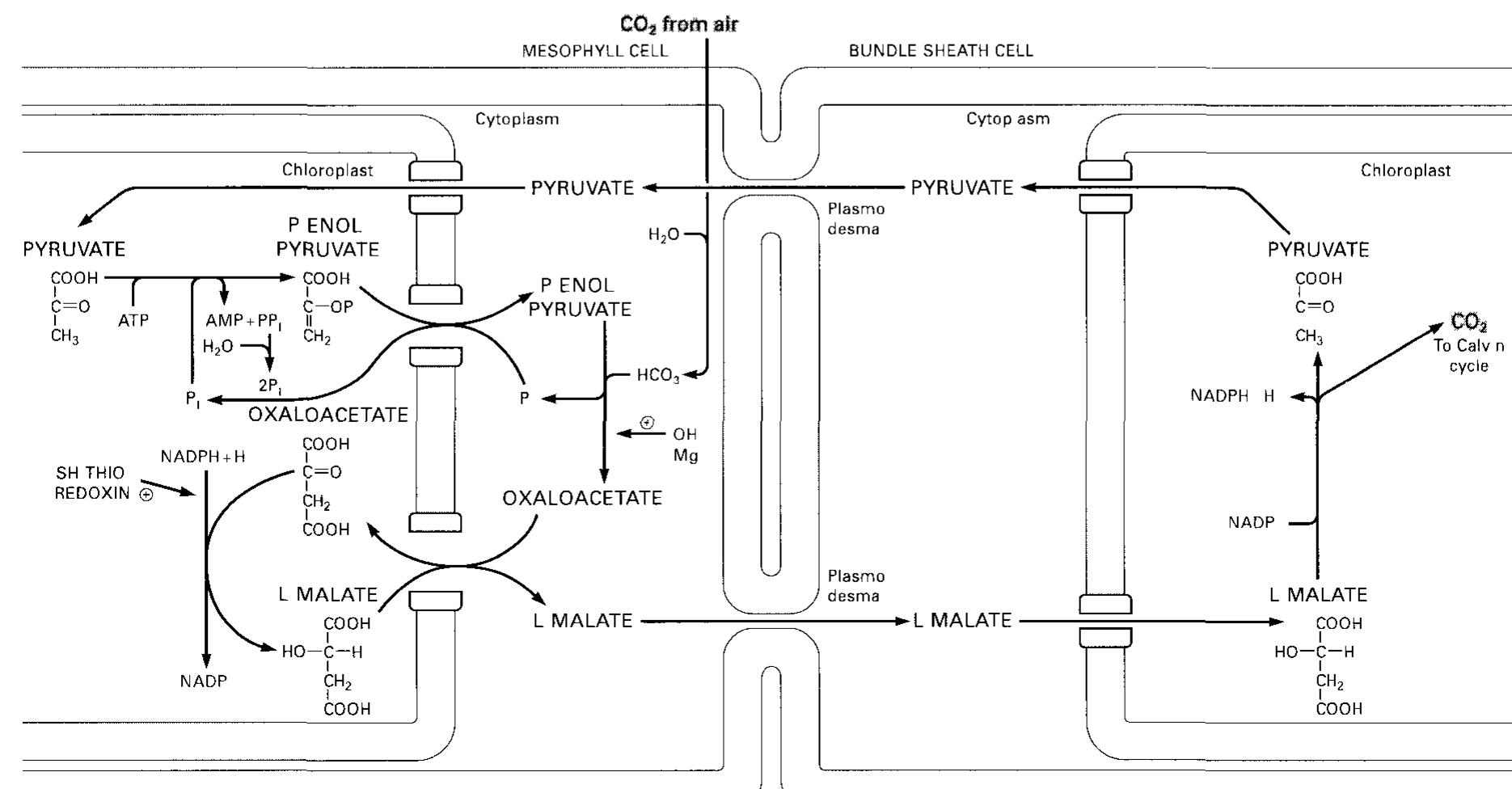
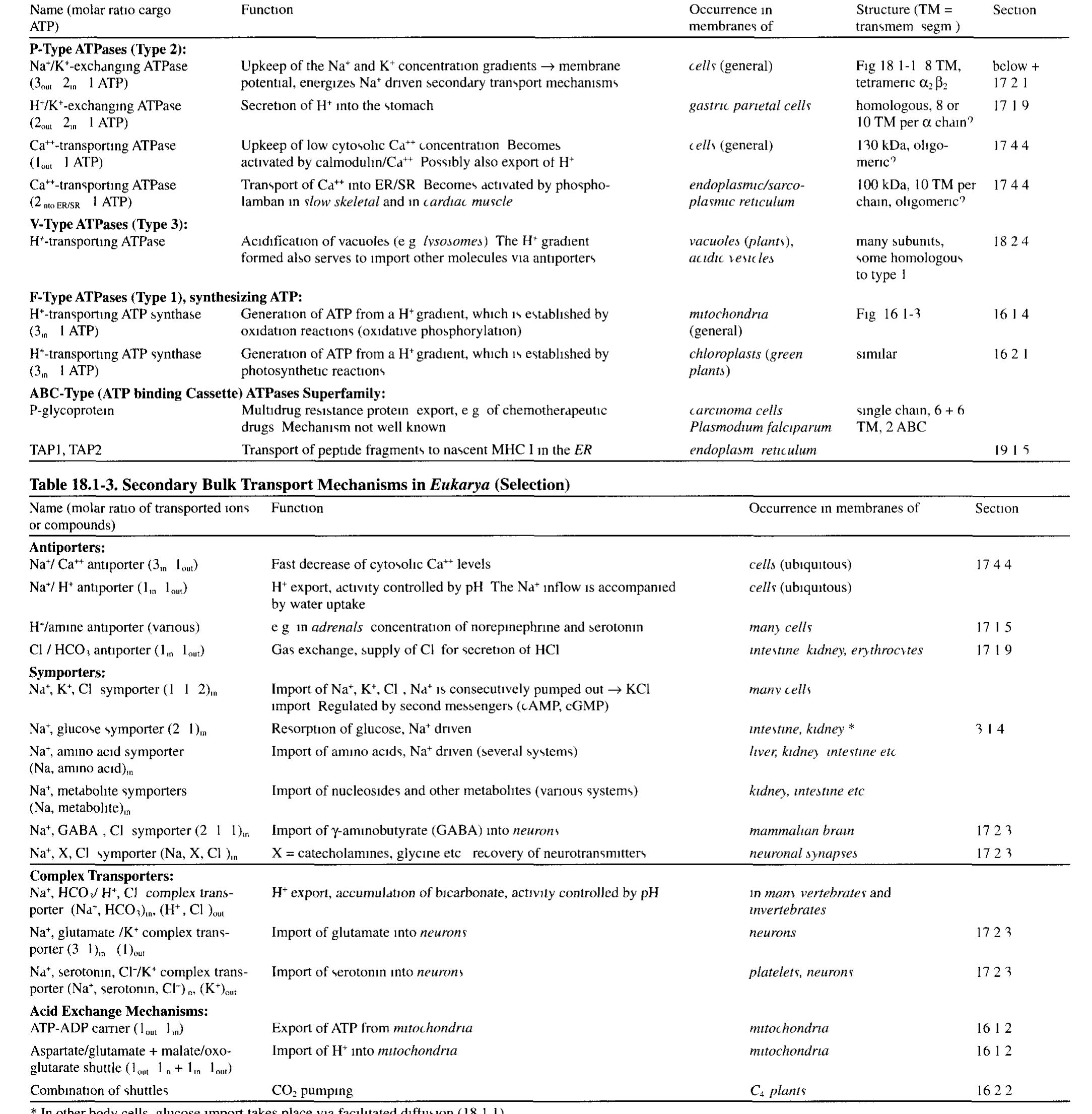
Biochemical Pathways.[1999 EN].G Michal OCR

Sign up for access to the world's latest research
Abstract
AI
AI
The book "Biochemical Pathways" aims to provide concise and comprehensive information on metabolic pathways, enzymatic reactions, and their regulation, without the extensive historical context typically found in textbooks. It focuses on a variety of biological systems, including bacteria, plants, and animals, presenting knowledge through clear illustrations and tables to facilitate quick understanding. The work is designed for readers looking for a systematic overview of biochemical interrelationships while omitting detailed experimental methods and the complete range of literature references.














