Local field correction particle image velocimetry (LFCPIV), which was first presented in 1997, is the only correlation PIV method able to resolve flow structures smaller than the interrogation window. It presents advantages over... more
Particle image velocimetry with local field correction (LFC PIV) has been tested in the past to obtain two components of velocity in a two dimensional domain (2D2C). When compared to conventional correlation based algorithms, this... more
The analysis of the internal flow structure and performance of a specific fluidic diverter actuator, previously studied by time-dependent numerical computations for subsonic flow, is extended to include operation with supersonic actuator... more
Experimental Study of the Power Profile Airfoil Equipped with Plasma Flow Control LIBIN DANIEL, JAMEY JACOB, Oklahoma State University -This presentation discusses results from an experimental study of the power profile airfoil at low... more
Thrust Vectoring Flow Control Using Plasma Actuators JAMEY JACOB, MICHAEL BOLITHO, Oklahoma State University -Thrust vectoring flow control is demonstrated using plasma synthetic jet actuators (PSJA). The PSJA is a geometric variant of a... more
Two independent spheres were placed in a side by side arrangement and flow structure in the wake region of the spheres was investigated with a Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) system when the spheres were in a boundary layer over a flat... more
Smart structures sense external stimuli, process the sensed information, and respond with active control to the stimuli in real or near-real time. The response to external stimuli can be through deforming or deflecting the structure, or... more
of motivation, accomplishments, and future plans This two-month visit at CTR was devoted to investigating possibilities in LES modeling in the context of the 3-D vortex particle method (=vortex element method, VEM) for unbounded flows. A... more
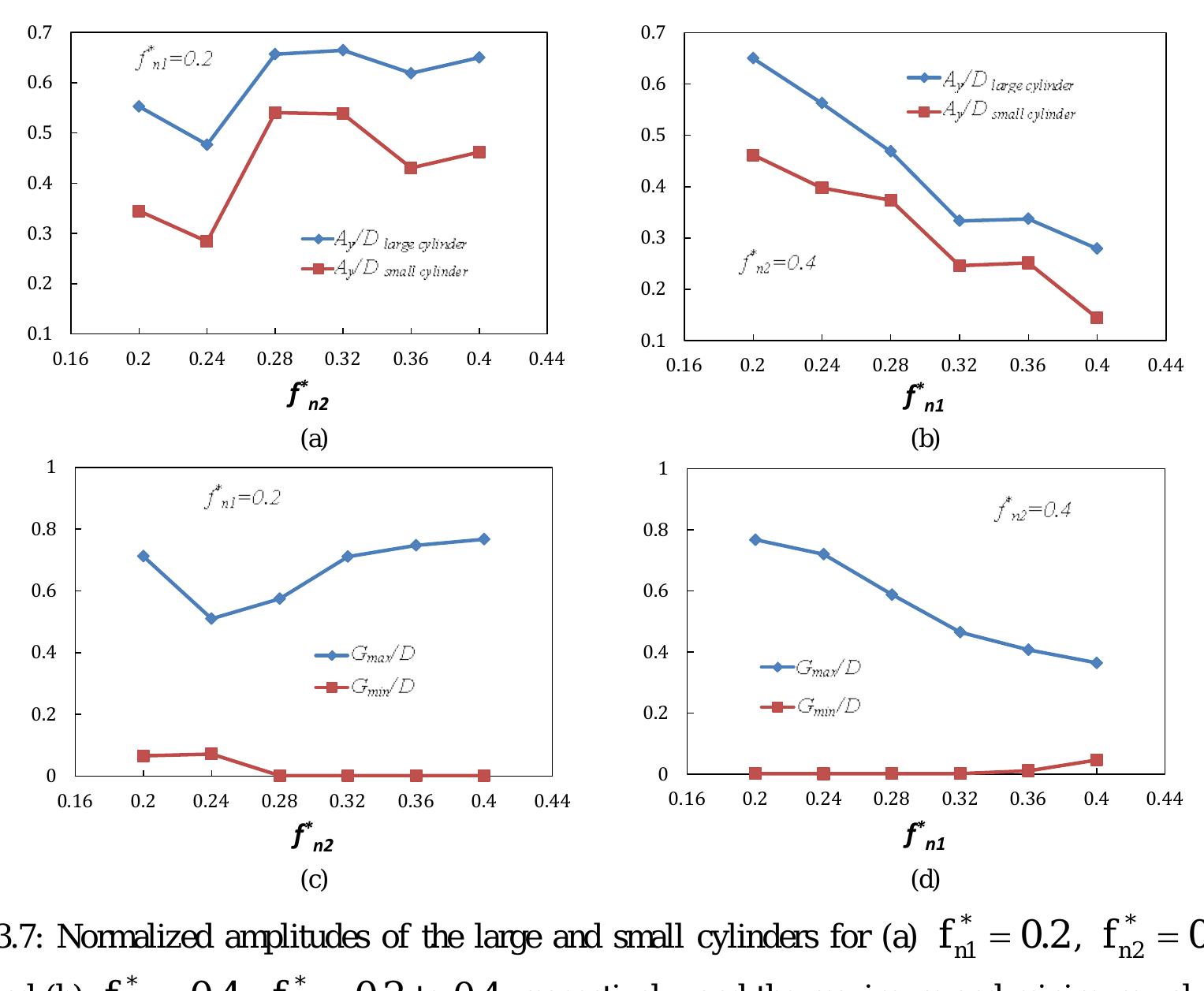
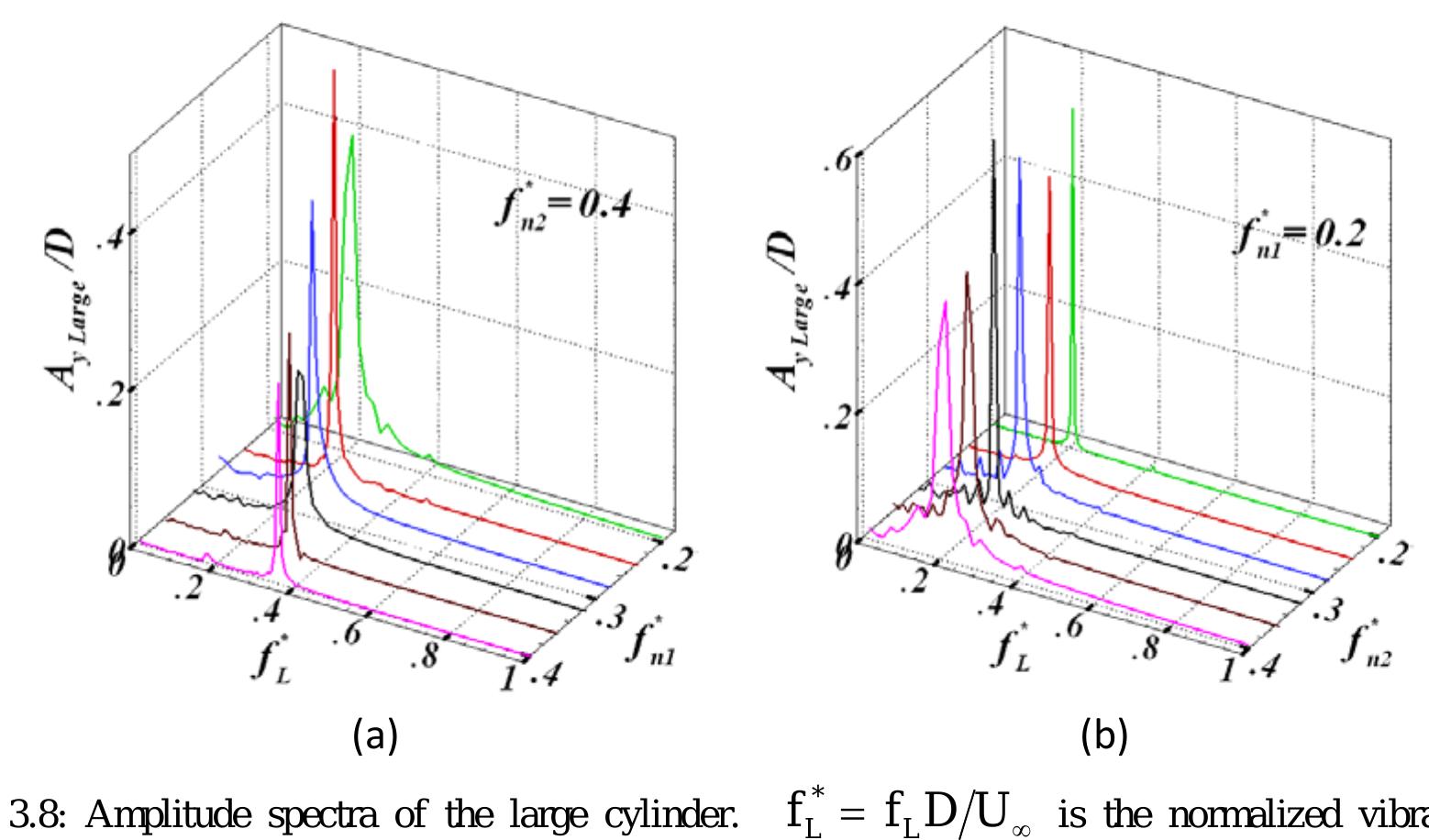
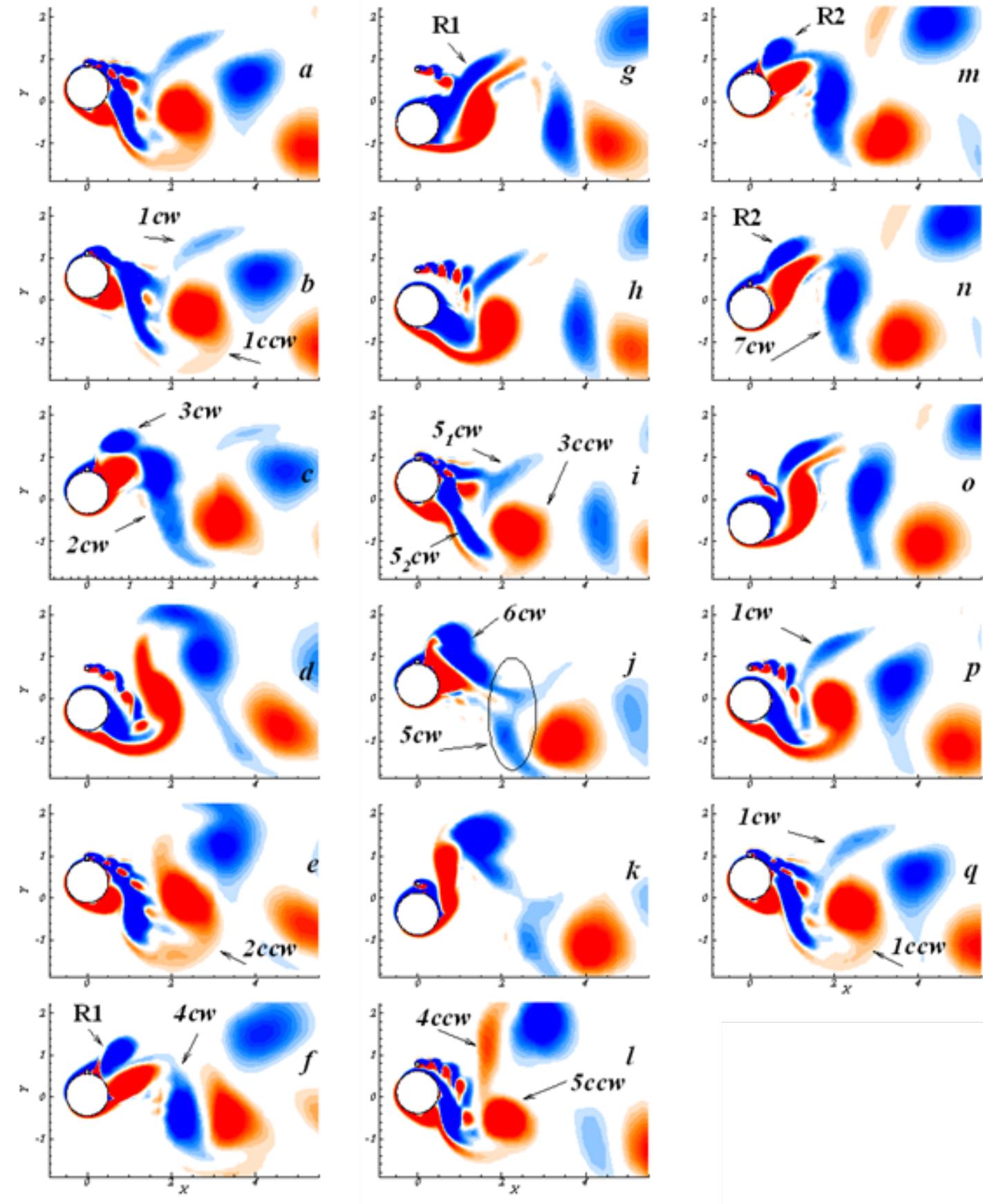
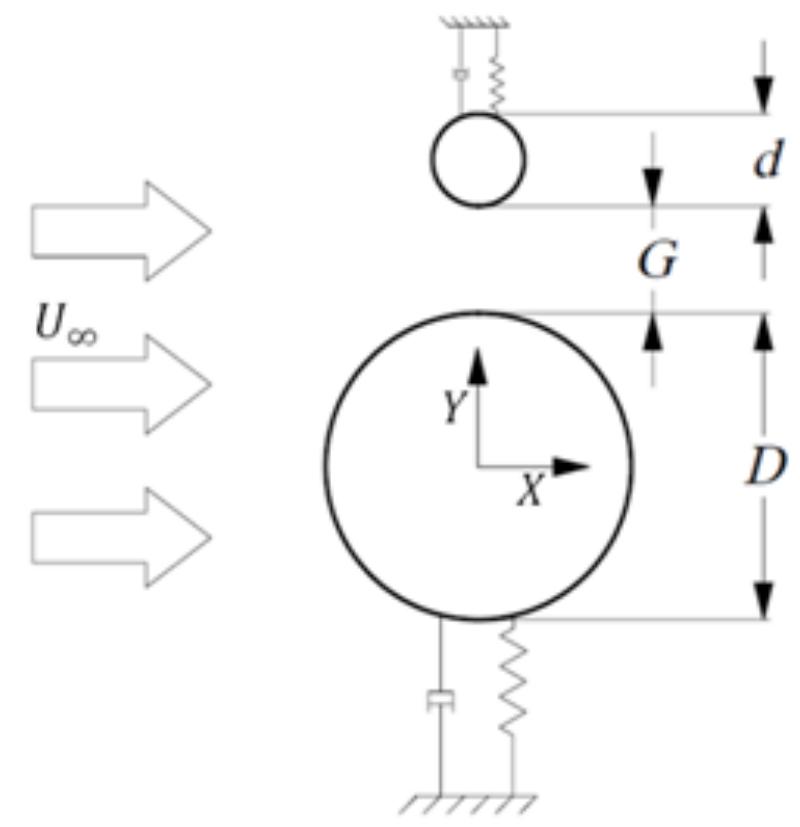
numerical investigations were unable to fully capture all flow regimes using the k-ω model (Guilminineau and Queutey 2003). It is observed that the SST model is able to cover all three branches of the flow-induced oscillation of the... more
The Gradient Scheme framework provides a unified analysis setting for many different families of numerical methods for diffusion equations. We show in this paper that the Gradient Scheme framework can be adapted to elasticity equations,... more
numerical investigations were unable to fully capture all flow regimes using the k-ω model (Guilminineau and Queutey 2003). It is observed that the SST model is able to cover all three branches of the flow-induced oscillation of the... more
