We aim to understand cloud formation in substellar objects. We combined our nonequilibrium, stationary cloud model DRIFT (seed formation, growth, evaporation, gravitational settling, element conservation) with the general-purpose model... more
"The cold dense phase of the interstellar medium consists of giant molecular clouds (GMCs), with masses from several hundred thousand to several million times the mass of the sun and gas kinetic temperatures of 10 K. They consist... more
We point out that the exchange of a Goldstone pseudo-scalar can provide an enhancement in the dark matter annihilation rate capable of explaining the excess flux seen in high energy cosmic ray data. The mechanism of enhancement involves... more
We compute the second-order matching conditions for tensor metric perturbations at an abrupt change in the equation of state. For adiabatic perturbations on large scales the matching hypersurface coincides with a uniform-density... more
We present a new evolutionary model that describes the population properties of radio sources at frequencies <5 GHz, thus complementing the De Zotti et al. (2005) model, holding at higher frequencies. We find that simple analytic... more
We reassess the estimate of the cross-correlation of the spatial distribution of the NRAO VLA Sky Survey (NVSS) radio sources with that of Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) anisotropies from the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe... more
Out of the known transiting extrasolar planets, the majority are gas giants orbiting their host star at close proximity. Both theoretical and observational studies support the hypothesis that such bodies emit significant amounts of flux... more
The search for life outside of the Solar System should not be restricted to exclusively planetary bodies; large moons of extrasolar planets may also be common habitable environments throughout the Galaxy. Extrasolar moons, or exomoons,... more
The hot Jupiter HD 209458b was observed during primary transit at 3.6, 4.5, 5.8 and 8.0 microns using the Infrared Array Camera (IRAC) on the Spitzer Space Telescope. We detail here the procedures we adopted to correct for the systematic... more
In this paper we investigate the detectability of a habitable-zone exomoon around various configurations of exoplanetary systems with the Kepler Mission or photometry of approximately equal quality. We calculate both the predicted transit... more
