirical evidence suggests that reasoners sometimes appear to violate... more
We present a Bayesian model of causal learning that incorporates generic priors on distributions of weights representing potential powers to either produce or prevent an effect. These generic priors favor necessary and sufficient causes.... more
The lateral posterior nucleus and pulvinar (LP-pulvinar complex) are the principal thalamic nuclei associated with the elaborate development of the dorsal and ventral streams of the parietal cortex in primates. In humans, a novel site of... more
Designing auditory displays requires understanding how different attributes of sound are processed. Operators must often listen to a particular stimulus dimension and make control actions contingent on the auditory information. Three... more
Research on auditory graphs has investigated mappings, scalings, and polarities , as well as the addition of some contextual design features , in order to improve performance. However, little has been done to quantify the performance... more
Two eye-movement experiments examined the processing of sentences containing reduced relative constructions. In the first experiment, animacy of the sentential subject, structural ambiguity, and parafoveal preview of syntactically... more
performing a single task (e.g., simply reading sentences), this would be evidence that both tasks are drawing upon the same cognitive resources. Further, the rate of slowdown may also indicate the degree of resource utilization.
The techniques of computer vision have reached excellent results when applied in the different areas. These methods are used in the discovery of knowledge from images of the real world. This project aims to apply these techniques in... more