The methods employed by Martin [1971] and Chandna et al. [1982] to steady plane flows have been applied to the plane viscous flows in a porous medium using the Darcy - Brinkman - Lapwood equation. Various flows and corresponding... more
Significant advancements have been made in the experimental investigation of drag reduction techniques for bluff bodies. This study explores various methods, including active and passive flow control strategies, surface modifications, and... more
In the state-of-the-art PIV, image sensors are growing in size and PIV algorithms are increasing in spatial resolution capabilities. These technological advances allow for the simultaneous measurement of increasingly larger spatial scales... more
Multigrid particle image velocimetry (PIV) is an open path in the search for high-resolution PIV methods. It is based on an iterative scheme that uses the information of initial processing to adapt the method parameters in order to... more
Conventional particle image velocimetry (PIV) processing techniques based on correlation show a limited range of application when they are used to describe a concentrated vorticity field. This work focuses on the evaluation of these range... more
Particle image velocimetry (PIV) is now applied with confidence in industrial facilities such as large wind tunnels, yielding data not possible before. Despite the difficulties that arise in such environments, the conventional PIV methods... more
Particle Image Velocimetry with Local Field Correction (LFC-PIV) has been tested in the past to obtain two components of the velocity in a two dimensional domain (2D2C). When compared with conventional correlation based algorithms, this... more
Two independent spheres were placed in a side by side arrangement and flow structure in the wake region of the spheres was investigated with a Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) system when the spheres were in a boundary layer over a flat... more
Motivated by growing demands for aircraft noise reduction and for revolutionary new aerovehicle concepts, the late twentieth century witnessed the beginning of a shift from singlediscipline research, toward an increased emphasis on... more
Direct numerical simulations of spatially developing turbulent boundary layers over riblets are conducted to examine the effects of riblets on skin friction at supersonic speeds. Zero-pressure gradient boundary layers with an adiabatic... more
We consider flow of dry granular matter down an inclined chute with a localized contraction. Measurements and analysis show that changes in particle volume fraction are important, especially across granular bores. For fixed upstream... more
This study investigates the local and global flow structures and mass transfer characteristics for a group of interacting side-by-side cylinders in unbounded flow. Configurations with 2, 3, 4, and 5 members are considered for a range of... more
