Clinical Neuroanatomy Waxman
…
1 file

Sign up for access to the world's latest research
Abstract
27 ed
Figures (508)




























![FIGURE 2-16 Main changes that take place in an injured nerve fiber. A: Normal nerve fiber, with its perikaryon and the effector cell (striated skeletal muscle). Notice the position of the neuron nucleus and the amount and distribution of Nissl bodies. B: When the fiber is injured, the neuronal nucleus moves to the cell periphery, Niss] bodies become greatly reduced in number (chromatolysis), and the nerve fiber distal to the injury degenerates along with its myelin sheath. Debris is phagocytized by macrophages. C: The muscle fiber shows pronounced disuse atrophy. Schwann cells proliferate, forming a compact cord that is penetrated by the growing axon. The axon grows at a rate of 0.5 to 3 mm/d. D: In this example, the nerve fiber regeneration was successful, and the muscle fiber was also regenerated after receiving nerve stimuli. E: When the axon does not penetrate the cord of Schwann cells, its growth is not organized and successful regenera tion does not occur. (Redrawn and reproduced, with permission, from Willis RA, Willis AT: The Principles of Pathology and Bacteriology, 3rd ed. Butterworth, 1972.)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35806578/figure_027.jpg)




























































































![FIGURE 7-14 Magnetic resonance image showing, in the sagittal plane, a mass lesion (arrow heads) in the patien described in Case Illustration 7-3. The mass lesion, which was shown on biopsy to be a germinoma, compressed the quadrigeminal plate and obstructed the cerebral aqueduct [arrow]. (Case illustration and image courtesy of Joachim Baehring, MD, Yale University School of Medicine.) This tragic case illustrates the locked-in syndrome. The in- farction, in the base of the pons, destroyed the corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts and thus produced paralysis of the limbs and bulbar musculature. Preservation of the oculomotor and trochlear nuclei and of their nerves permitted some](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35806578/figure_112.jpg)
































































































![FIGURE 11-19 An81-year-old woman was admitted with shortness of breath and fever. She was found to have a right middle lobe pneumonia, the third pneumonia in three months. Neurologic examination r evealed a vocal cord paralysis on the right side; the gag reflex was absent and there was loss of bulk of the trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles on the right side; the t ongue appeared slightly atrophic o1 the right and deviated to the right upon protrusion; there was asymmetric elevation of the soft palate (deviation to the left due to paralysis on the right side). The patient aspirated during a swallowing evaluation. Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain demonstrated amass lesion within the jugular foramen and the petrous bone on the right side [left image, arrow heads]. Computed t omography of the base of the skull showed osteolytic changes within the right petrous temporal and occipital bone [right: arrow heads; asterisk: jugular foramen]. A biopsy confirmed the clinically suspected diagnosis of glomus jugulare tumor which had impaired function of the ninth, t enth, eleventh and twelfth cranial nerves. The patient was treated with radiation. (Courtesy of Dr. Joachim Baehring.)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35806578/figure_201.jpg)























































![FIGURE 15-3 Neural components of the retina. C, cone; R, rod; MB, RB, FB, bipolar cells (of the midget, rod, and flat types, respectively); DG and MG, ganglion cells (of the diffuse and midget types, respectively); H, horizontal cells; A, amacrine cells. (Reproduced, with permission from Dowling JE, Boycott BB: Organization of the primate retina: Electron microscopy. ProcRoy Soc Lond Ser B [Biol] 1966;166:80.)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35806578/figure_251.jpg)











![FIGURE 15-18 Activation of visual cortex as shown by functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). A: An oblique axial anatomic MRI. The region showing increased activity in response to a full-field patterned stimulus has been assessed by fMRI (using a method known as echoplanar MRI) and is shown in white. B: Activation of the visual cortex on the left side in response to patterned visual stimulation of the right visual hemifield (black) and activation of the right-sided visual cortex in response to patterned stimulation of the left hemifield. The changes in signal intensity are the result of changes in flow, volume, and oxygenation of the blood in response to the stimuli. (Data from Masuoka LK, Anderson AW, Gore JC, McCarthy G, Novotny EJ: Activation of visual cortex in occipital lobe epilepsy using functional magnetic r esonance imaging. Epilepsia 1994;35[Supp 8]:86.) “ As visual information is relayed from cell to cell in the primary visual cortex, it is processed in increasingly complex](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35806578/figure_265.jpg)













































