Why do we remember some events and not others, and how does this change in old age? Although there are a variety of ways to address this question, the present perspective emphasizes how value can have a profound eVect on how we use our... more
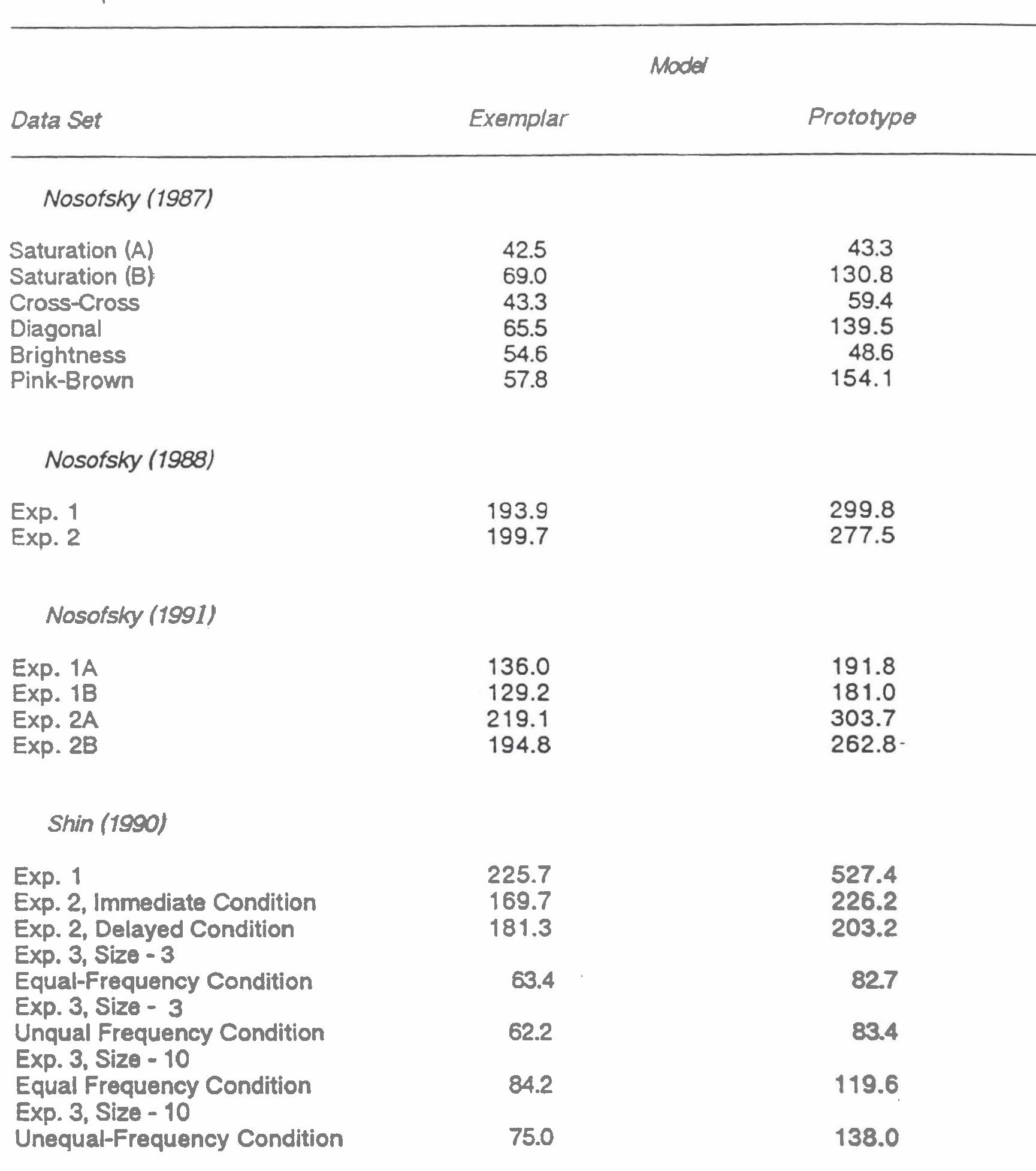
Observers were presented with pairs of objects varying along binary-valued attributes and learned to predict which member of each pair had a greater value on a continuously varying criterion variable. The predictions from exemplar models... more
The authors develop and test generalized versions of take-the-best (TTB) and rational (RAT) models of multiattribute paired-comparison inference. The generalized models make allowances for subjective attribute weighting, probabilistic... more
Speeded perceptual classification experiments were conducted to distinguish among the predictions of exemplar-retrieval, decision-boundary, and prototype models. The key manipulation was that across conditions, individual stimuli received... more
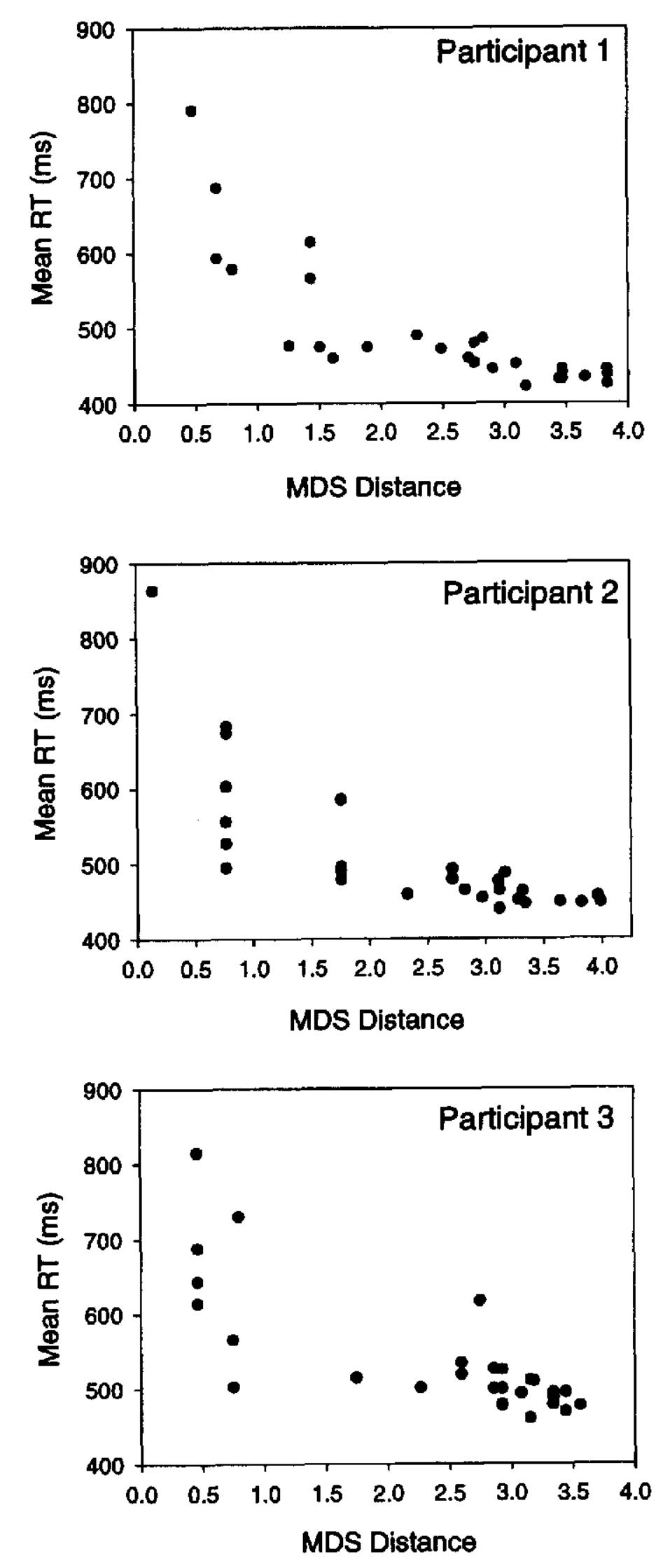
Multidimensional scaling (MDS) techniques provide a promising measurement strategy for characterizing individual differences in cognitive processing, which many clinical theories associate with the development, maintenance, and treatment... more
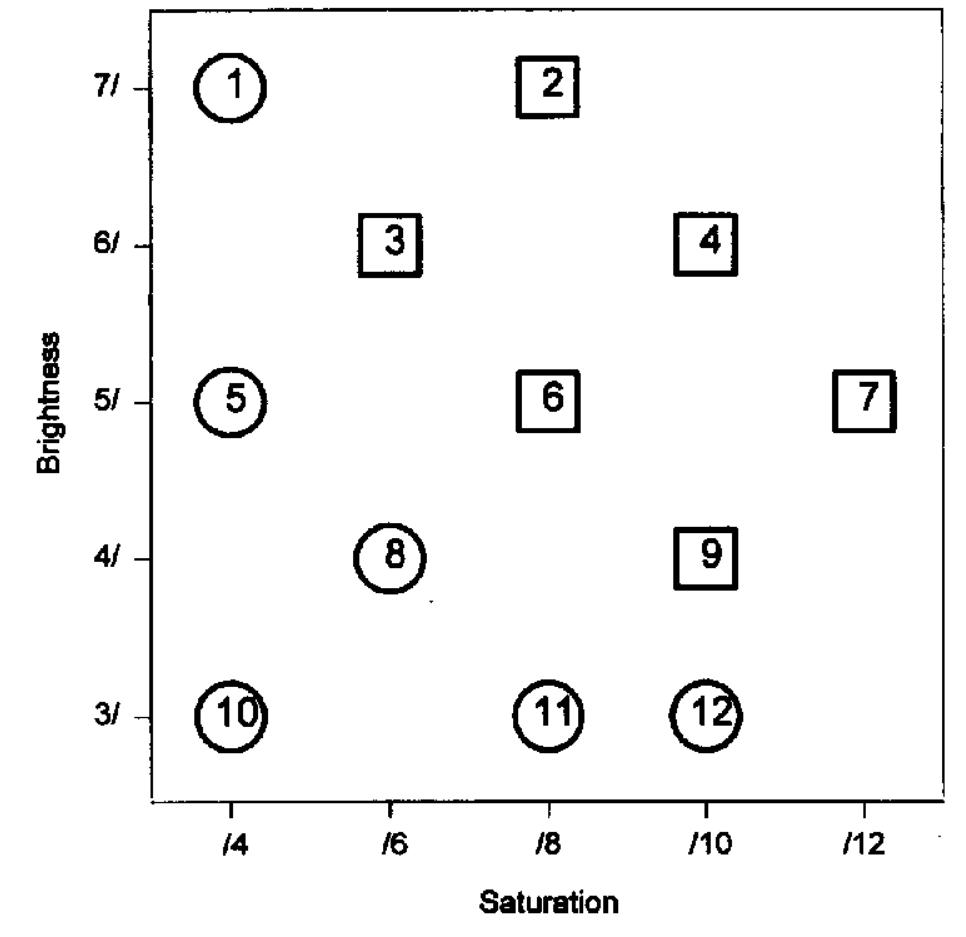
Experiments were conducted in which observers learned to classify simple perceptual stimuli into low-variability and high-variability categories. Similarities between objects were measured in independent psychological-scaling tasks. The... more