![The energy required tor its formation 1s called activation energy AG* which can be calculated from this equilibrium by applying Eq [1 5 4] as Arrow = shift of the plot when the concentration of the other substrate is raised “igure 1 5-5 Lineweaver-Burk Plots of Two-Substrate Reactions](https://figures.academia-assets.com/39117587/figure_009.jpg)

















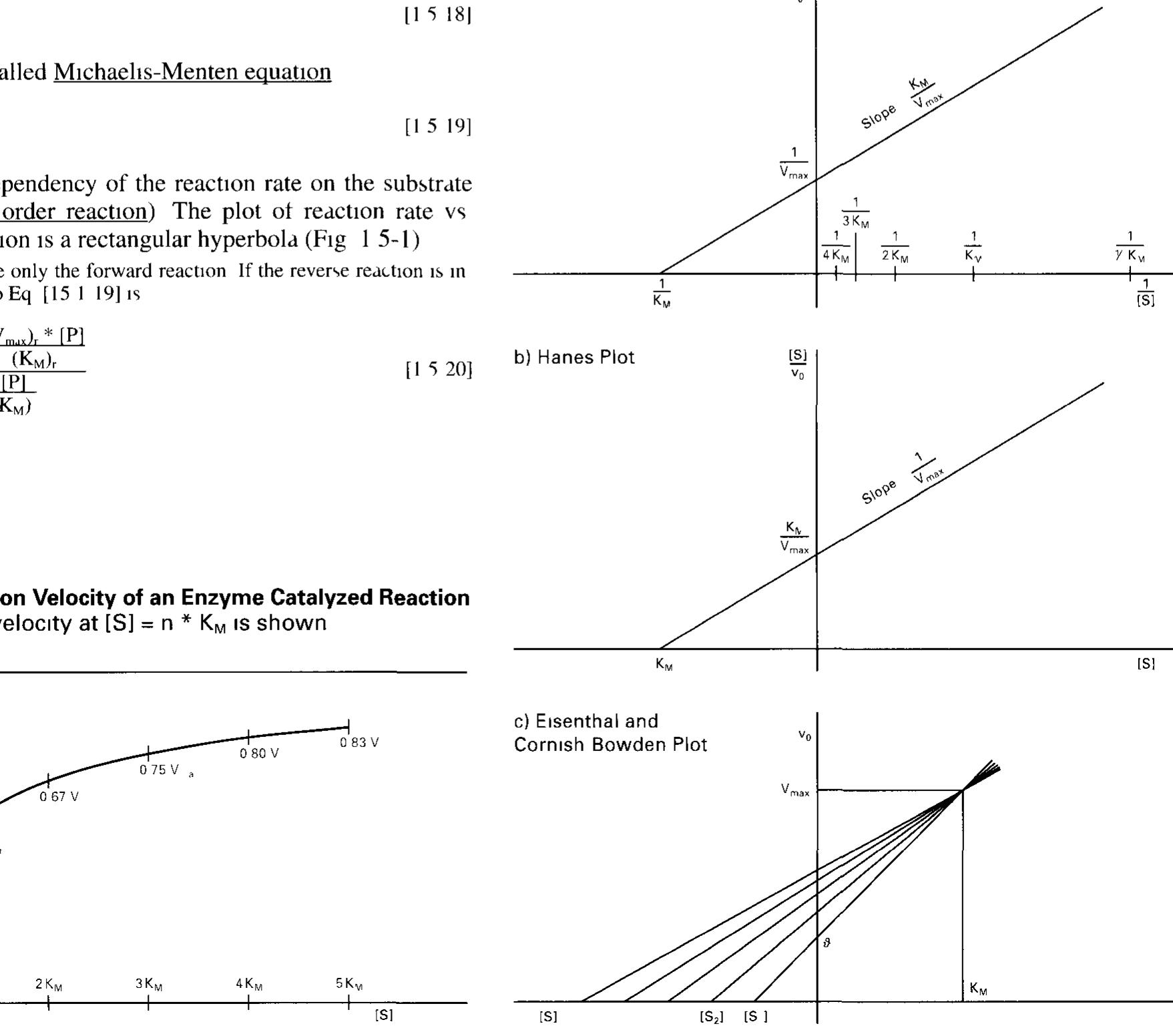
![2.5.2 Regulation of the Activity of Enzymes (For a Mathematical Treatment see 1.5.4) Dannlatian danandinag am onhocteaota Camneantratinn«s TA tha mance? SECACHICIIE SOO 1.0. F) Regulation depending on substrate concentration: In the most simple case, the dependency of the reaction rate on the substrate concentration according to the Michaelis-Menten equation (Eq. [1.5-19], Fig. 1.5-1) 1s a means of controlling the substrate through- put. Zymogen activation: Some enzymes are synthesized as mactive precursors (zymogens or proenzymes) which have to be processed into their active form by limited proteolysis. Examples are diges- tive enzymes such as chymotrypsinogen or trypsinogen (Fig. 2.5-1) They are synthesized in mammalian pancreas as zymogens. After hormone-controlled release into the small intestine they are irre- versibly processed by trypsin or enteropeptidase, respectively, to become active proteases (Fig. 17.1-11).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/39117587/figure_022.jpg)
































































![Using [Mb ] for the total myoglobin concentration [Mb] + |Mb O ] a derivation analogous to the Michaelis Menten equation [Eq 15 19] but without further turnover to products yields](https://figures.academia-assets.com/39117587/figure_087.jpg)






![Figure 6.1-3. Schematic Drawing of the Animal Fatty Acid Synthase Dimer Reaction sequence (Fig. 6.1-4): Specific acy] transferases (one in animals, two in yeast) transfer an acetyl residue from acetyl-CoA to a cysteine-SH of the 3-oxoacyl synthase component (‘peripheral SH group’) @ and a malonyl residue to the ‘central’ SH group of the ACP component of the multienzyme system. Condensation with an acetoacetyl chain (bound to the central SH group) occurs with simultaneous decarboxylation, thereby energetically favoring chain elongation @). This step is irreversible. Then the resulting C, residue is reduced by NADPH at the oxoacyl reductase component ©, dehydrated to a 2,3-desaturated intermediate @ and reduced again by the enoyl reductase ® (also using NADPH as a reduc- tant; NADH in E.coli). The yeast enzyme contains flavin. Finally, the butyryl chain is transferred to the ‘peripheral’ SH group ©. Condensation with another malonyl! residue initiates another round of chain elongation.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/39117587/figure_091.jpg)






















![Farnesylation takes place if X = serine methionine or glutamine Geranylgerany] 1s attached 1f X = leucine or phenylalanine By Pane EDN ay ar HARES pp eh SMMC DON OSL t ASemmnO RODS BR ce a ee Re is pee Many proteins are attached to cellular membranes by isoprenoid anchors (via a thioether bond to mostly farnesyl, sometimes ge- ranylgeranyl chains), e g Ras (175), G, proteins (17 4) and heme A (521) This prenylation determines the location and the func tron of the proteins The enzymatic reaction 1s shown 1n Fig 7 3-1 IS AUACTIEM TE ZN = IRGC OF POUCH Y taal Proteins of the Rab group which contain -C-C- or C X C-~ sequences ar geranylgeranylated similarly The enzyme 1s assisted by the Rep protein](https://figures.academia-assets.com/39117587/figure_110.jpg)

























































![ee nnn ee EN I NEI SAE ROE NESE! Only a few regulatory events during the elongation step are known so far The overall RNA chain elongation rate, however, 1s propor tional to the growth rate, ensuring that no excess RNA 1s produced when the translation system operates slowly under conditions of liamited nutritional supply Stringent control: Starvation for an amino acid in bacteria causes a drastic decrease im transcription levels, caused by a signal from the translation step In this stringent contro] mechanism, translat ing ribosomes whose A sites are occupied by non-aminoacylated tRNAs bind the stringent factor enzyme, which then synthesizes the unusual nucleotide guanosine tetraphosphate (PP 5’ G 2’-PP) This compound, 1n turn, reduces transcription of rRNA and tRNA genes (and others) 10- to 20-fold by decreasing the affinity of Pol to the respective promoters via an unresolved mechanism On the other hand, amino acid biosynthesis 1s stimulated](https://figures.academia-assets.com/39117587/figure_162.jpg)


























![Figure 11 3-4 Splicing Mechanism for mRNA Besides this mechanism (group III introns) other splicing mechanisms exist They proceed with an external guanosine nucleotide instead of the branching point A (group I rRNA) or with a hgation procedure after endonuclease split ting of the pre mRNA (group [IV tRNA) Splicing of group II introns (e g muito chondria and chloroplast mRNA) resembles the group If] mechanism but with out participation of snRNPs Frequently the group I or I procedures are per tormed by RNA activity only (self splicing e g rRNA in Tetrahymena) Exon ot ditterent RNA strands can also be combined by splicing mechanisms (trans splicing e g MRNA 1n Trypanosoma)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/39117587/figure_180.jpg)