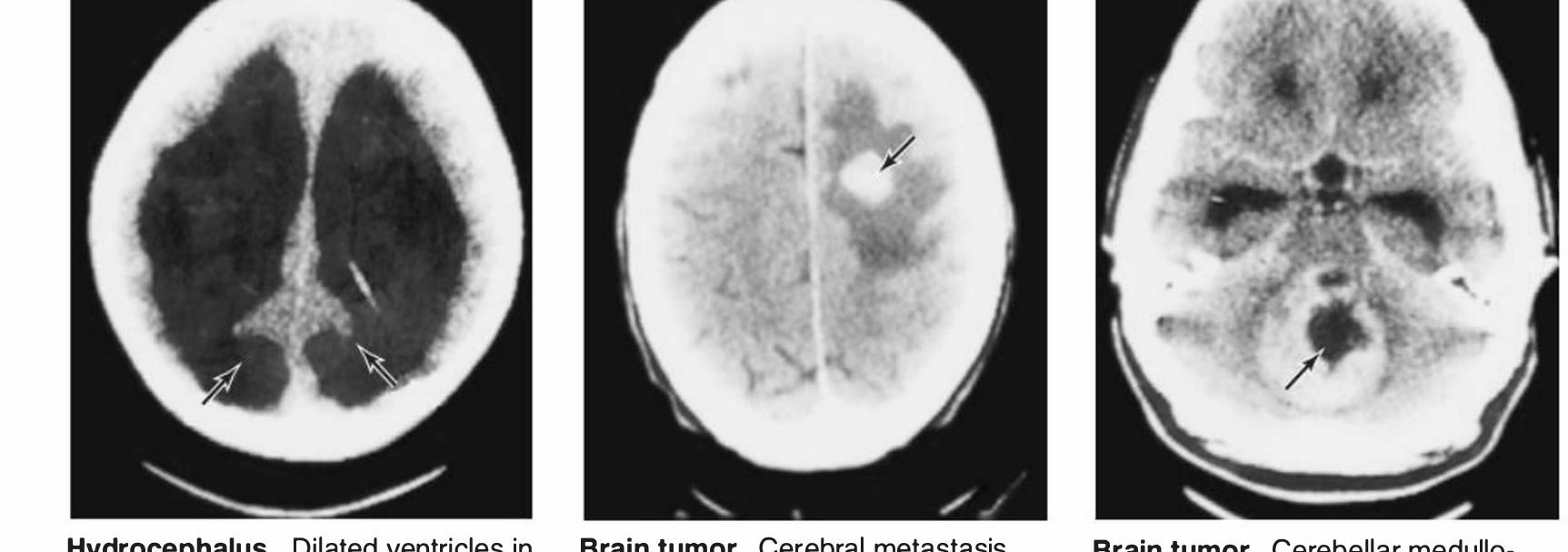
![The CT scanning apparatus rotates a narrow x-ray beam around the head. The quantity of x-ray absorbed in small vol- umes (voxels [volume elements, or units]) of brain, measuring approximately 0.5 mm? x 1.5 mm or more in length, is com- puted. The amount of x-ray absorbed in any slice of the head can be thus determined and depicted in various ways as pixels](https://figures.academia-assets.com/35806578/figure_337.jpg)



























































































































Related papers
Springer eBooks, 2008
, except for brief excerpts in connection with reviews or scholarly analysis. Use in connection with any form of information storage and retrieval, electronic adaptation, computer software, or by similar or dissimilar methodology now known or hereafter developed is forbidden. The use in this publication of trade names, trademarks, service marks, and similar terms, even if they are not identifi ed as such, is not to be taken as an expression of opinion as to whether or not they are subject to proprietary rights.
All trademarks are trademarks of their respective owners. Rather than put a trademark symbol after every occurrence of a trademarked name, we use names in an editorial fashion only, and to the benefi t of the trademark owner, with no intention of infringement of the trademark. Where such designations appear in this book, they have been printed with initial caps. McGraw-Hill eBooks are available at special quantity discounts to use as premiums and sales promotions, or for use in corporate training programs. To contact a representative please e-mail us at
Anatomy of the Brain - Mayfield Clinic
F unctional MRI is a noninvasive method used to localize critical cognitive functions. Accordingly, recent interest has grown toward understanding whether fMRI-in particular, the BOLD signal-can be used to aid presurgical planning of lesion resections involving eloquent cortex to minimize disruption of cognitive function and ensure maximal tumor tissue removal. The current gold-standard method of localization is electrical cortical mapping, which, while extremely precise and predictive of postoperative deficits, is also invasive and time consuming. 30, Thus, it would be beneficial to derive fMRI-based measures that not only match the utility of electrical cortical mapping, but also help to minimize patient morbidity. Although fMRI-based mapping and electrical cortical mapping have shown varied con-Object. Functional MRI (fMRI) has the potential to be a useful presurgical planning tool to treat patients with primary brain tumor. In this study the authors retrospectively explored relationships between language-related postoperative outcomes in such patients and multiple factors, including measures estimated from task fMRI maps (proximity of lesion to functional activation area, or lesion-to-activation distance [LAD], and activation-based language lateralization, or lateralization index [LI]) used in the clinical setting for presurgical planning, as well as other factors such as patient age, patient sex, tumor grade, and tumor volume.

Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
Related papers
Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, 1966
Journal of Neuro-Ophthalmology, 2004
Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy, 2007
World neurosurgery, 2010
AJNR. American journal of neuroradiology
 Ale Rmz
Ale Rmz