R. M. Nosofsky and T. J. Palmeri's (1997) exemplar-based random-walk (EBRW) model of speeded classification is extended to account for speeded same-different judgments among integral-dimension stimuli. According to the model, an important... more
The authors propose and test an exemplar-based random walk model for predicting response times in tasks of speeded, multidimensional perceptual classification. The model combines elements of R.M. Nosofsky's (1986) generalized context... more
The authors compared the exemplar-based random-walk (EBRW) model of and the decision-bound model (DBM) of on their ability to predict performance in Garner's (1974) speeded classification tasks. A key question was the extent to which the... more
A formal proof is pnnided that Anderson's {1990) rational model of categorization generalizes the Medin and Schaffer {1978) context model. According to the context model, people represent categ<>ries by storing individual exemplars in... more
A rule-instantiation model and a similarity-to-exemplars model were contrasted in terms of their predictions of typicality judgments and speeded classificalions-for-members-oflogically defined categories. In Experiment 1, subjects learned... more
Subjects learned to classify perceptual stimuli varying along continuous, separable dimensions into rule-described categories. The categories were designed to contrast the predictions of a selective-attention exemplar model and a simple... more
Previously published sets of classification and old-new recognition memory data are reanalyzed within the framework of an exemplar-based generalization model. The key assumption in the model is that, whereas classification decisions are... more