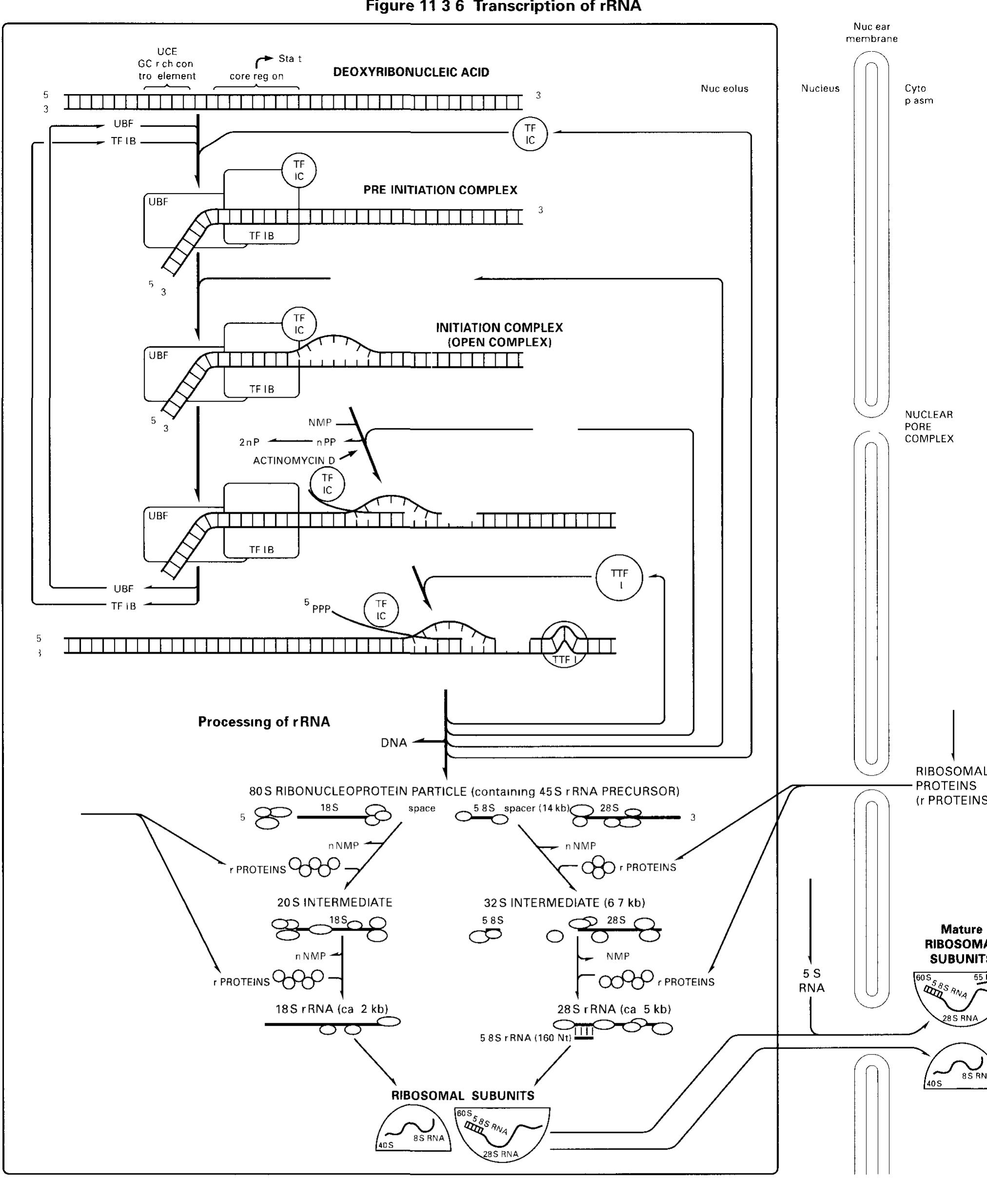
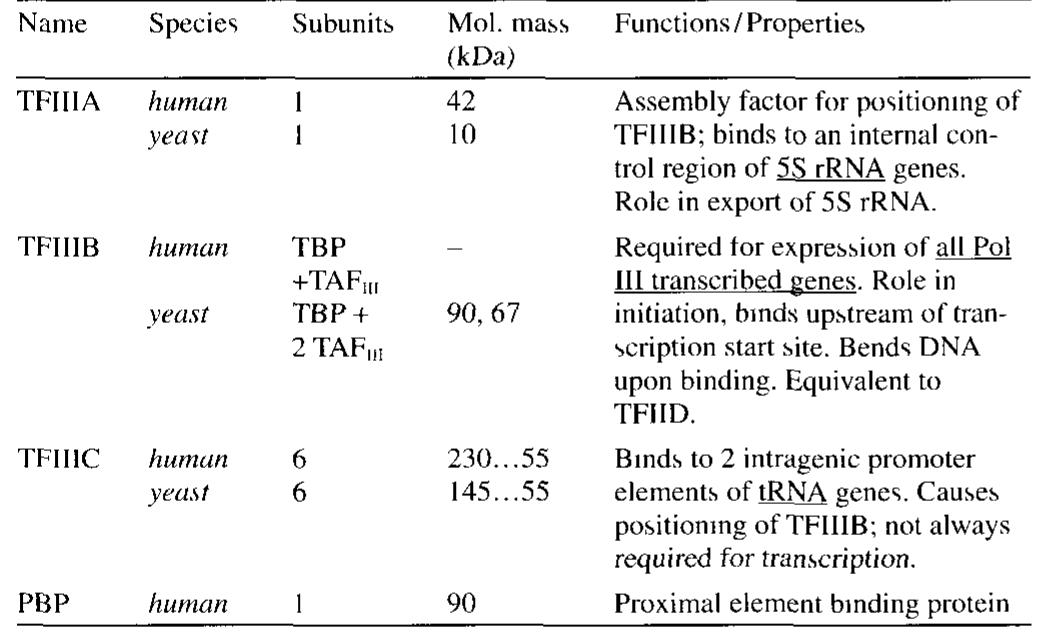






![RNA polymerase I core promoters (Fig. 11.4-3): RNA poly- merase I promoters (and the vast majority of RNA polymerase III] promoters) lack TATA boxes The core promoter (in mammals and amphibians) consists of two critically spaced sequences the upstream control element (UCE, location at -200 -—100 nucleo tides from the start site) and the core region (location at-50 +20 nucleotides therefore enclosing the start site) Only little tran scriptional control 1s exerted on pre-rRNA synthesis](https://figures.academia-assets.com/39117587/figure_190.jpg)

















![Infection of the bacterial cell (Figure 12.2-3): Adsorption to the E colt host cell takes place via specific interaction of the phage tai] fiber and a maltose group of the bacterial outer membrane Then the phage DNA 1s injected through the tail into the host cell The linear DNA 1s transformed into a cyclic form, whereupon the host DNA ligase closes the phage genome ring covalently and the DNA gyrase produces supercoiled phage DNA Now the phage enters one of two different states](https://figures.academia-assets.com/39117587/figure_203.jpg)



![The initiation complex for reverse transcription [consisting of the viral enzyme reverse transcriptase (RT), the nucleocapsid pro- teins and the viral primer t-RNA] 1s being activated by the viral](https://figures.academia-assets.com/39117587/figure_207.jpg)






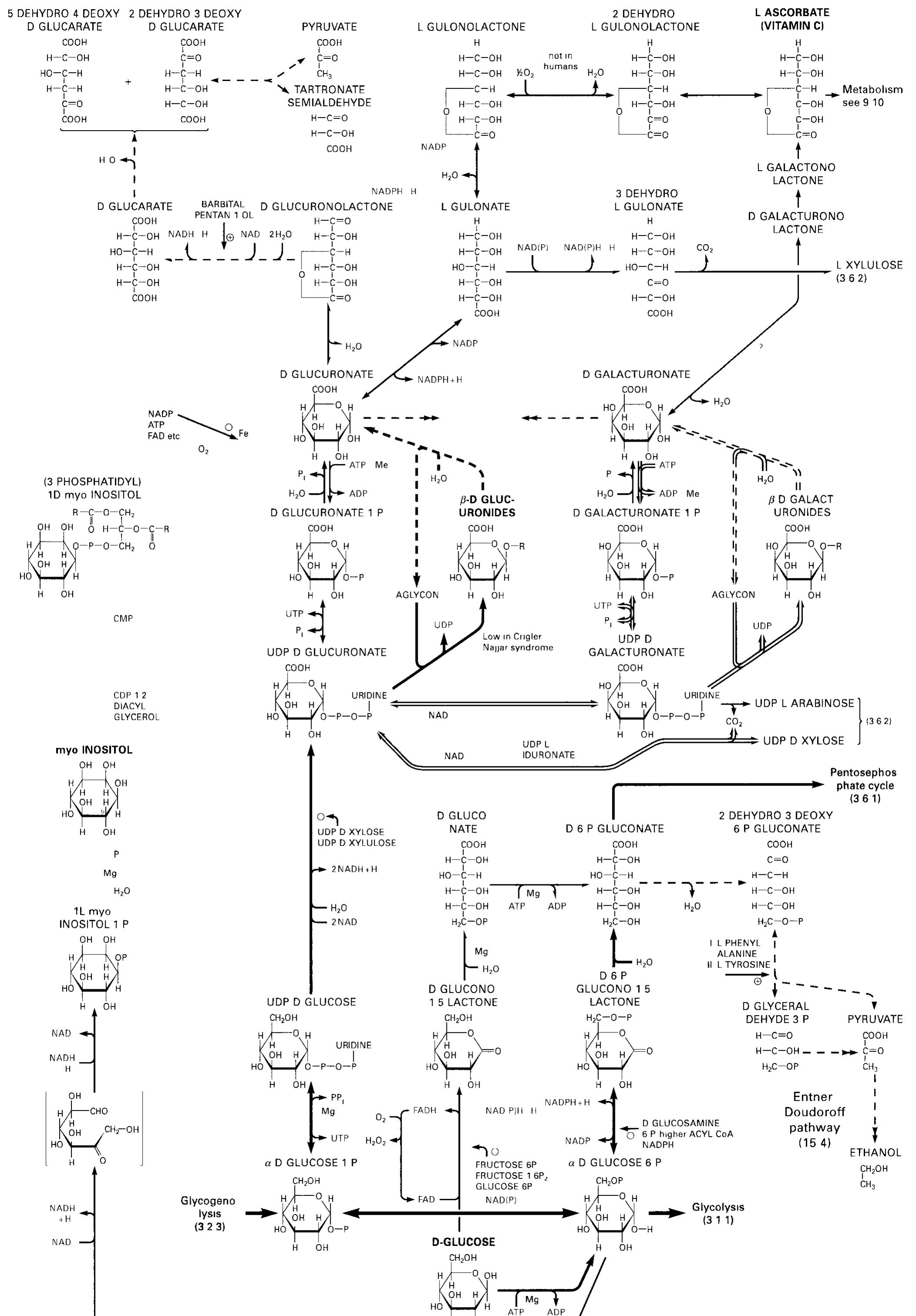
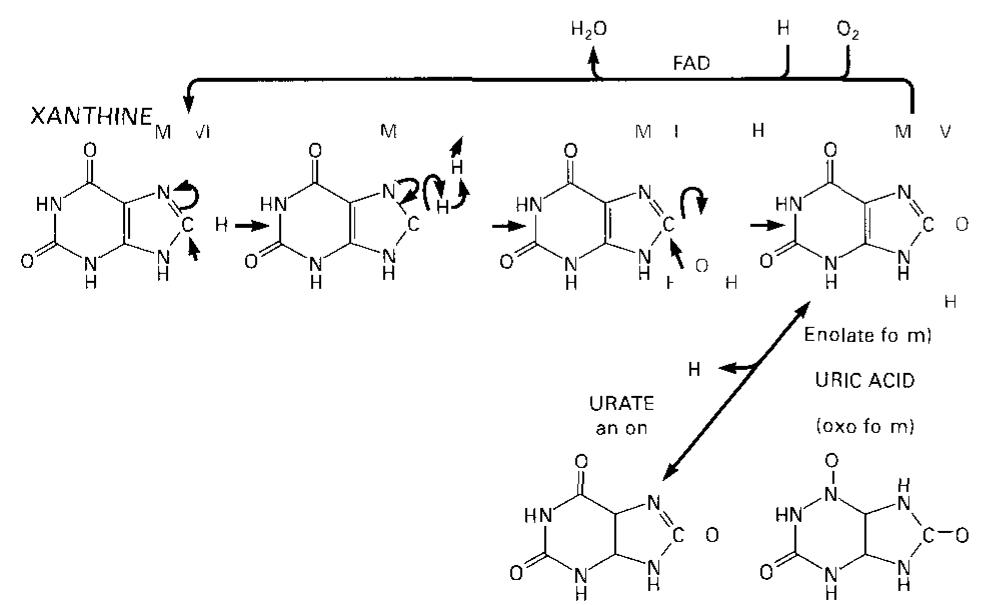
![[pb glucuronate (2 sulfate) (a1— 4) N sulfo b glucosamine (6 sulfate) (&@1— 4)] (mostly) HEPARIN 6* 10> 25*10'Da contains also some D-Gal and b xylose Large quantities are found in mast cells lung and liver Heparin ts an in hibitor of blood coagulation (20 3) by promoting complex forma tion between active proteases (Ila [Xa, Xa) and antithrombin II]](https://figures.academia-assets.com/39117587/figure_213.jpg)