We report the detection of a transit egress by the ~ 3.9-Jupiter-mass planet HD 80606b, an object in a highly-eccentric orbit (e ~ 0.93) about its parent star of approximately solar type. The astrophysical reality of the signal of... more
As the number of known exoplanets continues to grow, the question as to whether such bodies harbour satellite systems has become one of increasing interest. In this paper, we explore the transit timing effects that should be detectable... more
Transiting planet lightcurves have historically been used predominantly for measuring the depth and hence ratio of the planet-star radii, p. Equations have been previously presented by Seager & Mallen-Ornelas (2003) for the analysis of... more
Glaciations were attributed to variations of the Earth’s orbit (Milankovitch cycles). But the best ever dated paleoclimatic record (from a speleothem from Devils Hole, Nevada) demonstrated that the end of the last glacial period... more
Results from photographic observations of the white light solar corona conducted during the total phase of the total solar eclipse on March 29, 2006 in Manavgat, Turkey are shown in this work. Spectroscopic study of the green 530.3 nm... more
Glaciations were attributed to variations of the Earth’s orbit (Milankovitch cycles). But the best ever dated paleoclimatic record (from a speleothem from Devils Hole, Nevada) demonstrated that the end of the last glacial period... more
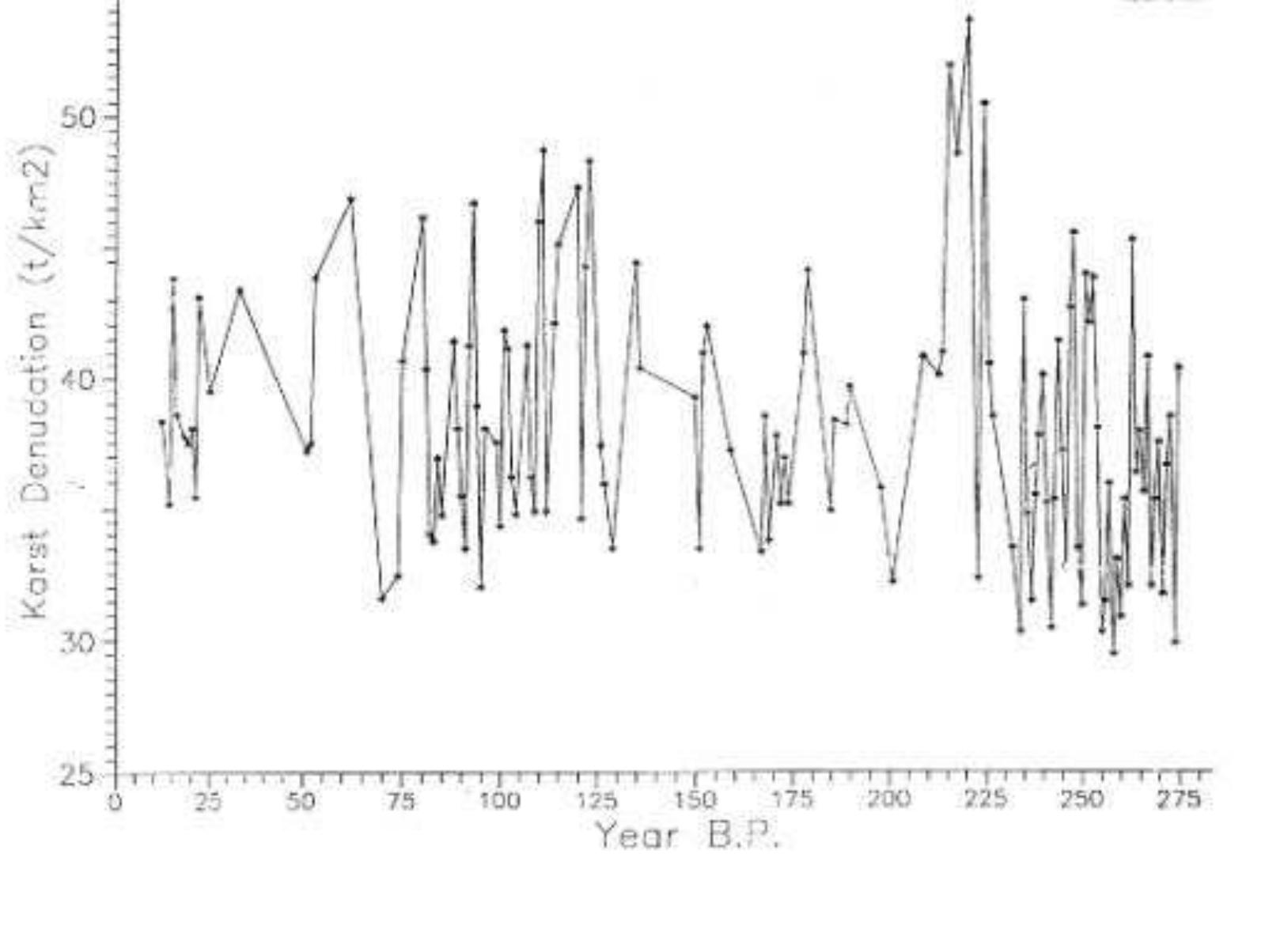
We used the quantitative theory of solubility of karst rocks of Shopov et. al, (1989, 1991a) in dependence of the temperature and other thermodynamic parameters to make reconstructions of past carbonate denudation rates. This theory... more
We have confirmed the solar origin of insolation cycles of 11,500, 4400, 3950, 2770, 2500, 2090, 1960, 1670, 1460, 1280, 1195, 1145, 1034, 935, 835, 750 and 610 yrs found in speleothem luminescence by their presence in other indices of the... more
We developed a new technique for registration of the far solar corona from ground-based observations at distances comparable to those obtained from space coronagraphs. It makes possible visualization of fine details of studied objects... more