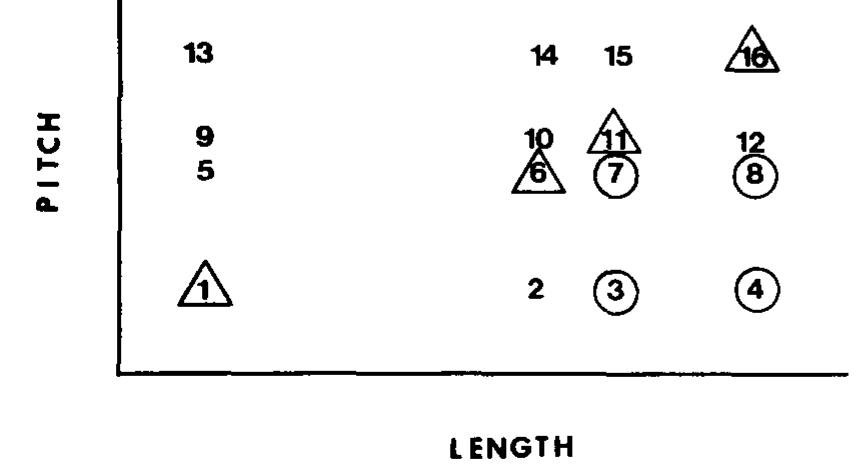
The bow and sequential effects in absolute identification are investigated in this paper by following two strategies: (1)Experiments are performed in which sequential dependencies in signal presentations are manipulated, and (2)analyses... more
In this chapter, I consider how objects might phenomenally look to beings with more coarse-grained visual systems than us. Many hold that to such beings, objects may phenomenally look red, without phenomenally looking a particular shade... more



















































![RAT-Easy and RAT-Hard Test Pairs Used in Experiment 2 Note. RAT = classic rational model; EvA = total evidence for A; EvB = total evidence for B; EVDIFF = |EvA = EvB]. The average difference in total evidence is 7.27 for six-mismatch, RAT-Easy pairs; 0.88 for six-mismatch, RAT-hard pairs; 4.47 for five-mismatch, RAT-easy pairs; and 0.57 for five- mismatch, RAT-hard pairs. Table 9](https://figures.academia-assets.com/3328/table_009.jpg)


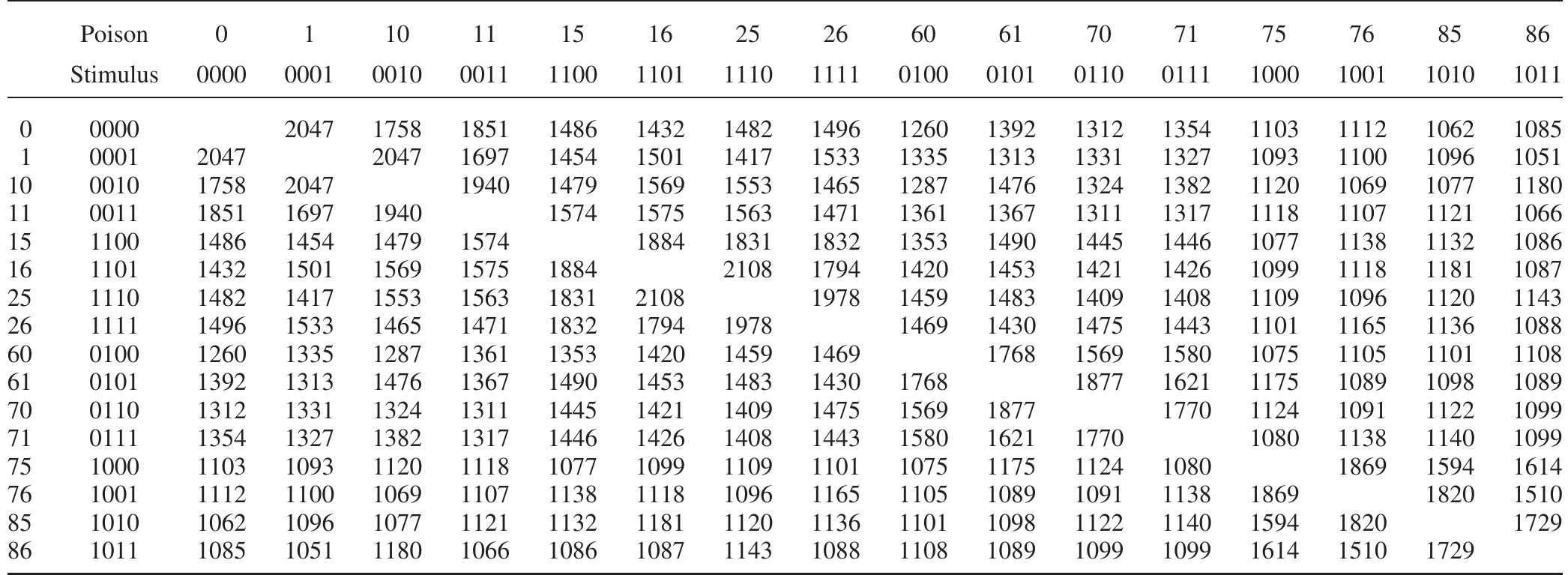
![Stimulus Pairs Used in Experiment 3 Note. EvA = total evidence for A; EvB = total evidence for B; EVDIFF = |EvA — EvB]. All pairs matched on Feature 6 and mismatched on all other features. The distribution of poisonous features (represented by Is) differed across pairs, with three types: those in which one insect had five poisonous features and the other had zero (5/0 pairs), those in which one insect had four poisonous features and the other had one (4/1 pairs), and those in which one