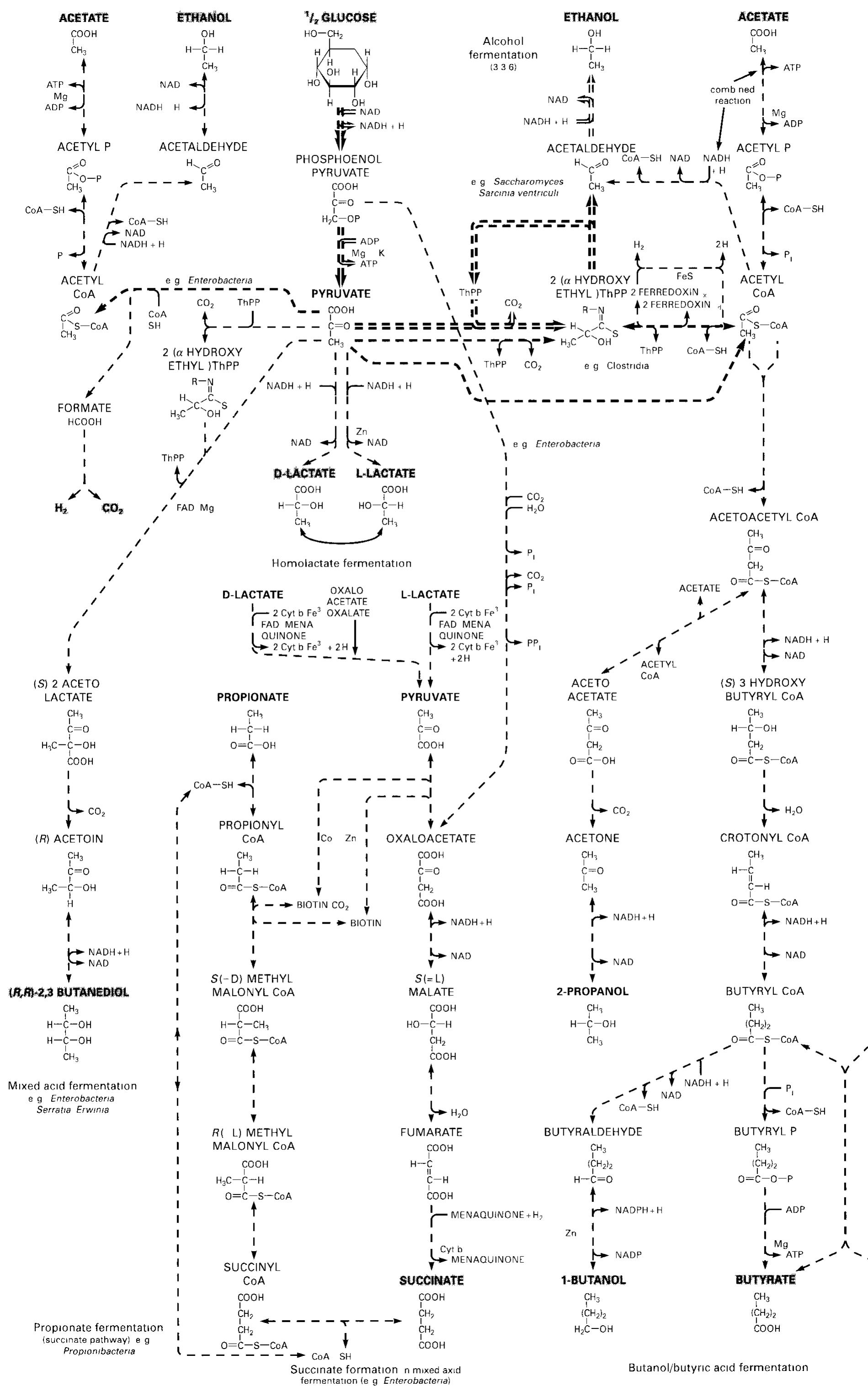









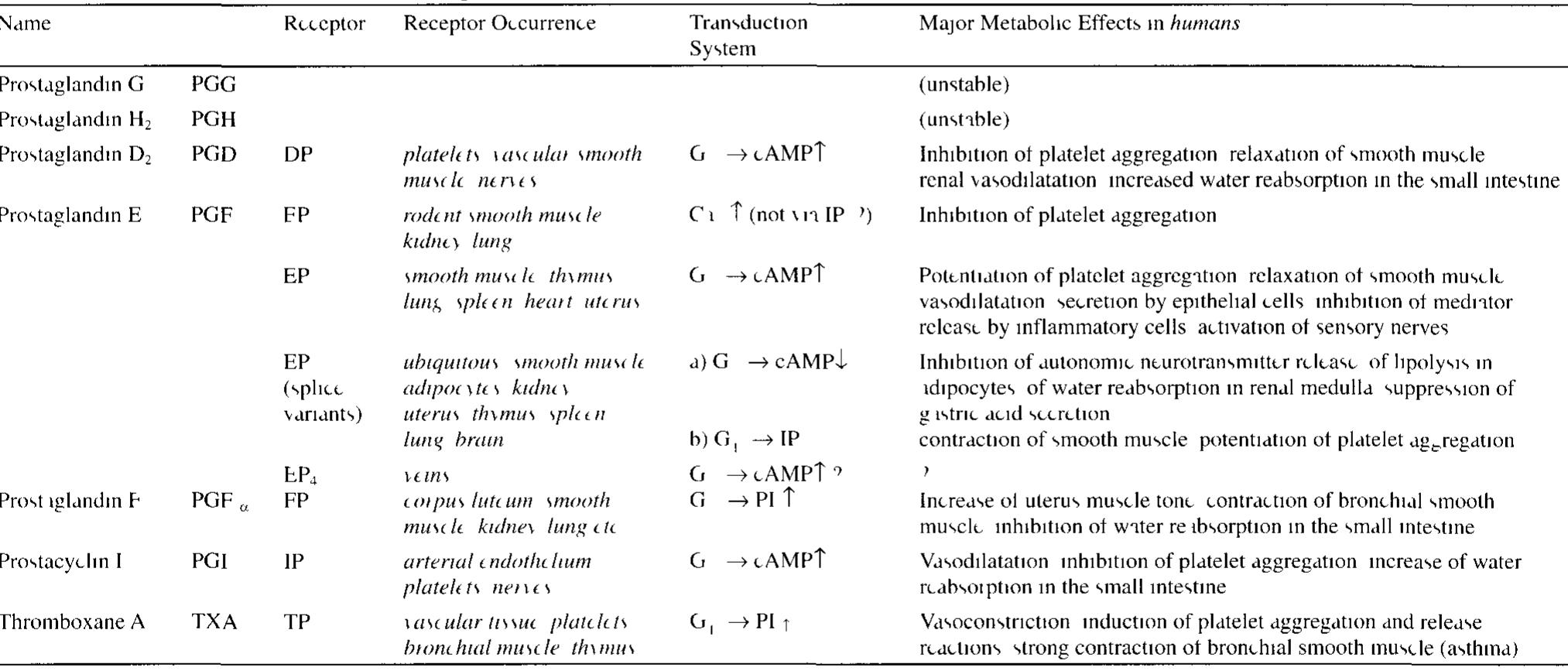
![Figure 15.6-2 Redox Potentials E4[mV, 25 °C, pH = 7 0] of Substrate Couples](https://figures.academia-assets.com/39117587/figure_240.jpg)

















