This work is devoted to the numerical solution of the three dimensional (3D) compressible Navier-Stokes system on unstructured mesh. The numerical simulation are performed using a fractional step method treating separately the convection... more
We analyse numerical errors (dissipation and dispersion) introduced by the discretisation of inviscid and viscous terms in energy stable discontinuous Galerkin methods. First, we analyse these methods using a linear von Neumann analysis... more
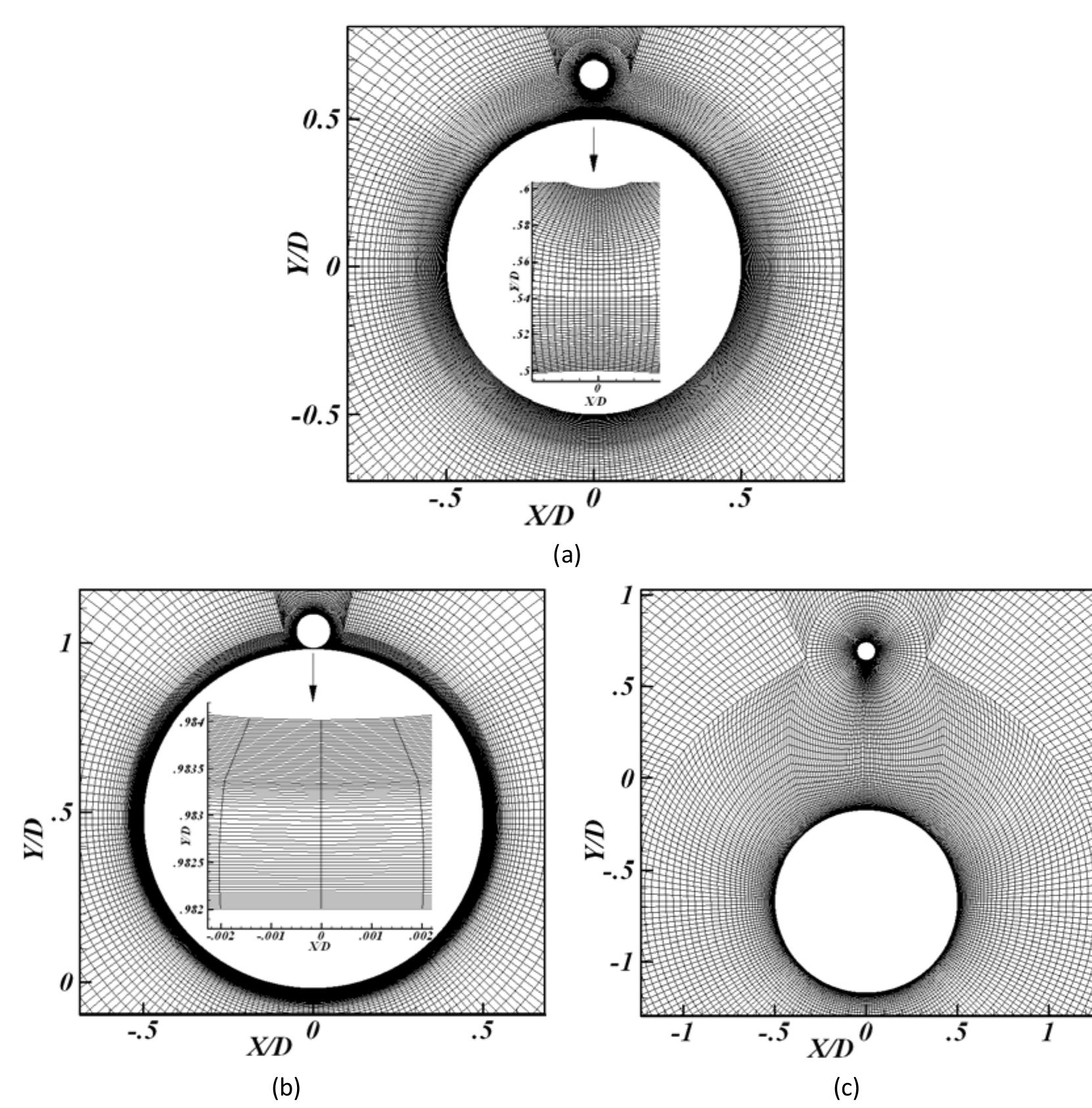
The direct numerical simulation of the flow over a sphere is performed. The computations are carried out in the sub-critical regime at Re = 3700 (based on the free-stream velocity and the sphere diameter). A parallel unstructured... more
In this paper a flexible finite element computational tool developed to investigate fluid-structure interaction applications in two dimensions is briefly described. We consider problems which can be modelled as a viscous incompressible... more
Traditionally turbulence modeling of industrial flows in complex geometries have been solved using RANS models and unstructured meshes based solvers. The lack of precision of RANS models in these situations and the increase of computer... more
The global stability analysis of the two-dimensional incompressible unsteady flow past a circular clinder cascade is studied using linear stability analysis. A new numerical technique is used to find the value of critical Reynolds number... more