insect had three poisonous features and the other had two (3/2 pairs). The 5/0 pairs and the 4/1 pairs were considered easy, and the 3/2 pairs were considered hard. The average difference in total evidence is 3.06 for easy pairs (5/0 and 4/1) and 0.919 for hard pairs (3/2). Table 11](https://figures.academia-assets.com/3328/table_012.jpg)






























![Figure 14. Scatterplot of observed mean correct response times (ms) in each type of speeded classification task against the predicted mean correct response times from the exemplar-based random walk (EBRW) mode], Experiment 3. Values in parentheses are the predicted proportions of correct responses in each task, according to the EBRW. The solid square for the condensation task is the prediction with the response criterion set at A = 4, whereas the open square for the condensation task is the prediction with the response criterion set at A = 6. Circle = correlated task; triangle (up) = control task; diamond = filtering task; triangle (down) = stretch-filtering task; square = condensation task.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/3356/figure_014.jpg)







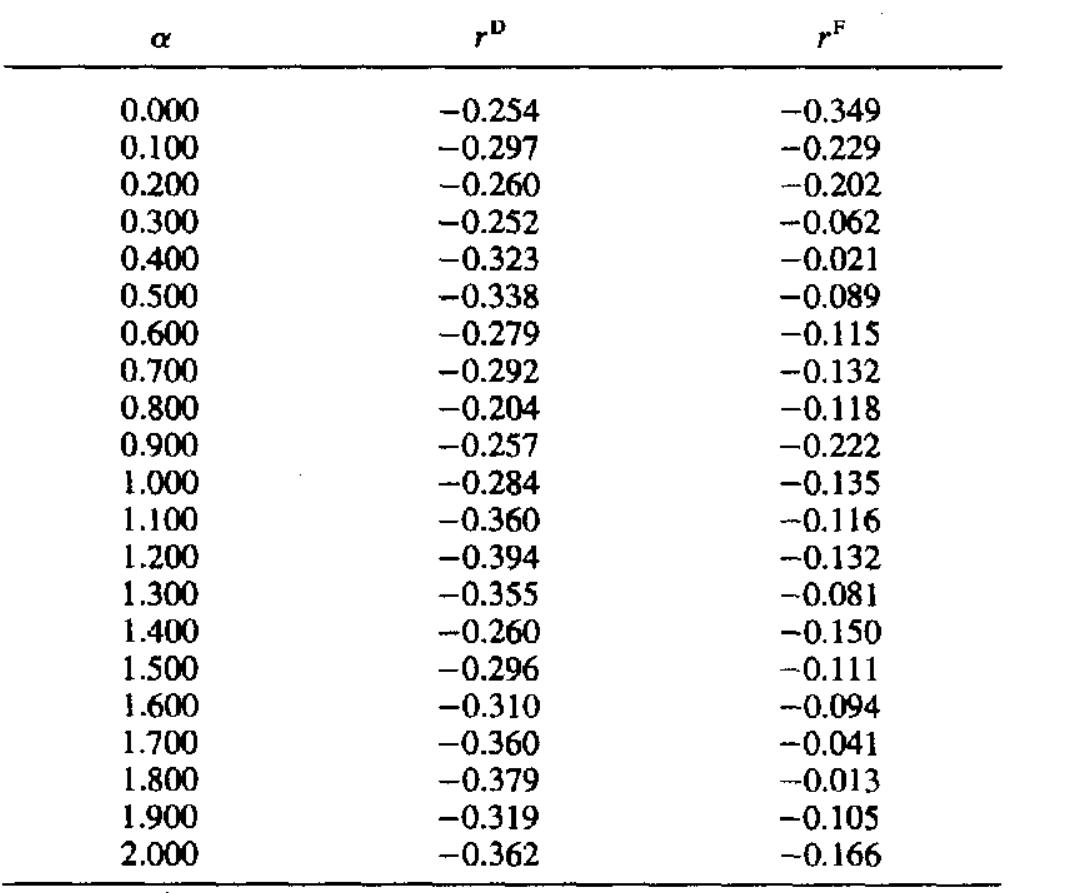






![Figure 4. Mean RTs (MRTs) and standard deviations of RTs (Stdevs) plotted as a function of task position. The power functions that best fit these curves are also illustrated. Mean RTs and accuracies across tasks. Before pre- senting the analysis of the individual stimulus RT distri- butions, we briefly characterize the global patterns of re- sults observed across the tasks. The mean correct RTs and accuracies for each of the eight tasks are presented in