![Table 17.4-2. Mammalian Gg, Proteins (Tightly Associated Complexes) Membrane anchored_ * by farnesy] at C terminal serine # by geranylgeranyl at C terminal leucine Also known B, B; ¥,(# pairs with B, and 8B, widespread occurrence) y;(# pairs with B and B widespread occurrence) y; (# pairs with B, and B) widespread occurrence) ys # in olfactory epithelium) y , G# pairs with B, and B.) y (* similar to y, pairs with B widespread occurrence)](https://figures.academia-assets.com/39117587/table_085.jpg)












































































Key takeaways
- Chains of amino acids form the proteins and peptides.
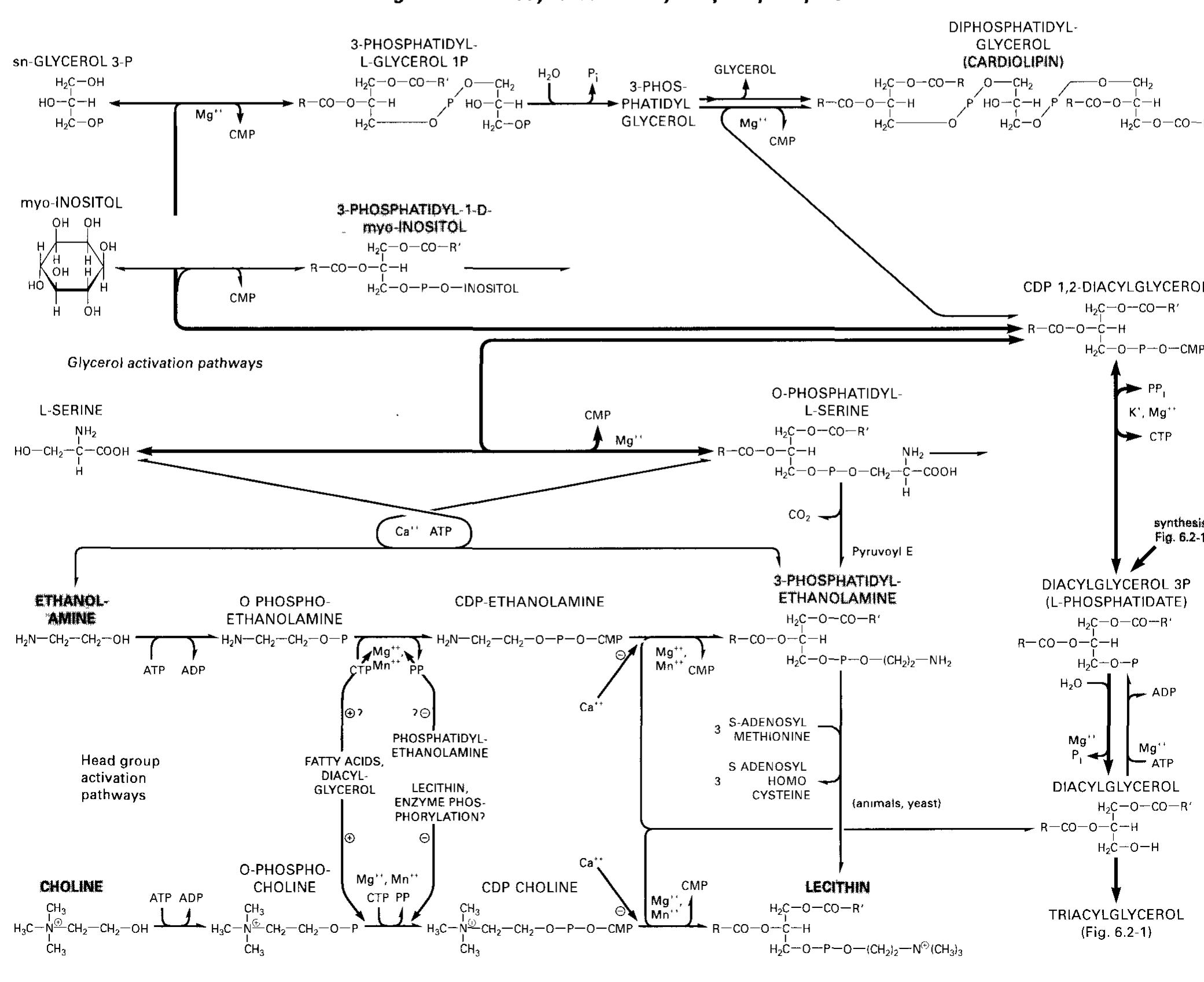
- The nucleus contains in addition to the DNA also the nuclear matrix which is composed of the enzymes and factors required for DNA replication DNA repair transcription and processing of the transcription products (111 114) The nucleus is surrounded by a double membrane of lipid bilayers with inte grated proteins Nuclear pores (14 3 2 ca 125 nm diameter) span the nuclear membrane and enable the transport of proteins rRNA etc The inner surface ot the nuclear membrane is covered by nuclear lamina a net of protein fibers which stabilizes the structure and provides attachment points for the chromatin (2 6 4) During cell division the nuclear membrane dissolves 2.2.2 rough ER is also the site of membrane phospholipid synthesis, thus providing membrane material for the departing vesicles (6. 3.2, 13.3.4).
- However, for most enzymes (as well as for other proteins) the production is regulated:
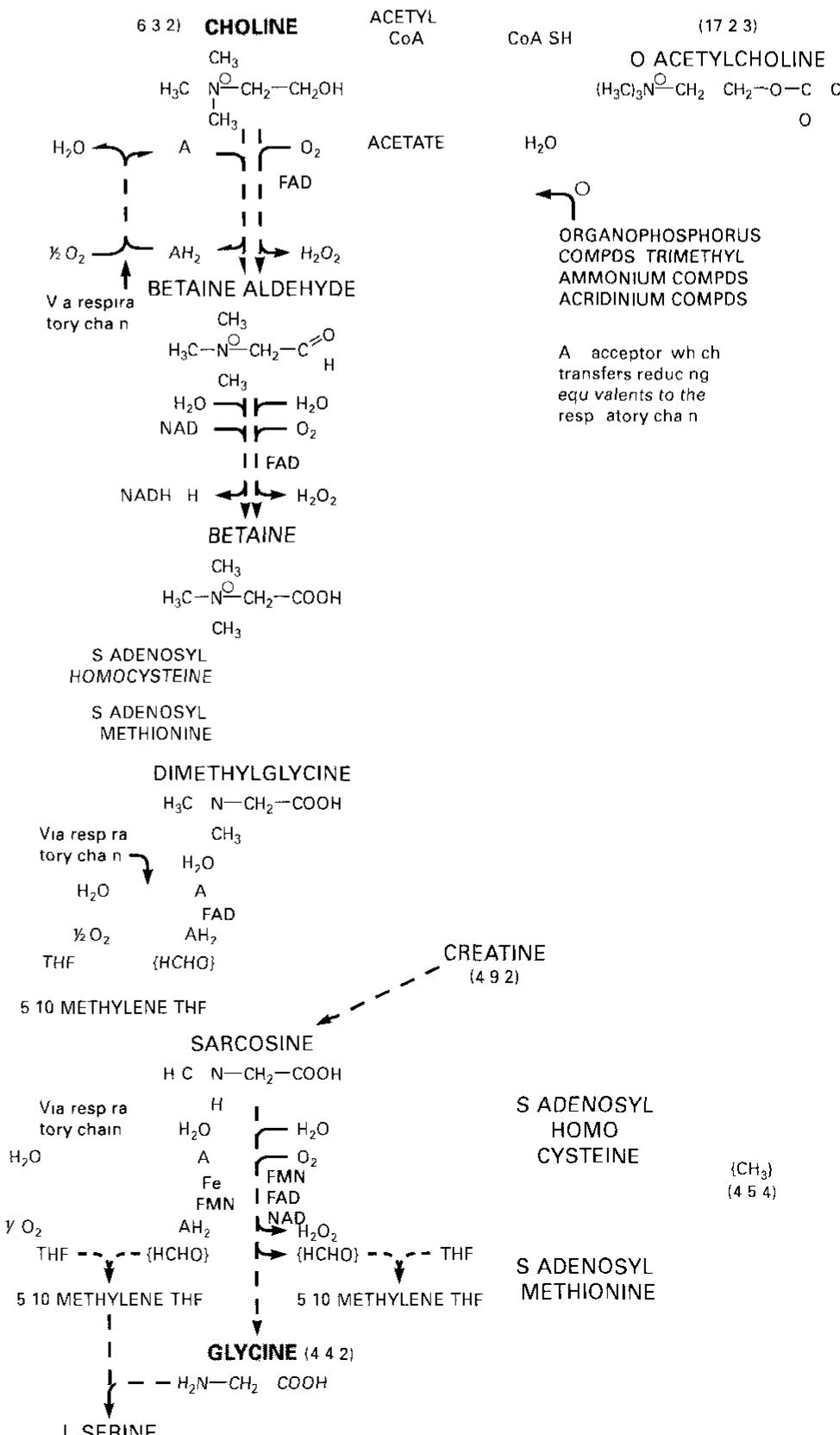
- The primary source for the biosynthesis of fatty acids in animals are carbohydrates, followed by a number of amino acids.
- The overall error rate of translation is ca 1/10000 Consequently, the probability for correct synthesis ot a protein with 300 amino acids is 0 97
Related papers
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 1965
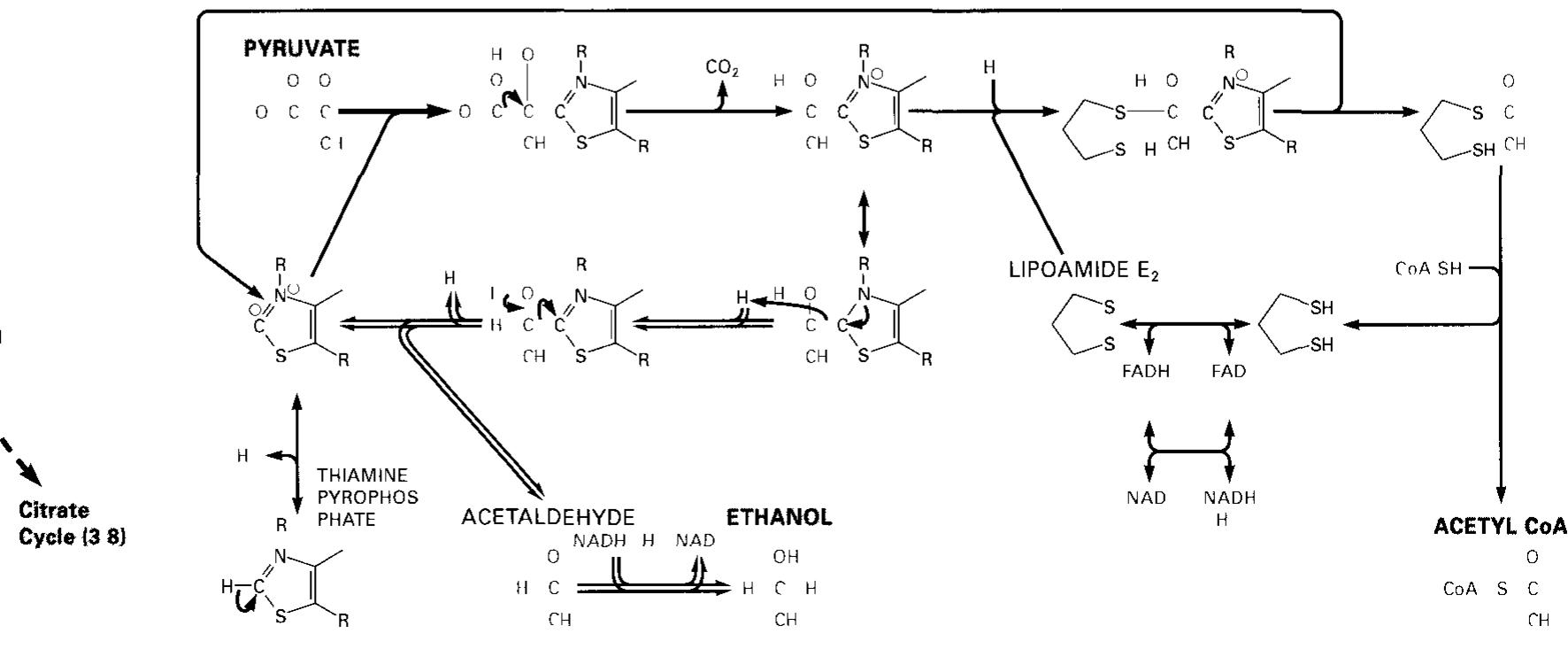
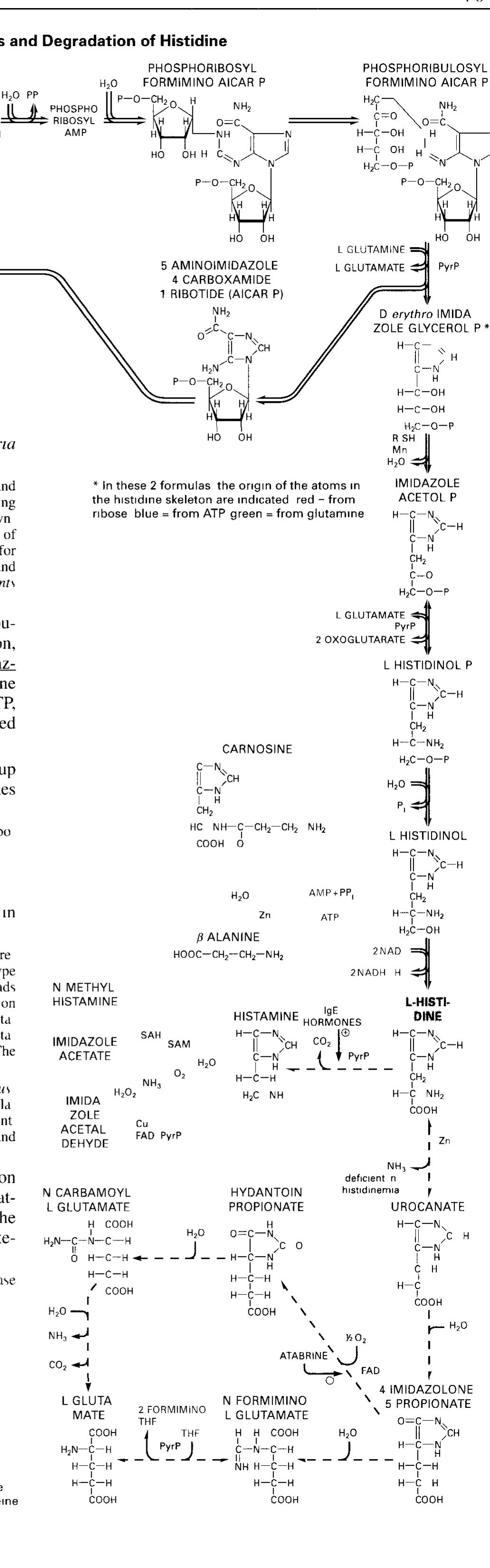
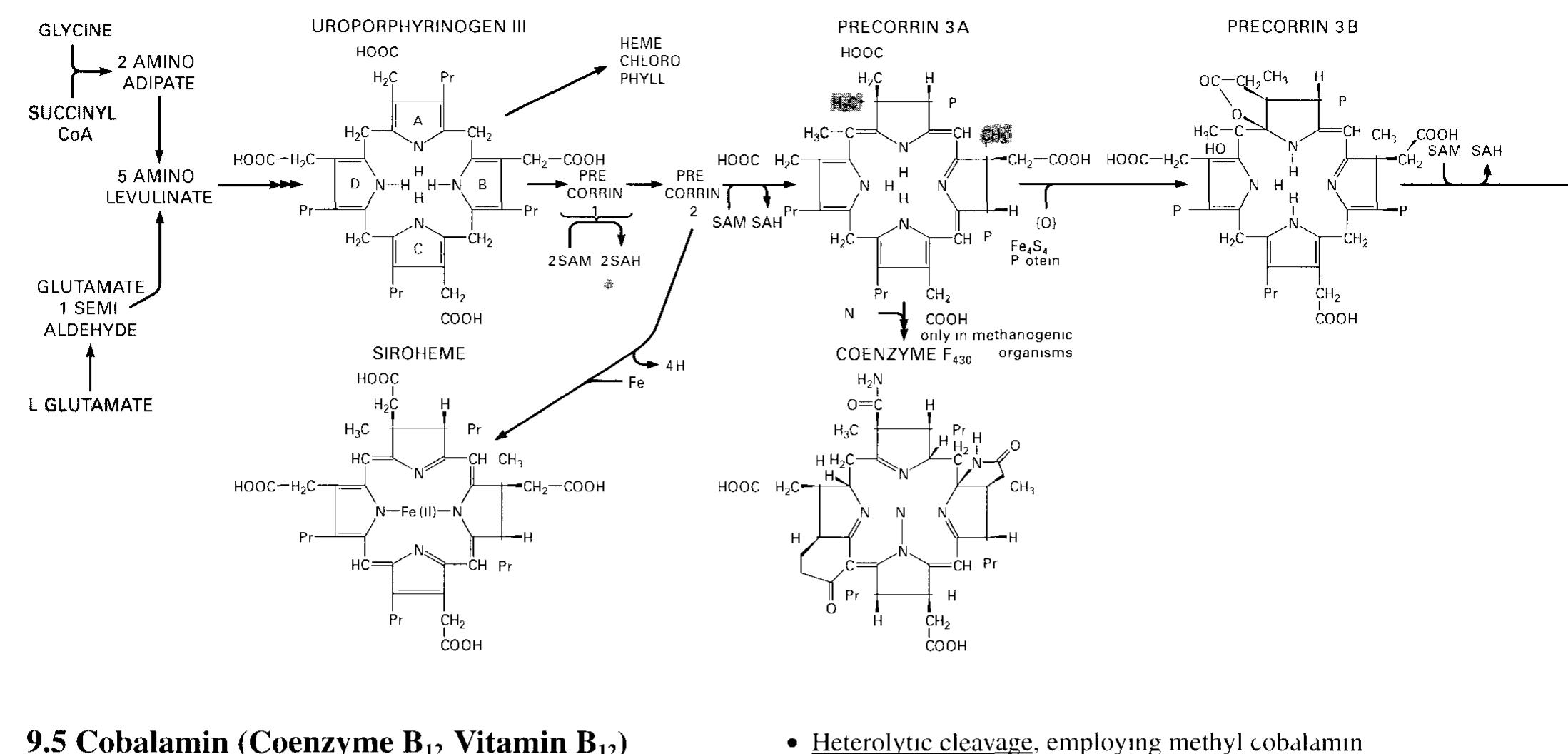
Dr. Popov began this half of the lecture by stating that memorizing structures of coenzymes would be unnecessary. We should instead know what they are used for I. The Structure of Coenzyme A [S30]: a. Coenzyme A is involved in the metabolism of fatty acids II. Enzyme-catalyzed transaminationsp [S31] III. Pridoxal phosphate, the prosthetic group of aminotransferases [S32] IV. Pyridoxal phosphate is bound to the enzyme through a Schiff-base linkage[S33] V. Role of biotin in carboxylation reactions [S34] a. Biotin is a water soluble vitamin. b. Biotin is utilized as a prosthetic group of several enzymes. c. The major function of Biotin is to serve as a cofactor for carboxylation reactions. d. Biotin will later be discussed as being associated with pyruvate carboxylase in the Citric Acid Cycle. e. A carboxylation reaction involves the incorporation of CO2 into a biological molecule.
Harper's Illustrated Biochemistry, 32th ed, 2023
Presently entitled Harper’s Biochemistry, the book continues, as originally intended, to provide a concise survey of aspects of biochemistry most relevant to the study of medicine. Various authors have contributed to subsequent editions of this medically oriented biochemistry text, which is now observing its 83rd year.
2021
Advertência Legal / Legal Warning |. Reservados todos os direitos. É proibida a duplicação, total ou parcial desta obra, sob quaisquer formas ou por quaisquer meios (electrónico, mecânico, gravação, fotocopiado, fotográfico ou outros) sem autorização expressa por escrito do editor / All rights reserved. Reproduction in part or as a whole by any process or in any media (electronic, mechanical, recording, copying, photographic or others) is extrictly forbidden without the written authorization of the editor.
Advances in Enzyme Regulation, 1963
THE present paper will mainly describe some metabolic changes in liver after thyroxine treatment as a result of what we believe to be an enzymic induction. Several features distinguish such a process from the immediate or short-term control of metabolic rates which we find in organs under voluntary state of activity. In the latter case, the control of metabolic flow operates in the presence of a constant pattern of enzymes. A short description of this might be helpful however.
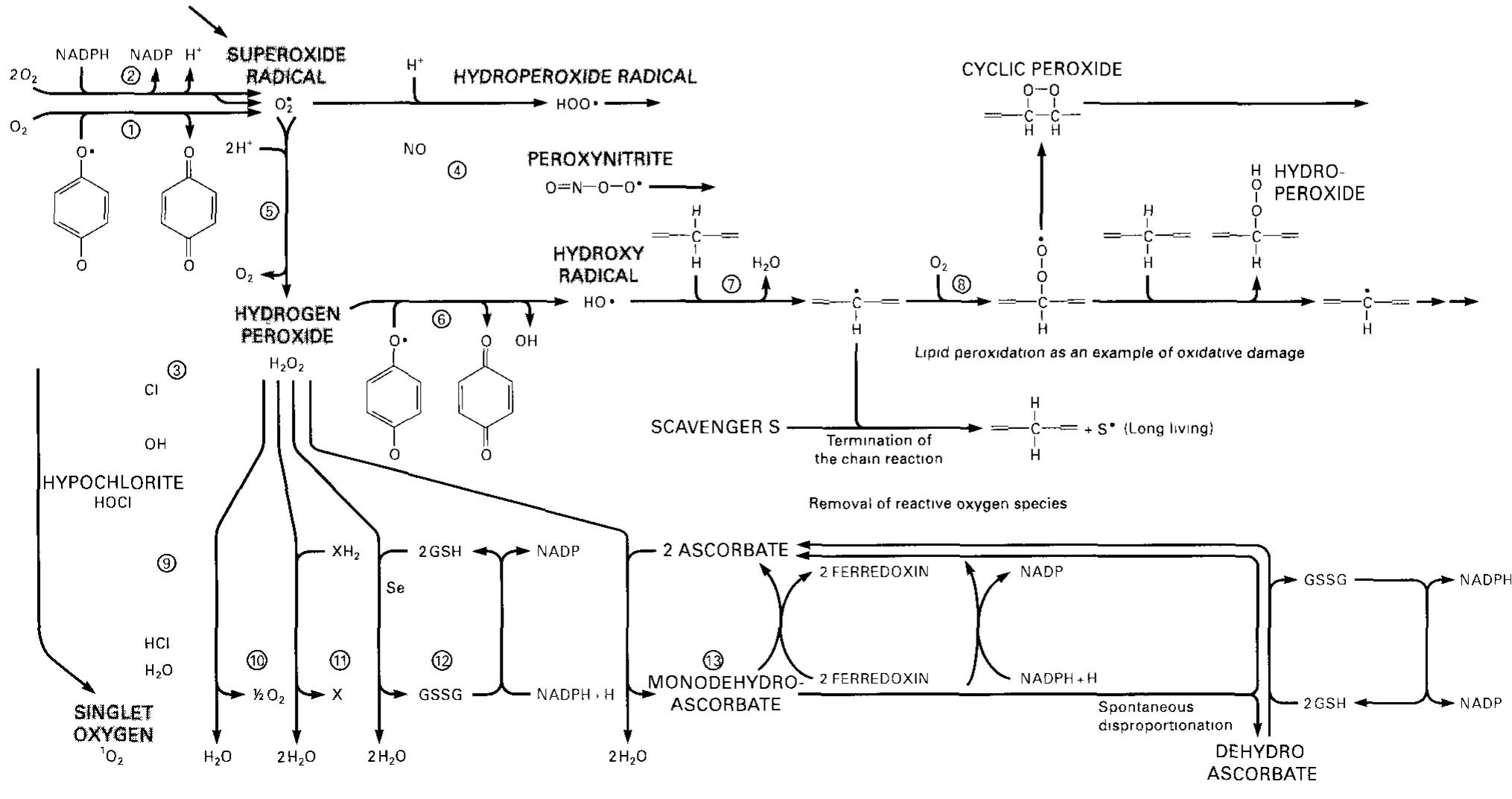