This paper presents the design of an active flow control (AFC) system for commercial aircraft based on a dense wired/wireless sensor and actuator network. The goal is to track gradients of pressure across the surface of the fuselage of... more
Flow-induced vibration (FIV) of a flexible cylinder with an upstream wake interference at a subcritical Reynolds number is numerically investigated in this study. Two cylinders are installed in a tandem arrangement with the tandem... more
Fixed-vane vortex generators (VGs) have been in existence for over 50 years and are still among the most effective available flow control devices. However once such fixed VGs have been configured to improve performance in one regime, they... more
This work presents a numerical study on self-induced flapping dynamics of an inverted flexible foil in uniform flow. The inverted foil considered in this study is clamped at the trailing edge and the leading edge is allowed to oscillate.... more
This report is a collection of documents written as part of the Laboratory Directed Research and Development (LDRD) project A Mathematical Framework for Multiscale Science and Engineering: The Variational Multiscale Method and Interscale... more
A flexible inverted flag immersed in a Poiseuille flow with heated walls was numerically modeled to investigate the dynamics of the flag and its effect on convective heat transfer. An immersed boundary method was used to analyze the... more
Turbulent fluid flows are ubiquitous in nature and technology, and are mathematically described by the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. A hallmark of turbulence is spontaneous generation of intense whirls, resulting from... more
Design of geotechnical systems is often challenging as it requires the understanding of complex soil behaviour and its influence on field-scale performance of geo-structures. To advance the scientific knowledge and the technological... more
The correction method is developed to correct the distribution of pressure coefficient around an airfoil for the aim of the post processing of measurement data from wind tunnel. The measured pressure coefficient is numerically corrected... more
Feedback control is applied to symmetrize the bimodal dynamics of a turbulent blunt body wake. The flow is actuated with two lateral slit jets and monitored with pressure sensors at the rear surface. The physicsbased controller is... more
This paper describes the structural design of an active flow-control experiment. The aim of the experiment is to investigate the increase in efficiency of an internally blown Coanda flap using unsteady blowing. The system uses tailor-made... more
In this work, we considered the flow around two circular cylinders of equal diameter placed in tandem with respect to the incident uniform flow. The upstream cylinder was fixed and the downstream cylinder was completely free to move in... more