Table 1. The main results replicate the classic patterns for integral-dimension stimuli. Mean RT was significantly slower in the filtering tasks than in the control tasks, in- dicating interference [pitch, #(25) = 3.86, p< .001; loud- ness, ¢(25) = 2.81, p < .01]. Mean RT in the correlated tasks was significantly faster than in either type of con- trol task, indicating facilitation [pitch, t(25) = 6.29, p< .001; loudness, #(25) = 5.63, p< .001]. Mean RTs for dis- criminating pitch were somewhat faster than for discrim- inating loudness [control, (25) = 2.90, p < .01; filtering, This transformation removes the estimated effect of task position on the mean RTs. Likewise, let P;(7) denote the standard deviation of RTs predicted by the power function for position i, and let G, denote the grand mean of these standard deviations. In the second step, all of the](https://figures.academia-assets.com/3357/figure_004.jpg)





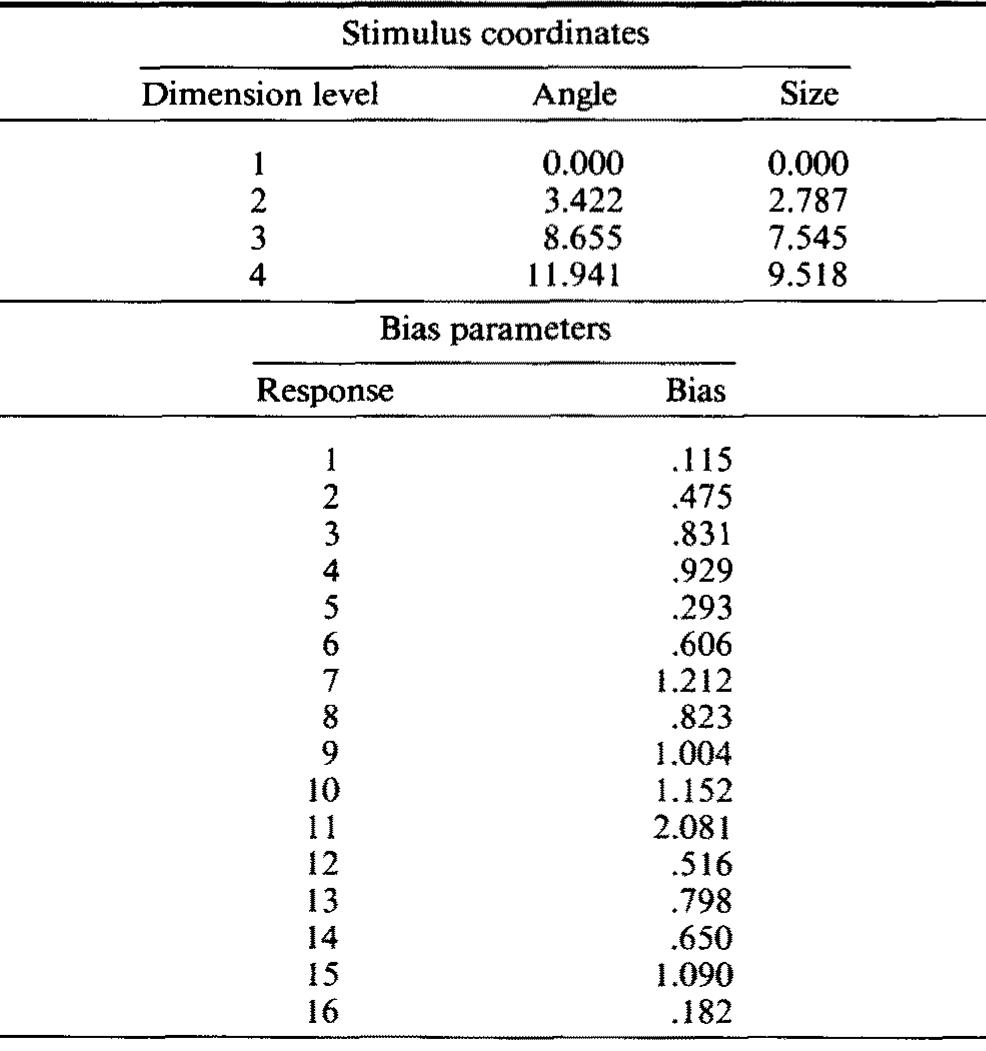
![Figure 10. Panel a: Stimulus coordinates derived by fitting the EBRW model to the RT dis- tribution data. Panel b: GRT representation derived by fitting the DBM to the RT distribu- tion data. filter-pitch MFRT on only 48% of the simulations, and the control-loudness MFRT was faster than the filter— loudness MFRT on only 48% of the simulations. Thus, the EBRW model predicts an advantage for the control MERTs, whereas the DBM predicts either no difference or a slight advantage for the filtering MFRTs. In our analysis of the actual observed data, we found that 65% of the participants had faster control—pitch MFRTs than filter—pitch MFRTs, and that 73% of the participants had