We evaluate the contribution of cosmic microwave background (CMB) polarization spectra to cosmological parameter constraints. We produce cosmological parameters using high-quality CMB polarization data from the ground-based QUaD... more
Abstract:-- This paper follows The Cartesian Theory (Hammond, New Ideas in Psychology Vol. 12(2), 1994) which advanced 3-axis brain cleavage as the cause of the Structural Model. This second paper reports gravitational curvature in... more
"We use the corrections ˙ to the standard Newtonian/Einsteinian perihelion precessions of the inner planets of the Solar system, recently estimated by E.V. Pitjeva by fitting a huge planetary data set with the dynamical models of the... more
Autonomous gravitational-wave searches -- fully automated analyses of data that run without human intervention or assistance -- are desirable for a number of reasons. They are necessary for the rapid identification of gravitational-wave... more
We study the (local) propagation of plane waves in a relativistic, non- dissipative, two-fluid system, allowing for a relative velocity in the “background” configuration. The main aim is to analyze relativistic two-stream instability.... more
This paper uses data obtained from the galaxy luminosity function (LF) to calculate two types of radial number densities statistics of the galaxy distribution as discussed in Ribeiro (2005), namely the differential density $\gamma$ and... more
Extending the formalism of Datta, Bharadwaj & Choudhury for detecting ionized bubbles in redshifted 21-cm maps using a matched filtering technique, we use different simulations to analyse the impact ofHI fluctuations outside the bubble on... more
A set of interpolating functions of the type f(v)={(sin[v pi/2])/(v pi/2)}^n is analyzed in the context of the smoothed-particle hydrodynamics (SPH) technique. The behaviour of these kernels for several values of the parameter n has been... more
A short poetical piece exploring power dynamics of the classroom using the analogy of the solar system.
Classical variable stars called RR Lyrae stars have pulsating outer envelopes constituted of excited atoms. Here we demonstrate that the qualitative and quantitative properties of RR Lyrae variables and one subclass of their atomic scale... more
The study of planets lends itself to the multiple intelligences approach in such a way that lessons can be designed seamlessly, moving through each of the seven intelligences, each modality resonating and enriching the others.