In the present work, the laminar flow through a circular cylinder with two crossed splitter plates is analyzed. The characteristic-based method has been used along with the unstructured grid. The current research has been done to detect... more
Direct and large-eddy numerical simulations have been performed for a heated sphere at Reynolds numbers 200, 300, 500, 750, 1000 and 104, in the context of the development of a spherical wind sensor for Mars atmosphere intended for... more
Accurate prediction of laminar-turbulent transition is a critical element of computational fluid dynamics simulations for aerodynamic design across multiple flow regimes. Traditional methods of transition prediction cannot be easily... more
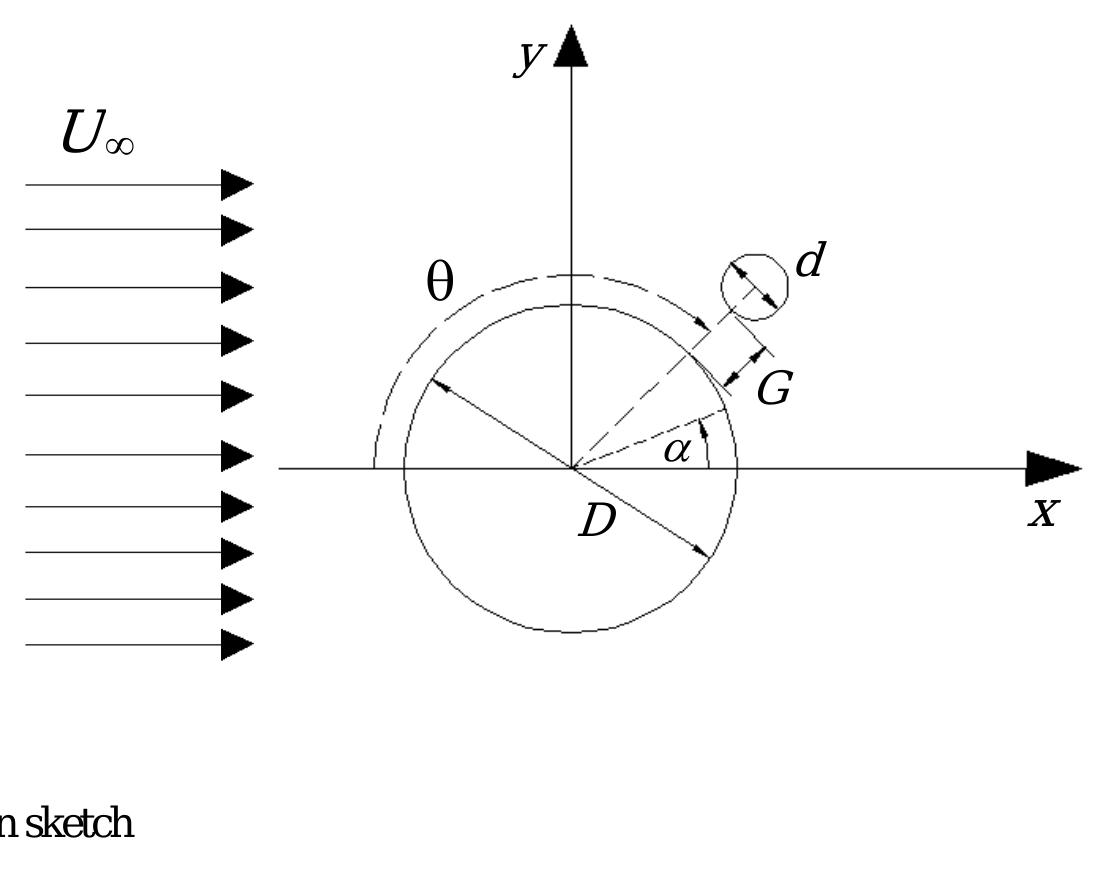
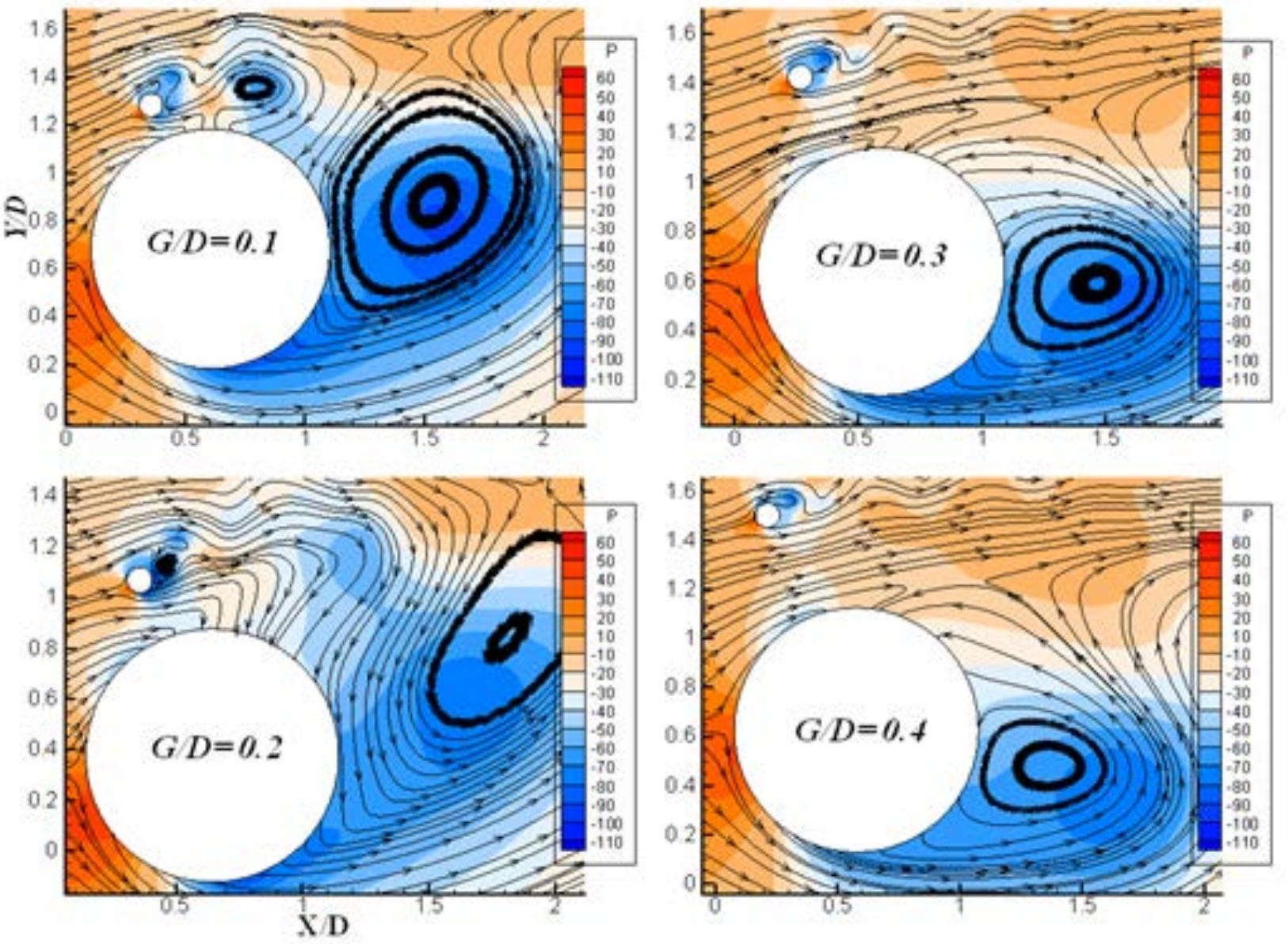
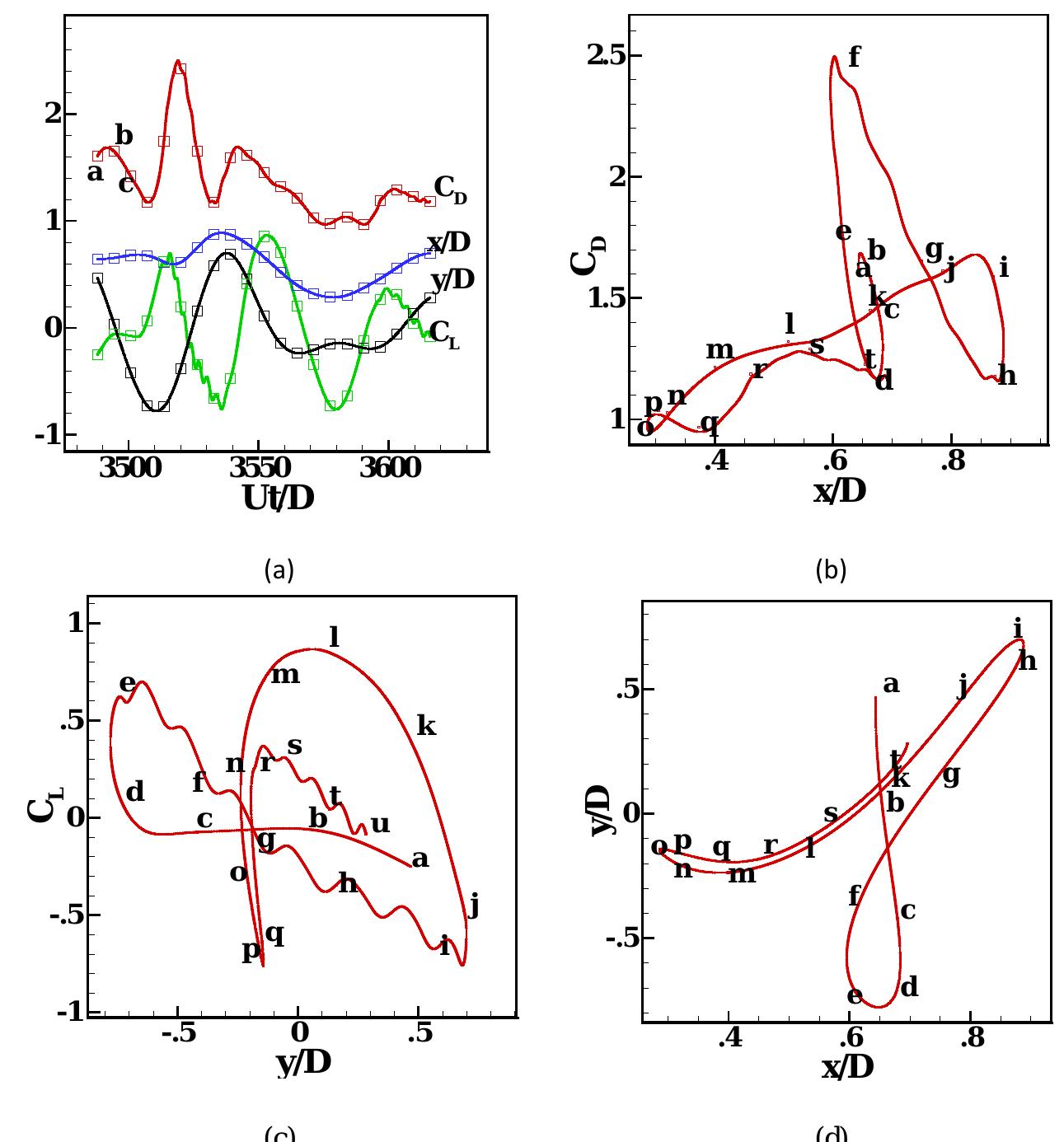
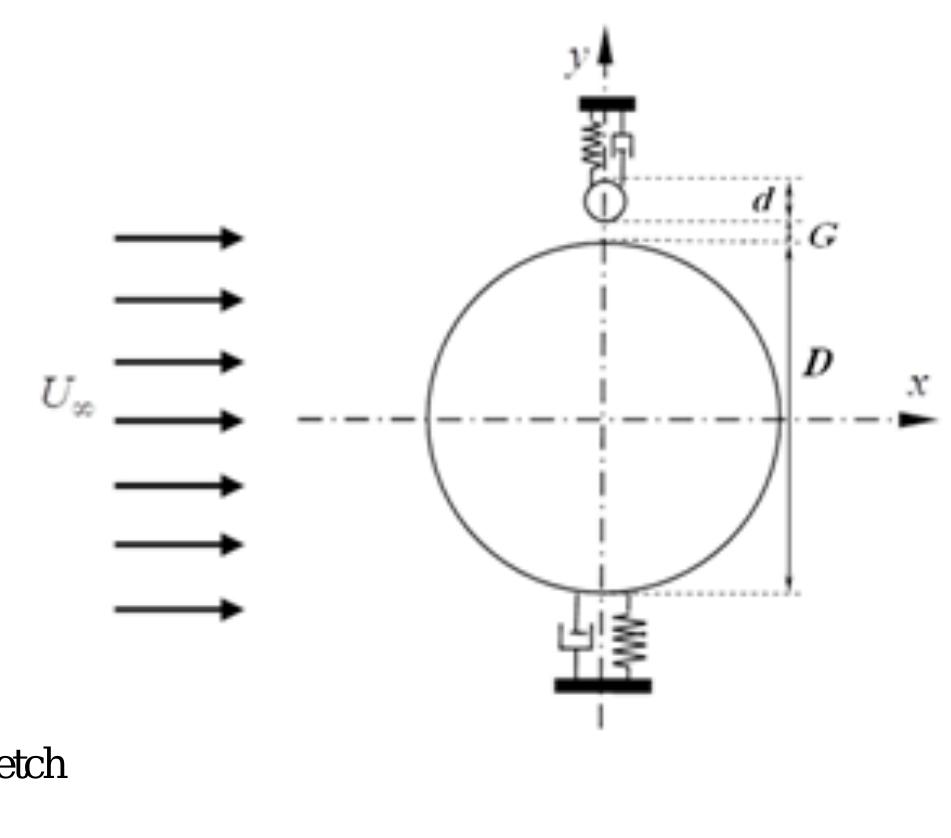
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International licence Newcastle University ePrints-eprint.ncl.ac.uk Assi GRS, Srinil N, Freire CM, Korkischko I. Experimental investigation of the... more
This study aims at clarifying the factors that cause transmission line galloping and the conditions influencing it, and at determining response evaluation indices of gallopings in turbulent flows. This is done using a three-dimensional... more
Over the last few years, superhydrophobic (SH) surfaces have been receiving an increasing attention in many scientific areas by virtue of their ability to enhance flow slip past solid walls and reduce the skin-friction drag. In the... more