faster control-loudness MFRTs than filter—loudness MFRTs. Overall, the observed MFRTs in the control tasks (M = 308.4 msec) were significantly faster than the MERTs in the filtering tasks (VM = 326.3 msec) [¢(25) = 6.46, p < .001]. Thus, with regard to the fastest RTs in the The shortcomings of the DBM can be conceptualized as follows. To account for filtering interference in the mean RTs, this model posits the existence of increased variance due to uncertainty effects (Figure 3c), mean-shift integral- ity (Figure 3d), or some combination of these two factors. The best-fitting parameters for the DBM seem to be try- ing to make use of both sources of interference. There is a mean-shift integrality (Figure 10b), and the standard- deviation multiplier in the filtering tasks is greater than one (kK = 1.04; see Table 5). If the magnitude of these pa- rameters were increased, the DBM would be more suc- cessful at predicting the overall interference effects in the](https://figures.academia-assets.com/3357/figure_010.jpg)

























![Mean Typicality Ratings for Each Type of Stimulus as a Function of Conditions in Experiment 2 Table 5 The 16 typicality ratings obtained for each subject were averaged to form three ratings corresponding to xy, xy (or xy), and xy stimuli. The mean ratings for these three stimulus types are shown as a function of conditions in Table 5. The pattern of typicality ratings mirrors the paired-comparison judgments. In Condition Poo, ratings for the xy (or xy) stimuli exceeded those for xy; the rat- ings were roughly equal in Condition Po; and ratings for xy exceeded those for xy (or xy) in Condition P33. A3 