The generalized Einstein action is treated quantum mechanically by using a quadratic lagrangian form. The canonical quantization of this action is obtained by using the auxiliary variable to define the generalized momentum. Physical... more
"The astronomer E.V. Pitjeva, by analyzing with the EPM2008 ephemerides a large number of planetary observations including also two years (2004-2006) of normal points from the Cassini spacecraft, phenomenologically estimated a... more
The accuracy reached in the past few years by Satellite Laser Ranging (SLR) allows for measuring even tiny features of the Earth's gravitational field predicted by Einstein's General Relativity by means of artificial satellites. The... more
In this paper we determine dynamically the mass of the Kuiper Belt Objects by exploiting the latest least-squares determinations of the extra rates of perihelia of the inner planets of the Solar system. By modelling classical Kuiper Belt... more
"We consider the recently estimated corrections ̟˙ to the Newtonian/ Einsteinian secular precessions of the longitudes of perihelia ̟ of several planets of the Solar System in order to evaluate whether they are compatible with the... more
"By processing more than 400 000 planetary observations of various types with the dynamical models of the EPM2006 ephemerides, E.V. Pitjeva recently estimated a correction to the canonical Newtonian-Einsteinian Venus' perihelion... more
The nonlinear dynamics of whistler waves in magnetized plasmas is studied. Since the plasmas and beam-plasma systems considered here are assumed to be weakly collisional, the point of reference for the analysis performed in the present... more
This second part contains these chapters, in two files: 1 Chemistry: Reading Spectrograms 2 Performance Art: Problems of Documentation 3 Field Geology: Deductions from Beach Stones 4 Economics: Sirens in Classics, in Philosophy, and... more
To date, more than 300 planets orbiting stars other than our sun have been discovered using a range of observing techniques, with new discoveries occuring monthly. The work in this thesis focused on the detection of exoplanets using the... more
We report the discovery of the first high-amplitude δ Scuti star in an eclipsing binary, which we have designated UNSW-V-500. The system is an Algol-type semi-detached eclipsing binary of maximum brightness V = 12.52 mag. A best-fitting... more