Since the discovery of enzymic fermentation by Louis Pasteur, the idea has been widespread in biochemistry that molecular interconversions and interactions in living systems are mediated by enzymes. However, recent advances in sensitivity and separation power of analytical methods has led to isolation and identification of a variety of products that cannot be mapped to specific enzyme-catalyzed biochemical pathways. These products appear in the organism because chemical characteristics of biomolecules are not limited to the needs of living systems realized through enzyme-catalyzed processes. This review provides a summary of such nonenzymic interactions. The following are discussed: I) products of biogenic amine binding to carbonyl-containing compounds in the Pictet-Spengler reaction (endogenous neurotoxins, which impair mitochondrial functions and seem to contribute to development of age-related neurological disorders including parkinsonism); 2) products of Schiff base formation with subsequent Amadori rearrangement (nonenzymic protein glycation involved in age-related diabetes-like disorders and atherosclerosis; 3) prod ucts of Michael addition of methylglyoxal: 4-hydroxynonenal, and other derivatives of nonenzymic conversions of carbohydrates and lipids; 4) products of modification of biomolecules with nitrogen-and oxygen-derived free radicals, which contribute to cancer and aging. Some evolutionary and biomedical implications of nonenzymic parametabolic processes are discussed .
Microbial Biotechnology, 2008
Overproduction of microbial metabolites is related to developmental phases of microorganisms. Inducers, effectors, inhibitors and various signal molecules play a role in different types of overproduction. Biosynthesis of enzymes catalysing metabolic reactions in microbial cells is controlled by well-known positive and negative mechanisms, e.g. induction, nutritional regulation (carbon or nitrogen source regulation), feedback regulation, etc. The microbial production of primary metabolites contributes significantly to the quality of life. Fermentative production of these compounds is still an important goal of modern biotechnology. Through fermentation, microorganisms growing on inexpensive carbon and nitrogen sources produce valuable products such as amino acids, nucleotides, organic acids and vitamins which can be added to food to enhance its flavour, or increase its nutritive values. The contribution of microorganisms goes well beyond the food and health industries with the renewed interest in solvent fermentations. Microorganisms have the potential to provide many petroleum-derived products as well as the ethanol necessary for liquid fuel. Additional applications of primary metabolites lie in their impact as precursors of many pharmaceutical compounds. The roles of primary metabolites and the microbes which produce them will certainly increase in importance as time goes on. In the early years of fermentation processes, development of producing strains initially depended on classical strain breeding involving repeated random mutations, each followed by screening or selection. More recently, methods of molecular genetics have been used for the overproduction of primary metabolic products. The development of modern tools of molecular biology enabled more rational approaches for strain improvement. Techniques of transcriptome, proteome and metabolome analysis, as well as metabolic flux analysis. have recently been introduced in order to identify new and important target genes and to quantify metabolic activities necessary for further strain improvement.
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution and sharing with colleagues. Other uses, including reproduction and distribution, or selling or licensing copies, or posting to personal, institutional or third party websites are prohibited. In most cases authors are permitted to post their version of the article (e.g. in Word or Tex form) to their personal website or institutional repository. Authors requiring further information regarding Elsevier's archiving and manuscript policies are encouraged to visit: http://www.elsevier.com/copyright
Archives of Organic and Inorganic Chemical Sciences, 2018
2012
This Dissertation is brought to you for free and open access by the Theses and Dissertations at Loyola eCommons. It has been accepted for inclusion in Dissertations by an authorized administrator of Loyola eCommons. For more information, please contact ecommons@luc.edu.
Annals of The New York Academy of Sciences, 1987
2007
HAL is a multi-disciplinary open access archive for the deposit and dissemination of sci-entific research documents, whether they are pub-lished or not. The documents may come from teaching and research institutions in France or abroad, or from public or private research centers. L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est destinée au dépôt et a ̀ la diffusion de documents scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, émanant des établissements d’enseignement et de recherche français ou étrangers, des laboratoires publics ou privés.
Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 1988
You may also complete your request on-line via the Elsevier website at http://www.elsevier.com/permissions.
2012
Learning biochemistry is difficult for many life science students because, in essence, they are asked to learn a very complicated language, filled with many new concepts, all within a sixteen-week time frame. This "field manual" is a concise guide to biochemistry concepts and is intended as an efficient, pared-down aid to help students assimilate the key ideas. It presents a self-contained sixteen-week course, at a level that will help students proceed successfully to professional and medical school course work. Biochemistry: Essential Concepts (BEC) has evolved over many years of teaching introductory biochemistry. In one concise volume it contains (a) a textual summary of the essential information distilled from a standard encyclopedic biochemistry textbook, and (b) relevant review questions and sample tests with answers. BEC thus serves as a complete and self-contained handbook, notebook, and study guide. Because BEC presents material in the same sequential order as most biochemistry textbooks, it may easily be used alongside another text. The content in BEC is intended to provide a backbone. It is not intended to replace a full textbook but, rather, through concurrent use, is designed to assist students in the learning process by presenting to them a clear, pared-down presentation of the basics together with problem-solving and review tools. We have taught graduate-and undergraduate-level biochemistry and biophysics courses at North Carolina State University for over twenty-five years. The main challenges we have experienced are: (1) students arriving to take a biochemistry course who have not retained basic concepts from freshman and organic chemistry; and (2) the vastness of the field of biochemistry itself. Many students have relied on memorization in their previous science courses without grasping fundamental concepts such as pH, pK a , nucleophilic attack, equilibrium, and thermodynamics. Reliance on rote memorization in a biochemistry course is a very ineffective approach and does not result in a deep understanding of more subtle aspects of biochemical processes, such as assessing the poise of a reaction equilibrium, predicting enzyme reactivity and substrate-dependent regulation. Our goals in writing BEC were therefore twofold: (1) To carefully extract and present the essential core concepts imbedded in a typical biochemistry textbook, (2) to reiterate in a variety of contexts those most fundamental chemical concepts that are essential to understand the processes of biochemistry and related biological science, not simply memorize them. The text contains several key features: Textbook Flexibility. The approach used in BEC focuses on teaching the fundamental structure of the field within a single semester time frame. It is not based on a single textbook. As a result, it is compatible xvi Preface for use as a study guide with any of a wide variety of much more definitive tomes, several of which are cited in context within the text. Integration of Concepts Into The Big Picture. BEC is a clear, concise guide to biochemical concepts, which is readily accessible and provides a wealth of well-chosen examples. A key strength is that one is rapidly orientated regarding a given subject, with emphasis on the big picture, and then shown how fundamental concepts become integrated to produce more complex linked processes. These lessons are reinforced by an extensive set of practice exercises and tests designed to reinforce key concepts and relationships, highlighting techniques from medicine and other biotechnological fields. Many Real-World Applications. These notes are a map so that students can continually look at the big picture and see how the subject of the moment fits. The same fundamental principles govern many aspects of biological processes, so once students have built a set of models into their memory, they can use this knowledge to dissect some new, yet related, biological setting, predict the pertinent chemistry and sort out the processes that matter. Students can then use this kind of circumspect viewpoint to realistically understand the complexity of new situations. In the long view, this knowledge can be used to understand a process, develop new procedures, troubleshoot methodological problems, design a new pharmaceutical, and otherwise be applied to use in medicine, agriculture, and biotechnology. A Concise, Clear Format. How does a professor decide what to