x3 analysis of variance with conditions (Poo, Pio, P33) and stimuli (xy, xy, xy) as factors revealed that this interac- tion of typicality ratings with learning conditions was highly significant [F(4,174) = 12.07, MS. = 2.90, p < .01]. This dramatic influence of exemplar frequency on the goodness-of-example judgments is consistent with a model in which it is assumed that individual exemplars form an important component of the mental representa- tion for logically defined concepts.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/3373/table_005.jpg)


























![Note. N = number of observations on which each probability is based (number of probes per category [4, 8, or 12] times number of subjects [18]). Observed values in each cell were estimated from Omohundro’s (1981) Figure 2, Predicted values were based on 1,000 simulated experiments.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/3380/table_002.jpg)


![Note. N= number of observations on which each probability is based (number of subjects per condition [24] times number of probe-pair tests per subject [4 or 8]). Predicted and Observed Probabilities With Which the First Member of Each Pair Was Chosen as the Better Example of the Concept in Bourne’s (1982) Experiment](https://figures.academia-assets.com/3380/table_005.jpg)
![Note, N = number of observations on which each probability is based (number of subjects per condition [24] times number of xy tests [5]). Predicted and Observed Probabilities With Which xy Instances Were Called Positive in Bourne’s (1982) Speeded Classification Test Table 6](https://figures.academia-assets.com/3380/table_006.jpg)