We present a new catalogue of variable stars compiled from the data taken for the University of New South Wales Extrasolar Planet Search. From 2004 October to 2007 May, 25 target fields were each observed for one to four months, resulting... more


































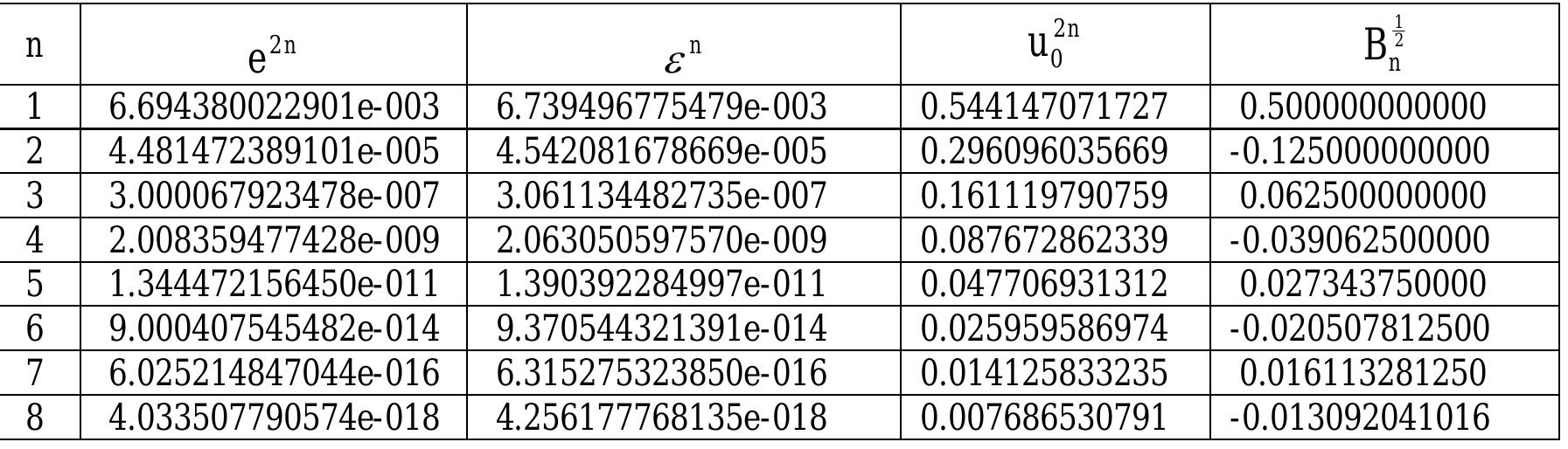
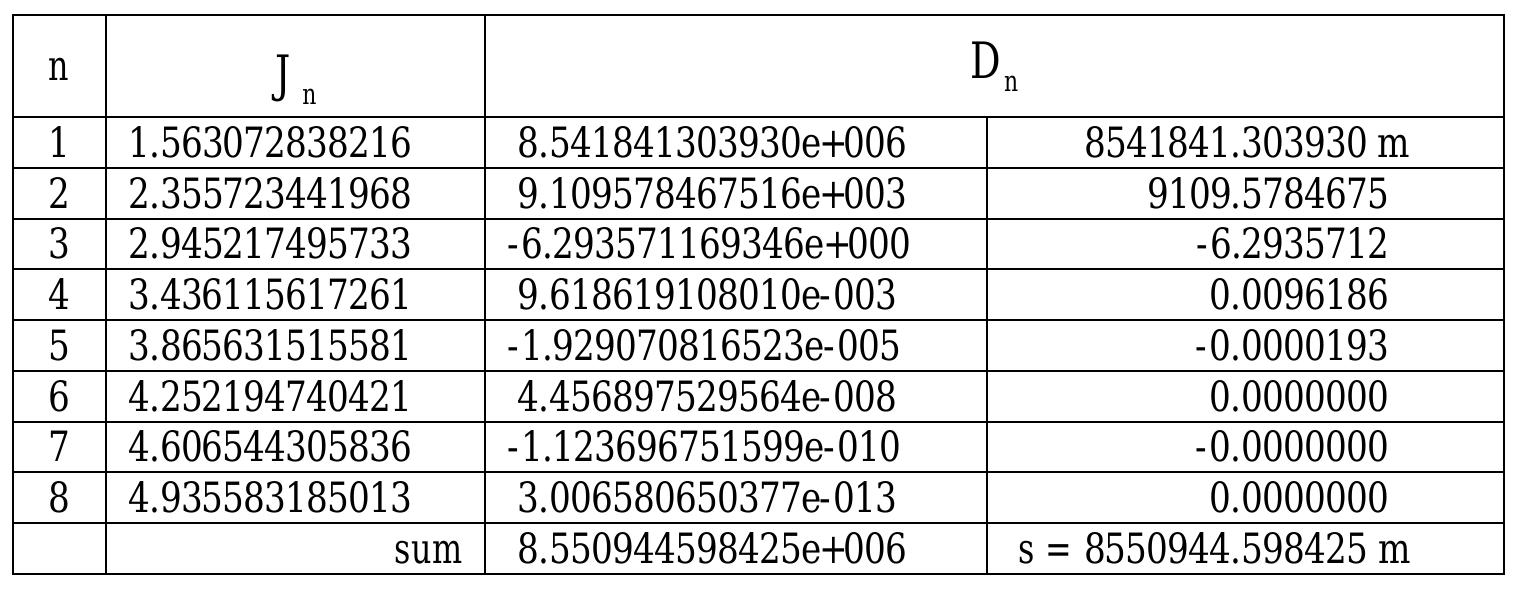
![Table 3: Recurrence formula values and longitude components for equation (47 Inspection of these numerical values indicates than an upper limit of N =8 in the summations is more than sufficient for accuracies of 0.000001 metre in distances and 0.000001 second of arc for longitude differences. [Results for s and A” can be confirmed using V incenty's equations (Vincenty 1975) that have been programmed in a Microsoft™ Excel workbook that can be downloaded from the website of Geoscience Australia at http://www.ga.gov.au/]](https://figures.academia-assets.com/1965194/table_002.jpg)





















































































































































![candidates with a period < 1 day are generally rejected to eliminate significant 1 day aliases (e.g. Kane et al. (2008)). This is discussed in more detail in Section 2.7.1. The duration of a transit depends on the period of the orbit and the inclination angle of the transit, with 90 degrees being directly across the center of the disk. With a period of 1-10 days and a radius of ~ 1 Ry, a typical Hot Jupiter transit will last ~ 2-5 hours. The depth of the transit is proportional to the square of the size ratio of the star and planet, shown in Figure 1.5. Physical constraints caused by Coulomb forces and electron degeneracy pressure allow objects with a mass of Jupiter to 80 times the mass of Jupiter to have a roughly the same radius (Hubbard et al., 2002). The range of transiting planet radii, to date, are 0.4 < Rp < 1.8 R;. The largest exoplanets known to date, Tr] HS-4 and WASP-12 b', both have a radius of ~ 1.68 Ry (Mandushev et al., 2007). Lower main sequence stars are generally targeted for transit searches, as spectral type A, LA cen pp nnnt na cent aanenaahktliahnad ASannssnwese Litter. | leceeceeee ct pean pare lean nlannta htm](https://figures.academia-assets.com/34630404/figure_005.jpg)












