keep and what to leave out when faced with a twelve-hundred-page textbook and sixteen weeks to teach the course? Current textbooks tend to be encyclopedic, requiring careful choice of the material to emphasize if one is to effectively transmit both a working knowledge of the fundamental tools of the discipline as well as their breadth and importance in medicine, materials science, genetics, cell biology, and so forth. In the streamlined presentation of BEC, the focus is on concepts that govern and regulate biological processes. Those concepts include equilibrium, pK a , K d , K M , pH, nucleophilic attack, the relation between bond polarity and reactivity, the enthalpic and entropic contributions to ΔG, and so forth. This emphasizes the more difficult-to-learn physical and mechanistic concepts and leaves the more digestible, qualitative and familiar biological foci for class discussion. Reiteration of Core Concepts. The best way to show students that the same fundamental principles govern many aspects of biological processes is to reiterate those principles, where applicable, throughout the course in various contexts. If students grasp these core concepts, they can understand at a fundamental level the biochemical processes that underlie much of biological science. Reiteration is built into BEC at several levels. For example, the concept of pK a is reiterated a total of fourteen times: nine times in various text sections, twice in review material, and three times in the sample tests. The concept is first discussed on in the context of acid-base ionization and the relation to protonation and deprotonation. It reappears again in the context of the bicarbonate blood buffering mechanism and again a discussion of the functional groups of amino acids. It occurs twice in a table of pK a values and in a section that defines the isoelectric point and explains how it is calculated. It appears again during the explanation of pK a shifts at the C-terminus of amino acids on incorporation into a polypeptide, in a Preface xvii discussion of the allosteric control of oxygen binding to hemoglobin, in an explanation of enzyme activity at different pH values, and in a discussion of the charge of backbone phosphates in nucleic acids. The concept occurs in several contexts in the review sessions. Sample Exam 1 makes use of the pK a concept in a question that requires students to draw a specified oligopeptide structure and the corresponding pH titration curve. Sample Exam 1 also contains a multiple-choice question that focuses on the comparison of pK a with pH and the partial pressure of oxygen (pO 2). The final occurrence of the concept is in the sample Final Exam in a question regarding factors that control the catalytic capability of an enzyme. Similar reiteration strategies are employed for other fundamental principles. The material in BEC produces an interwoven set of reiterated ideas that shows how analogous chemical principles govern a large number of biological reactions. The intent of this reiteration is to help students retain the basics, understand how they apply to a variety of biological processes, and develop the ability to dissect new analogous situations on their own. Reinforcement Through Review. Several review tools have been incorporated into BEC, complete with answers, to foster integration of the textbook material with the questions. A single volume contains a concise summary of the lecture material, the students' own class notes, and directly linked review questions and sample tests, with answers. This integrated format encourages students to work problems and think about results in a well-organized and efficient way. The first six sets of review questions do not have an answer key per se, but the answers are easily located in the text of BEC. The expectation is that students can read the relevant portions of the text and BEC and use the information to answer the assigned questions. However, the material covered in review sessions 7-13 is more challenging and requires a more concept-driven approach. We've also found that students begin to feel frustration and fatigue at this stage of the course. We've therefore provided answers for each of the questions in these sections. In addition, four sample tests and a final exam are supplied with complete answer keys. These review tools provide a completely integrated curriculum that stresses the core concepts of biochemistry and greatly facilitates student comprehension. By writing and drawing out the answers to the practice questions in BEC, students exercise and refine their use of the tools and language of biochemistry.

Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
 andrey khorst
andrey khorst